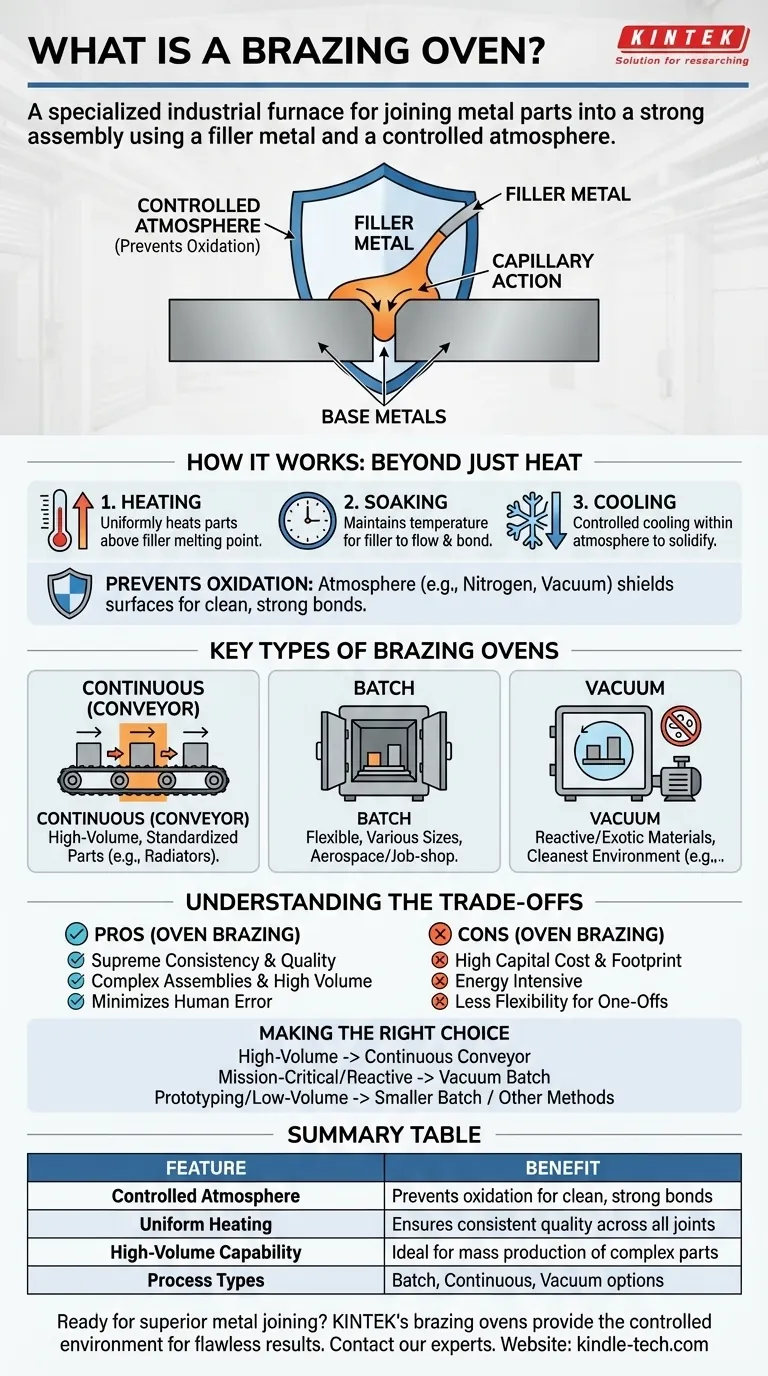
At its core, a brazing oven is a specialized industrial furnace used for joining multiple metal components into a single, robust assembly. It functions by precisely heating the parts in a controlled atmosphere to a temperature that melts a filler metal, but not the base metals themselves. This molten filler flows into the gaps between the parts via capillary action and, upon cooling, solidifies to form a strong, permanent metallurgical bond.
Brazing success is less about applying heat and more about controlling the environment where heat is applied. A brazing oven's primary function is not just to melt the filler metal, but to create a chemically controlled atmosphere that prevents oxidation, ensuring a clean, strong, and repeatable bond.

How a Brazing Oven Works: Beyond Just Heat
Understanding a brazing oven requires looking past the high temperatures and focusing on the carefully managed chemical environment it creates.
