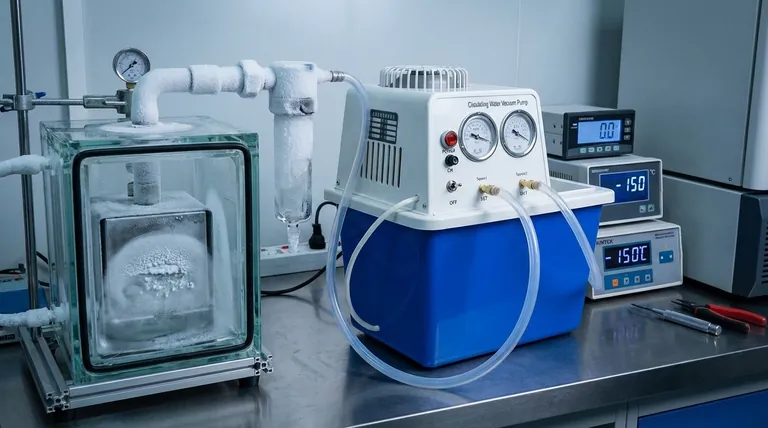
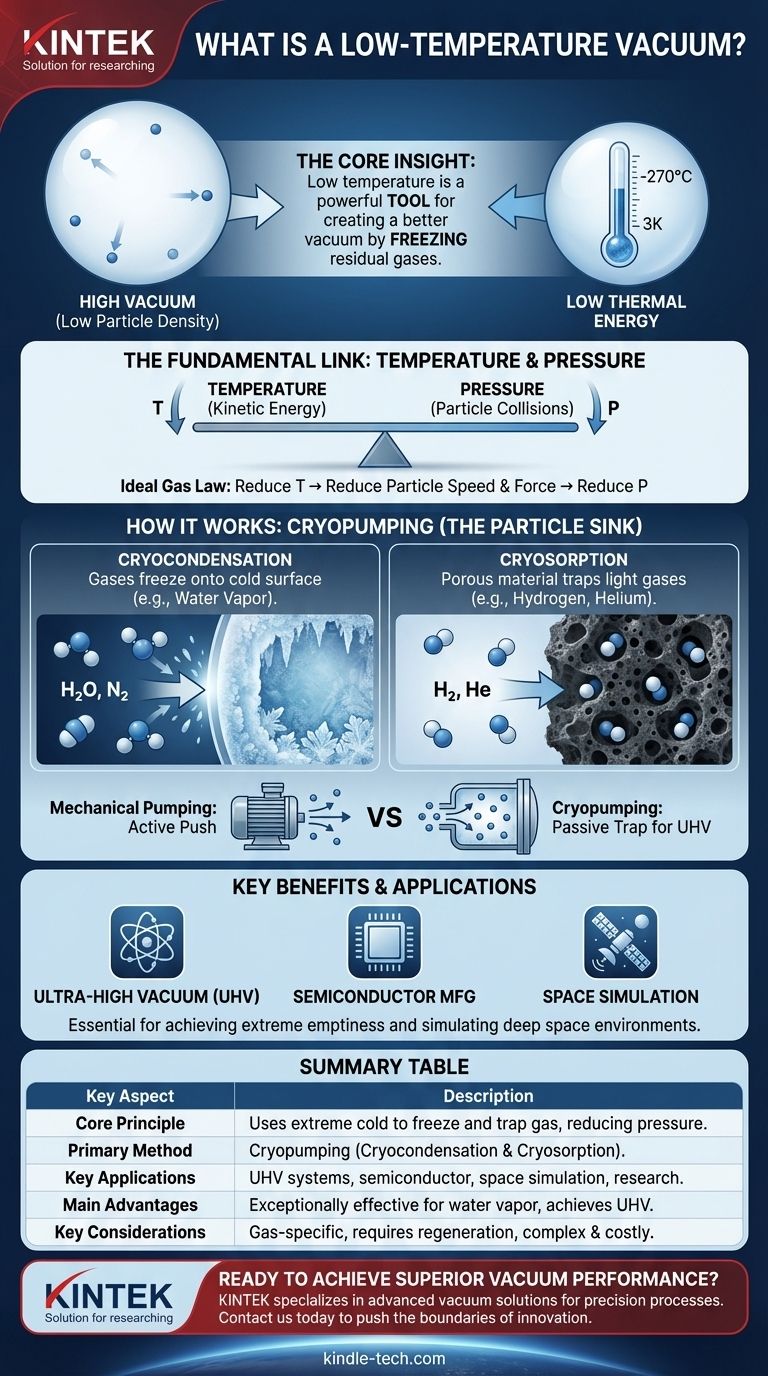
At its core, a low-temperature vacuum is a volume of space characterized by both extremely low particle density (a high vacuum) and extremely low thermal energy. The few particles that remain in the space are moving very slowly. This dual state is not a coincidence; temperature and pressure are fundamentally linked, and reducing temperature is a primary method for achieving a better vacuum.
The critical insight is that low temperature is not just a concurrent condition but a powerful tool for creating a high vacuum. By freezing residual gases out of a volume, we can achieve levels of emptiness that are impossible with mechanical pumps alone.

The Fundamental Link Between Temperature and Pressure
To understand a low-temperature vacuum, we must first look at what temperature and pressure represent at a molecular level. They are two sides of the same coin: the behavior of particles in a system.
