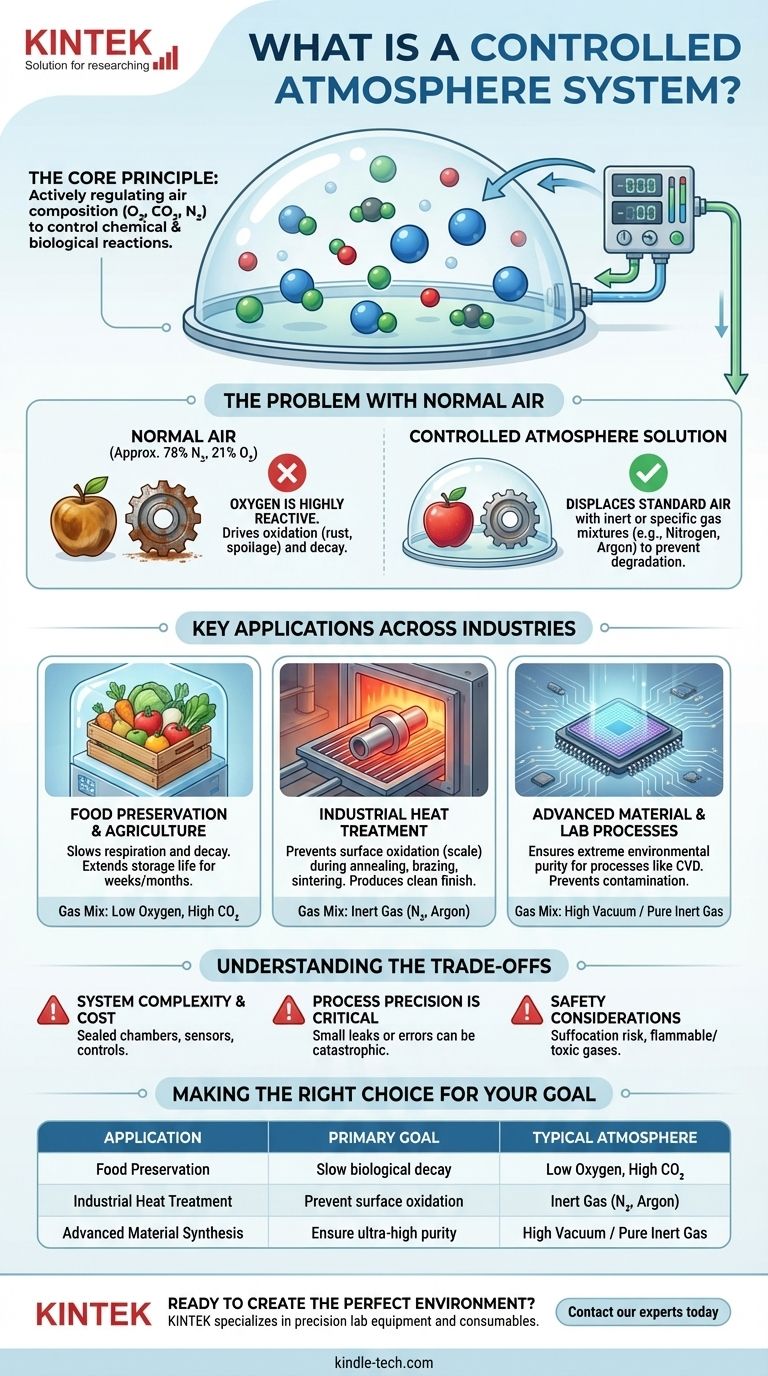
In essence, a controlled atmosphere system is an environment where the composition of the air is precisely managed to achieve a specific outcome. This involves actively regulating the levels of gases like oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen within a sealed space, creating an atmospheric composition that is fundamentally different from the air we breathe.
The core purpose of a controlled atmosphere is not just to change the air, but to fundamentally control chemical and biological reactions. By removing reactive gases or introducing specific ones, these systems can prevent degradation in sensitive products or enable precise transformations in industrial materials.

The Core Principle: Preventing Unwanted Reactions
The air around us is approximately 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and a mix of other gases. For many processes, that 21% oxygen is a significant problem.