The Principle of Controlled Atmosphere Brazing
Brazing relies on a filler metal (the brazing alloy) with a lower melting point than the base metals being joined. The oven heats the entire assembly uniformly just above the filler's melting point.
This allows the molten alloy to be drawn into the tight-fitting joint, wetting the surfaces of the base metals. This process is known as capillary action.
Preventing Oxidation: The Critical Task
When metals are heated, they rapidly react with oxygen in the air to form oxides on their surface. This oxide layer acts as a barrier, preventing the molten filler metal from properly bonding with the base metal, resulting in a weak or failed joint.
A brazing oven's most important job is to displace the oxygen with a controlled atmosphere. This atmosphere acts as a protective shield, keeping the metal surfaces perfectly clean throughout the heating and cooling cycle. Common atmospheres include nitrogen, dissociated ammonia, or a vacuum.
The Brazing Cycle: Heat, Soak, Cool
A typical process involves three distinct phases:
- Heating: The parts are brought up to the target brazing temperature at a controlled rate.
- Soaking: The assembly is held at the brazing temperature for a specific duration to ensure complete melting of the filler and its flow throughout the joint.
- Cooling: The assembly is cooled in a controlled manner, still within the protective atmosphere, to solidify the joint without introducing thermal stress or oxidation.
Key Types of Brazing Ovens
The choice of oven depends heavily on production volume, part size, and material requirements.
Continuous (Conveyor) Ovens
These ovens use a mesh belt conveyor to move parts through different temperature zones. They are the workhorses of high-volume manufacturing, ideal for producing thousands of identical parts like automotive radiators and air conditioning components.
Batch Ovens
In a batch oven, a single load or "batch" of parts is placed inside, the door is sealed, and the entire brazing cycle is performed. They offer greater flexibility for handling parts of various sizes and complexities and are common in aerospace and job-shop environments.
Vacuum Ovens
A vacuum oven is a type of batch oven where the "atmosphere" is the absence of gas. By pumping out the air, oxidation is virtually eliminated. This is the gold standard for brazing reactive or exotic materials like titanium, aluminum, and superalloys used in aerospace and medical implants.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Oven vs. Other Methods
Oven brazing is a powerful technique, but it's not always the right choice. It competes with other methods like manual torch brazing and induction brazing.
Advantage: Supreme Consistency and Quality
Because the entire part is heated uniformly in a controlled environment, oven brazing produces exceptionally consistent and high-quality joints across an entire production run. Human error is minimized.
Advantage: Complex Assemblies and High Volume
An oven can braze dozens or even hundreds of joints on a complex assembly in a single cycle. This makes it vastly more efficient for intricate parts or mass production compared to brazing one joint at a time with a torch.
Disadvantage: High Capital Cost and Footprint
Industrial brazing ovens are significant capital investments. They are large, require substantial factory floor space, and consume considerable energy, making them unsuitable for small-scale operations.
Disadvantage: Less Flexibility for One-Off Jobs
While batch ovens offer some flexibility, the setup and cycle time for oven brazing makes it impractical for quick, one-off repairs or simple prototypes. Torch or induction brazing is often faster and more cost-effective for these tasks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct brazing strategy requires matching the technology to your specific operational needs.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of standardized parts: A continuous conveyor oven offers the most efficient and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is mission-critical, complex components or reactive metals (like titanium): A vacuum batch oven provides the cleanest environment and the highest possible joint integrity.
- If your primary focus is prototyping, repairs, or low-to-medium volume production: A smaller batch oven or alternative methods like torch or induction brazing will likely be more practical and economical.
Ultimately, viewing a brazing oven as an environmental control system, rather than just a heat source, is the key to understanding its value in modern manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Controlled Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation for clean, strong bonds |
| Uniform Heating | Ensures consistent quality across all joints |
| High-Volume Capability | Ideal for mass production of complex parts |
| Process Types | Batch, Continuous (Conveyor), and Vacuum ovens |
Ready to achieve superior metal joining with precision and consistency?
Whether you are in high-volume manufacturing or working with mission-critical components, KINTEK's brazing ovens provide the controlled environment necessary for flawless results. Our expertise in lab and industrial equipment ensures you get a solution tailored to your specific materials and production goals.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss how a KINTEK brazing oven can enhance your manufacturing process and deliver the strong, reliable bonds your products demand.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What is brazing in heat treatment? Achieve Superior Joint Quality and Efficiency



















