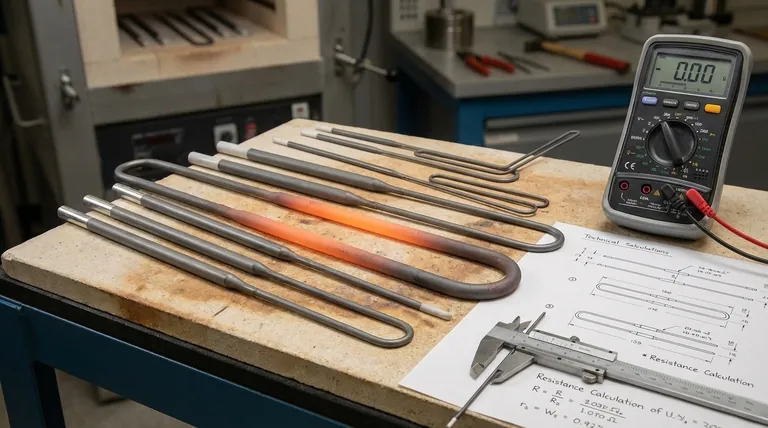
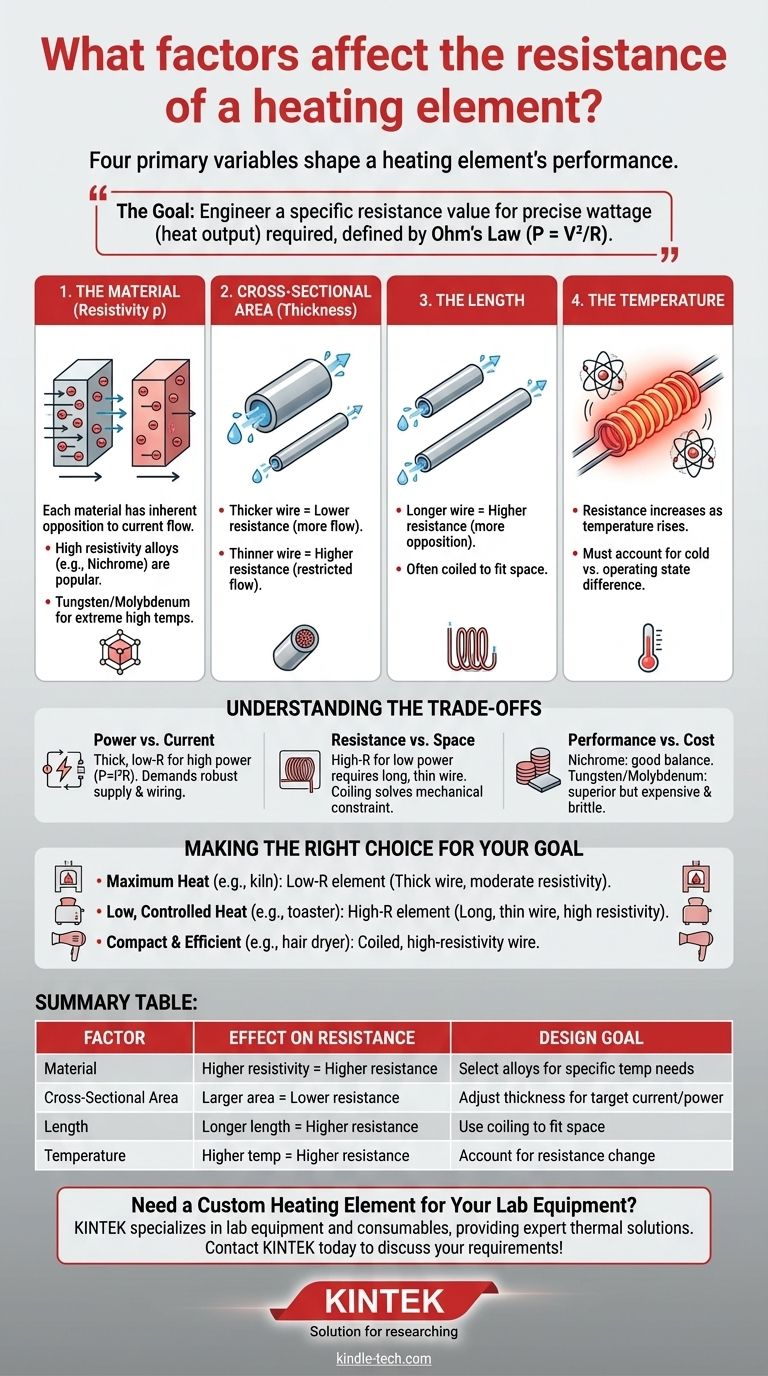
The resistance of a heating element is determined by four primary physical factors: the material it is made from, its length, its cross-sectional area (thickness), and its operating temperature. These variables are not independent; they are interconnected levers that engineers use to achieve a specific and predictable heat output for a given electrical supply.