What Temperature Truly Represents
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a system. High temperatures mean particles are moving or vibrating rapidly and energetically. Low temperatures mean they are moving very slowly, with minimal energy.
What Vacuum Truly Represents
A vacuum is a measure of the density of particles in a given volume. Pressure, the inverse of a vacuum, is caused by these particles colliding with the walls of their container. A high vacuum simply means there are very few particles present to cause collisions.
The Inescapable Connection
The relationship is described by the Ideal Gas Law. For a fixed volume, pressure is directly proportional to both the number of particles and their temperature. To lower the pressure (i.e., create a better vacuum), you have two options: remove particles or reduce their temperature, causing them to move slower and strike surfaces with less force and frequency.
How Low Temperatures Create High Vacuums
The most effective vacuum systems leverage this connection through a process known as cryopumping. A cryopump uses an extremely cold surface to trap gas molecules, effectively removing them from the chamber.
The Mechanism of Cryocondensation
Most gases have a boiling point and a freezing point. When a gas molecule, like water vapor or nitrogen, collides with a surface that is colder than its condensation point, it loses its thermal energy and freezes onto the surface. This phase change effectively removes the molecule from its gaseous state, drastically reducing the chamber's pressure.
The Power of Cryosorption
Some light gases, like hydrogen and helium, have extremely low condensation points and are difficult to freeze. To capture them, cryopumps use adsorption materials like activated charcoal, which are also cooled to cryogenic temperatures. The cold charcoal's vast, porous surface area acts like a molecular sponge, trapping these highly mobile gas particles.
Why This Method Is So Effective
Mechanical pumps physically push molecules out of a chamber, which becomes increasingly difficult as the number of molecules dwindles. Cryopumping, however, is a passive process. It creates a "particle sink" inside the chamber that captures any molecule that touches it, making it exceptionally good at removing the last few residual particles to achieve ultra-high vacuum (UHV) levels.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While incredibly powerful, creating a low-temperature vacuum is not a universal solution. It involves specific limitations and engineering challenges that are important to recognize.
Gas-Specific Performance
A cryopump's effectiveness is highly dependent on the type of gas being pumped. It is extremely efficient at removing water vapor, which is often the dominant residual gas in a vacuum system. However, its capacity for gases like hydrogen and helium is much lower, requiring specialized design considerations.
Saturation and Regeneration
The cold surface has a finite capacity. Once it becomes coated with condensed or adsorbed gas, its pumping speed drops significantly. At this point, the pump must be regenerated—warmed up to release the captured gases, which are then vented or removed by a roughing pump before the cryopump is cooled down again.
The Cost and Complexity of Cold
Achieving and maintaining the cryogenic temperatures required (often below -150°C) is energy-intensive. The equipment, such as closed-cycle helium compressors and cryocoolers, is complex, expensive, and requires regular maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding to use low-temperature techniques to achieve a vacuum depends entirely on the level of emptiness your application requires.
- If your primary focus is general vacuum applications: Mechanical and turbomolecular pumps are often sufficient for medium to high vacuum needs without the complexity of cryogenics.
- If your primary focus is achieving ultra-high vacuum (UHV): Cryopumping is essential for removing residual water vapor and reaching the pressures required for semiconductor manufacturing, surface science, or particle accelerators.
- If your primary focus is simulating deep space: A low-temperature vacuum chamber is non-negotiable, as it's the only way to accurately replicate the extreme cold and emptiness of the operational environment for satellites and probes.
Ultimately, mastering vacuum is about mastering energy, and using cold is the most effective way to control the energy of the final particles in a system.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Uses extreme cold to freeze and trap gas molecules, creating a high vacuum by reducing particle energy and density. |
| Primary Method | Cryopumping, which includes cryocondensation (freezing gases) and cryosorption (trapping gases on cold surfaces). |
| Key Applications | Ultra-high vacuum (UHV) systems, semiconductor manufacturing, surface science, and space environment simulation. |
| Main Advantages | Exceptionally effective at removing water vapor and achieving pressures unattainable with mechanical pumps alone. |
| Key Considerations | Performance is gas-specific; systems require regeneration and involve higher cost and complexity due to cryogenics. |
Ready to Achieve Superior Vacuum Performance in Your Lab?
Mastering ultra-high vacuum is critical for precision processes in semiconductor manufacturing, materials science, and research. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including vacuum systems and components, to meet these demanding needs.
We provide the reliable, high-performance solutions your laboratory requires to push the boundaries of innovation. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific vacuum challenges and help you achieve your research and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Laboratory Vertical Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the use of resistance furnace? Achieve Precise, Clean High-Temperature Processing
- What are the 5 methods of carburizing? A Guide to Choosing the Right Case-Hardening Process
- What is high temperature annealing? A Precision Tool for Engineering Materials at the Atomic Level
- What is the significance of using a high-temperature sintering furnace for PRP? Optimize Preform Structural Engineering
- At what temperature is sintering done? Find the Thermal Sweet Spot for Your Material
- What is the hazard of heat treatment? Uncontrolled Processes Risk Product Failure and Safety
- How does a reaction furnace contribute to the synthesis of uranium nitride precursor (U2N3) powder? High-Purity Controls
- What is the hottest temperature a furnace? From 1100°C to 2000°C+



