The Problem with Normal Air
Oxygen is highly reactive. It drives oxidation, which is responsible for everything from an apple turning brown and metal rusting to the unwanted scaling that forms on steel during high-temperature heat treatment.
In biological terms, oxygen is essential for the respiration process that causes produce to ripen, decay, and spoil.
How Controlled Atmospheres Solve This
A controlled atmosphere system directly counteracts these effects by displacing the standard air. It replaces it with a carefully selected gas mixture tailored to the specific application.
Often, this involves using an inert gas like nitrogen or argon, which does not easily react with other materials. This effectively blankets the product, protecting it from oxidation and degradation. In other cases, specific reactive gases are introduced in precise amounts to cause a desired chemical change.
Key Applications Across Industries
The ability to control chemical reactions by managing the surrounding atmosphere is a powerful tool used in a surprising number of fields.
Food Preservation and Agriculture
This is one of the most common applications. By lowering oxygen levels and increasing carbon dioxide, the respiration rate of fruits and vegetables is dramatically slowed.
This process extends the storage life of produce for weeks or even months, allowing for long-distance transportation and year-round availability without freezing or chemical preservatives.
Industrial Heat Treatment
In metallurgy, heating metal in the presence of oxygen causes a brittle, flaky layer of oxide to form on its surface. This is almost always undesirable.
Processes like annealing (softening metal), brazing (joining metals), and sintering (fusing powdered material) are performed in controlled atmosphere furnaces to produce a clean, bright, and scale-free finish.
Advanced Material and Laboratory Processes
High-tech manufacturing requires extreme environmental purity. Processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), where thin films are grown on a substrate, would be impossible in normal air.
Any oxygen or moisture would contaminate the process, ruining the final material. These applications often use a high vacuum or a constant flow of ultra-pure inert gas to create the perfect reaction environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, implementing a controlled atmosphere is not a simple undertaking. It comes with significant considerations.
System Complexity and Cost
Creating and maintaining a perfectly sealed environment with precise gas mixtures requires specialized equipment. This includes sealed chambers, gas supply lines, sophisticated sensors, and computer control systems, all of which add to the initial and operational cost.
Process Precision is Critical
The "control" aspect is paramount. A small leak in a container or a faulty sensor can compromise the entire process. An incorrect gas mixture can lead to the spoilage of an entire shipment of produce or the failure of a batch of critical industrial parts.
Safety Considerations
The gases used can introduce hazards. An environment with low oxygen can be a suffocation risk for personnel, while some processes use flammable (hydrogen) or toxic (ammonia for nitriding) gases that require strict engineering controls and safety protocols.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific atmospheric composition you need depends entirely on the outcome you wish to achieve.
- If your primary focus is preservation: Your goal is to create a biologically inactive environment, typically by reducing oxygen to slow respiration and decay.
- If your primary focus is material processing: Your goal is to prevent unwanted reactions like oxidation or to intentionally introduce specific elements into a material's surface (e.g., carbon for carburizing).
- If your primary focus is high-purity synthesis: Your goal is to create an ultra-clean, non-reactive environment, often using a high vacuum or pure inert gas to eliminate all potential contaminants.
Ultimately, a controlled atmosphere transforms a simple space into a highly specific chemical reactor, enabling processes that would be impossible in open air.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Goal | Typical Atmosphere |
|---|---|---|
| Food Preservation | Slow biological decay | Low Oxygen, High CO₂ |
| Industrial Heat Treatment | Prevent surface oxidation | Inert Gas (Nitrogen, Argon) |
| Advanced Material Synthesis | Ensure ultra-high purity | High Vacuum / Pure Inert Gas |
Ready to create the perfect environment for your process?
Whether your goal is preventing oxidation in metal heat treatment, extending the shelf life of produce, or enabling high-purity synthesis, the right controlled atmosphere system is critical. KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables to meet your specific laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you design a reliable and efficient solution for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- How does an atmosphere furnace facilitate the post-treatment of nickel-plated carbon fibers? Ensure Peak Bonding
- What is the role of an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace in Cu-Mo sintering? Achieve High-Purity Densification
- What is meant by inert atmosphere? A Guide to Preventing Oxidation & Ensuring Safety
- What is the purpose of inert atmosphere? A Guide to Protecting Your Materials and Processes










