In short, annealing is a heat treatment process that systematically alters a material's internal structure to make it softer, more flexible (ductile), and easier to work with. It involves heating the material to a specific temperature, holding it there for a period, and then slowly cooling it. This controlled cycle relieves internal stresses that build up during manufacturing processes like casting or bending.
Annealing is not just about heating and cooling; it is a precise microstructural reset. The process allows a material's deformed and stressed internal crystal structure to reform into new, strain-free grains, fundamentally changing its mechanical properties from hard and brittle to soft and workable.
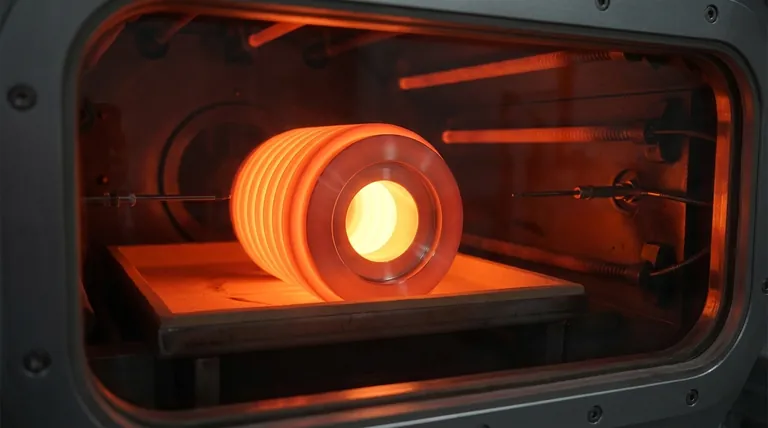

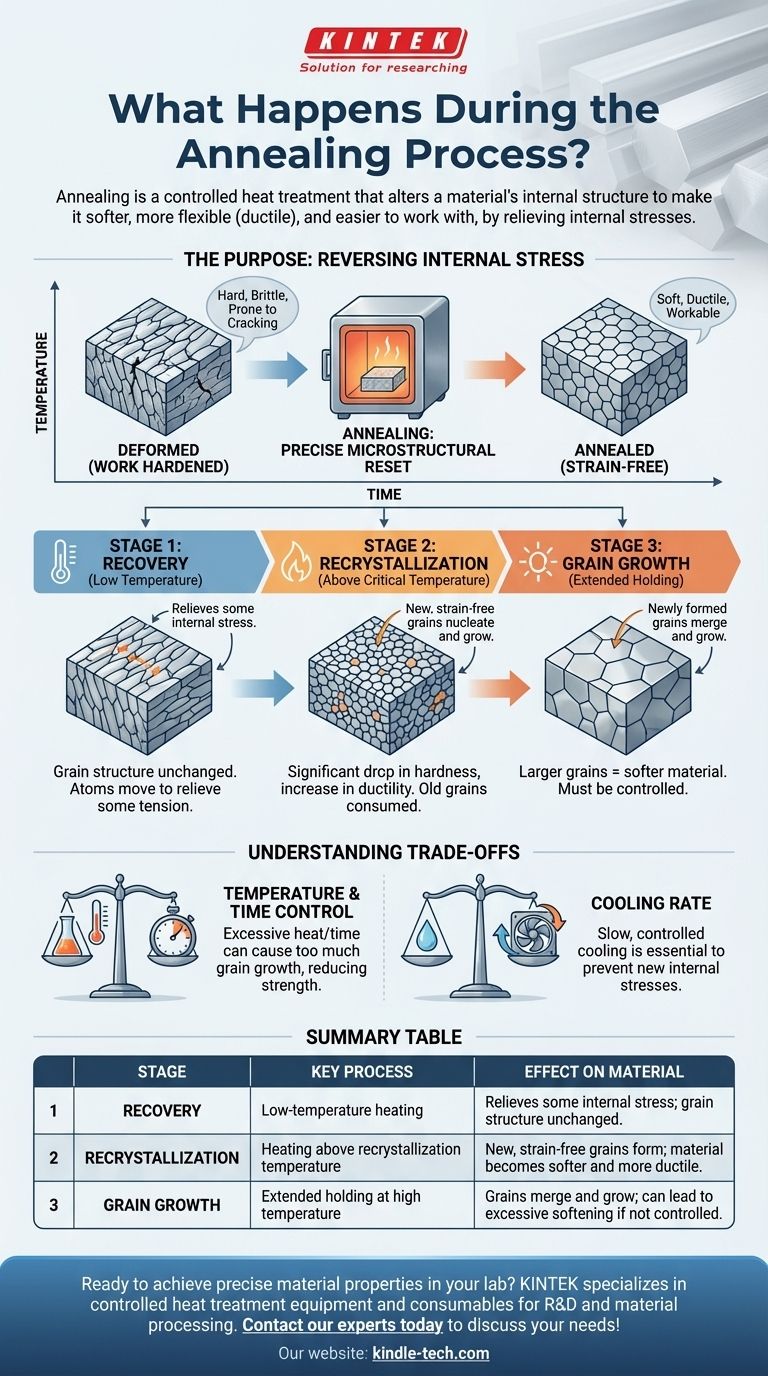
The Purpose: Reversing Internal Stress
When a metal is bent, forged, or cast, its internal crystal structure, known as its grain structure, becomes deformed and stressed.