The core principle is not to simply minimize or maximize resistance. The goal is to engineer a specific resistance value that, when combined with the intended voltage, produces the precise wattage (heat output) required for the application, as defined by Ohm's Law and the power formula (P = V²/R).

The Fundamental Factors of Resistance
To understand how a heating element is designed, it helps to think of electricity as water flowing through a pipe. The resistance is anything that impedes that flow.
The Material (Resistivity)
Each conductive material has an inherent property called resistivity (symbolized by ρ, rho), which measures how strongly it opposes the flow of electric current.
Materials like nickel-chromium (Nichrome) alloys are popular because they have high resistivity and are resistant to oxidation at high temperatures. Tungsten and molybdenum are used for even higher temperatures.
The Cross-Sectional Area (Thickness)
The cross-sectional area of the element is its thickness or diameter. This is one of the most critical design factors.
A thicker wire is like a wider pipe—it has a larger cross-sectional area, which lowers its resistance and allows more current to flow for a given voltage.
Conversely, a thinner wire has a smaller cross-sectional area, which increases its resistance and restricts current flow.
The Length
The length of the heating element is directly proportional to its total resistance.
A longer wire forces electrons to travel a greater distance through the resistive material, increasing the total opposition to flow. This is like forcing water through a longer pipe, which results in more friction and pressure loss.
This is why high-resistance elements are often very long and coiled tightly to fit into a small space.
The Temperature
For most heating element materials, resistance increases as temperature rises. This property is known as the temperature coefficient of resistance.
As the element heats up, its atoms vibrate more vigorously, making it more difficult for electrons to pass through. This change must be accounted for in designs that require precise temperature control, as the element's resistance when "cold" will be lower than its resistance at its target operating temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right parameters for a heating element involves balancing competing physical and economic constraints. Resistance is the outcome of these design choices.
Power Output vs. Current Draw
A thick, low-resistance element is necessary for high-power applications (like an electric furnace). It allows a large amount of current to flow, generating significant heat (P = I²R).
However, this high current demands a robust power supply and thicker, more expensive wiring throughout the circuit to handle the load safely.
Resistance Target vs. Physical Space
To achieve a high resistance value for a low-power application (like a heated blanket), you need a very long and thin wire.
The challenge then becomes a mechanical one: how to fit this long, delicate wire into the available physical space without it breaking. This is why coiling is a near-universal design solution.
Performance vs. Material Cost
Nichrome offers a fantastic balance of high resistivity, durability, and cost for many common applications.
For extreme high-temperature environments like a vacuum furnace, materials like tungsten or molybdenum are required. While their performance is superior at these temperatures, they are significantly more expensive and can be more brittle, complicating the manufacturing process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal heating element design is dictated entirely by the application's specific requirements for heat output, operating voltage, and physical form factor.
- If your primary focus is maximum heat output (e.g., a kiln or furnace): Your design will favor a low-resistance element, achieved by using a material with moderate resistivity and a large cross-sectional area (a thick wire).
- If your primary focus is low, controlled heat at a standard voltage (e.g., a floor heater or toaster): Your design will require a higher resistance to limit the current, achieved by using a long, thin wire made of a high-resistivity alloy like Nichrome.
- If your primary focus is compact size and efficiency (e.g., a hair dryer): You will use a coiled, high-resistivity wire to achieve the necessary resistance in a small volume, relying on forced air to transfer the heat effectively.
Mastering these variables gives you precise control over the thermal performance of your design.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Resistance | Design Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Material (Resistivity) | Higher resistivity = Higher resistance | Select alloys (e.g., Nichrome) for specific temperature needs |
| Cross-Sectional Area | Larger area = Lower resistance | Adjust wire thickness for target current/power |
| Length | Longer length = Higher resistance | Use coiling to fit required length into space |
| Temperature | Higher temperature = Higher resistance | Account for resistance change from cold to operating state |
Need a Custom Heating Element for Your Lab Equipment?
Designing the right heating element is critical for achieving precise temperature control and reliable performance in your laboratory applications. Whether you're building a furnace, oven, or any thermal system, the material, dimensions, and configuration of the heating element directly impact your results.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert solutions for your specific thermal needs. We can help you select or custom-engineer heating elements that deliver the exact wattage, temperature range, and durability your project demands.
Let our experts help you optimize your thermal design. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What temperature can graphite handle? Unlocking its extreme heat resistance in inert environments
- What causes heating element failure? Prevent Downtime by Understanding the Degradation Process
- Why is tungsten so heat resistant? Unlocking Its Atomic Secrets for Extreme Temperatures
- Is tungsten brittle at high temperature? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Performance
- What Roles Do Graphite Heaters and Carbon Insulation Play in SiC Coating? Mastering Thermal Precision
- What is used for high temperature heating? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heating Elements
- What are the disadvantages of tungsten? Navigating its brittleness and high fabrication costs
- Why is the resistance of a heating element high? To Efficiently Convert Electricity into Heat