This condition, often called work hardening, makes the material harder and stronger, but also more brittle and prone to cracking.
Annealing serves as a "reset button" to reverse this state. It relieves the built-up internal stresses, preventing potential failures and restoring the material's ability to be shaped without fracturing.
The Three Stages of Microstructural Change
The transformation during annealing doesn't happen all at once. It progresses through three distinct stages as the temperature of the material is increased and held.
Stage 1: Recovery
As the material first heats up, it enters the recovery stage. At this point, the temperature is not yet high enough to create new crystals.
Instead, the atoms have enough energy to move slightly, allowing the internal crystal lattice to relieve some of its stored stress. The fundamental grain structure remains unchanged, but the material sheds some of its internal tension.
Stage 2: Recrystallization
This is the most critical stage. As the temperature rises above the material's recrystallization temperature, a profound change begins.
New, tiny, strain-free grains begin to nucleate and grow within the old, deformed structure. These new grains act like seeds, consuming and replacing the stressed, elongated grains created during fabrication.
At the end of recrystallization, the material has a completely new, refined microstructure that is free of the vast majority of its prior internal stress. This is what causes the significant drop in hardness and increase in ductility.
Stage 3: Grain Growth
If the material is held at the annealing temperature after recrystallization is complete, the grain growth stage begins.
The newly formed, strain-free grains will start to merge and grow larger. A larger grain size generally results in a softer material. This stage must be carefully controlled, as excessive grain growth can sometimes be detrimental to other desired properties, like toughness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Annealing is a powerful process, but its success depends on precise control over temperature, time, and cooling rate.
The Risk of Improper Control
Holding the material at too high a temperature or for too long can cause excessive grain growth, which may reduce the material's strength or toughness below the desired level.
The Importance of Cooling Rate
The cooling phase is just as important as the heating phase. If the material is cooled too quickly, new internal stresses can be introduced, partially or completely negating the benefits of the process. Slow, controlled cooling is essential to allow the new microstructure to set properly.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Annealing is used to achieve several distinct engineering outcomes. Your specific goal determines which aspect of the process is most important.
- If your primary focus is improving workability: The key is to complete the recrystallization stage to significantly increase ductility and soften the material, allowing for further cold working, drawing, or forming operations.
- If your primary focus is preventing in-service failure: The main goal is relieving internal stresses from processes like welding or casting that could otherwise lead to premature cracking under load.
- If your primary focus is creating a uniform structure: Annealing is used to homogenize the material, ensuring its mechanical properties are predictable and consistent throughout the entire part.
Ultimately, annealing is a foundational metallurgical tool that gives engineers control over a material's most fundamental properties.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Effect on Material |
|---|---|---|
| Recovery | Low-temperature heating | Relieves some internal stress; grain structure unchanged. |
| Recrystallization | Heating above recrystallization temperature | New, strain-free grains form; material becomes softer and more ductile. |
| Grain Growth | Extended holding at high temperature | Grains merge and grow; can lead to excessive softening if not controlled. |
Ready to achieve precise material properties in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables needed for controlled heat treatment processes like annealing. Whether you are working on R&D, quality control, or material processing, our solutions help you ensure consistent, reliable results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific annealing and material testing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of graphite material? Leveraging Extreme Heat and Precision for Industrial Processes
- Does graphite have a melting point? Unlocking the Extreme Heat Resistance of Graphite
- What is the temperature of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C
- What are the advantages of graphite furnace? Achieve High-Temperature Precision and Purity
- What temperature can graphite withstand? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential



















