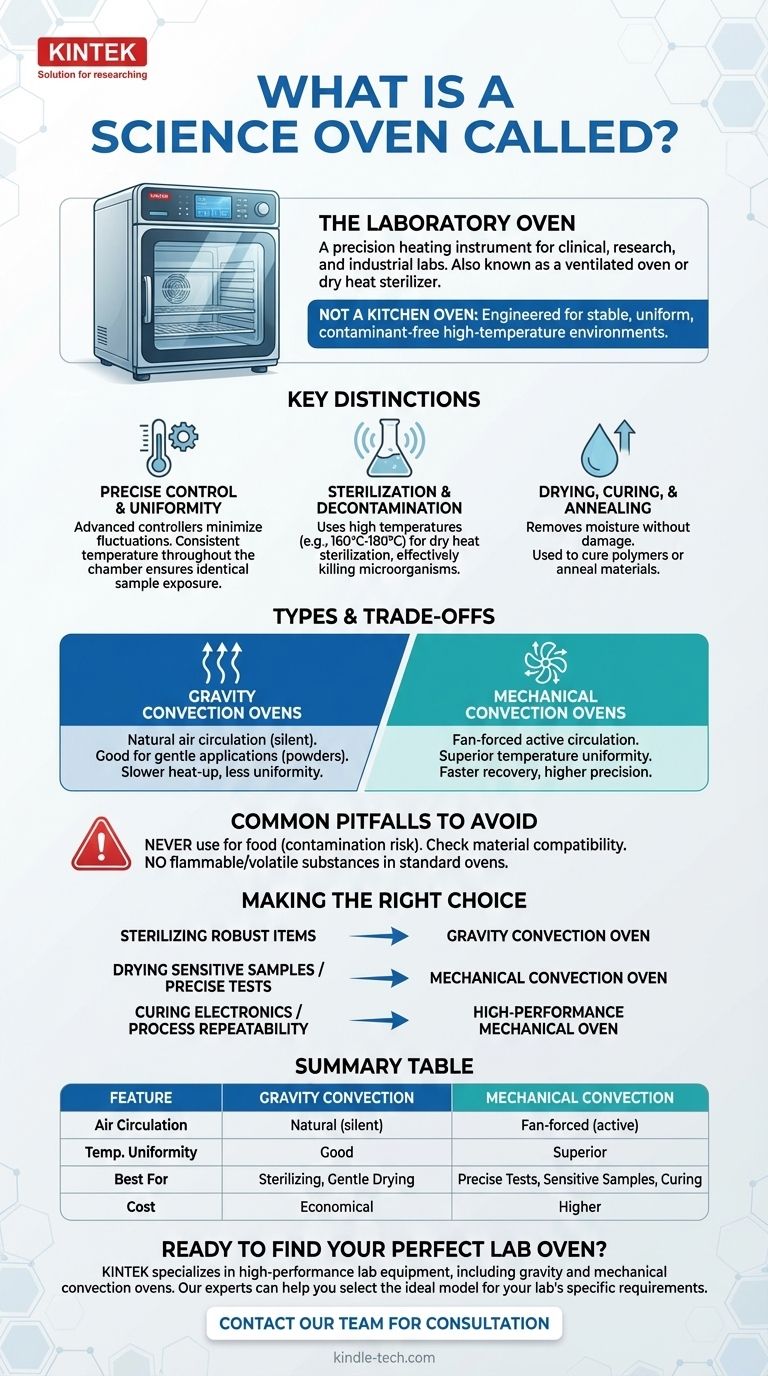
In a scientific setting, an oven is most commonly called a laboratory oven. It is a precision heating instrument also sometimes referred to as a ventilated oven or a dry heat sterilizer, and it is a foundational piece of equipment in clinical, research, and industrial labs.
A laboratory oven is not designed for cooking. It is a high-precision tool engineered to provide a stable, uniform, and contaminant-free high-temperature environment for tasks like sterilization, drying, and materials testing.
What Distinguishes a Laboratory Oven?
While it shares a basic function with a kitchen oven, a laboratory oven is fundamentally different. Its design prioritizes accuracy, safety, and repeatability for scientific applications.
Precise Temperature Control and Uniformity
A key requirement in any experiment is minimizing variables. Laboratory ovens use advanced controllers and sensors to maintain a specific temperature with very little fluctuation.
More importantly, they ensure temperature uniformity, meaning the temperature is consistent in every corner of the chamber. This guarantees that all samples are exposed to the exact same conditions.
Sterilization and Decontamination
One of the most common uses for a lab oven is dry heat sterilization.
By holding items like glassware or metal instruments at a high temperature (e.g., 160°C to 180°C) for a set duration, the oven effectively kills all microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and spores.
Drying, Curing, and Annealing
Laboratory ovens are essential for carefully removing moisture from chemical samples or biological specimens without damaging them.
They are also used in material science and electronics to cure polymers, adhesives, and coatings, or to anneal materials by heating and cooling them to alter their physical properties.
Understanding the Key Types and Trade-offs
Not all laboratory ovens are the same. The primary difference lies in how they circulate air, which directly impacts their performance and cost.
Gravity Convection Ovens
These are the simplest and most cost-effective models. They rely on the natural movement of hot air rising and cool air sinking to circulate heat.
This method is silent and gentle, making it suitable for delicate powders or samples that could be disturbed by airflow. However, it can result in less temperature uniformity and slower heat-up times.
Mechanical Convection Ovens
Also known as forced-air ovens, these units use a fan to actively circulate hot air throughout the chamber.
This forced circulation provides superior temperature uniformity and much faster recovery times after the door is opened. It is the standard for applications that demand the highest level of precision.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The most critical rule is to never use a laboratory oven for food. The chamber can be contaminated with hazardous chemicals from previous experiments, posing a serious health risk.
Additionally, always ensure the materials you place inside can withstand the set temperature. Flammable or volatile substances should never be placed in a standard lab oven; they require a specialized vacuum or explosion-proof model.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct type of oven is critical for achieving reliable and safe results.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing robust glassware or metal tools: A simple gravity convection oven is often a reliable and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is drying sensitive samples or performing precise temperature tests: A mechanical convection oven is necessary for its superior temperature uniformity.
- If your primary focus is curing electronics or processing materials: A high-performance mechanical convection model with programmable controls is essential for process repeatability.
Ultimately, understanding the function of a laboratory oven ensures you select and use this critical lab instrument correctly and safely.

Summary Table:
| Feature | Gravity Convection Oven | Mechanical Convection Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Air Circulation | Natural convection (silent) | Fan-forced (active) |
| Temperature Uniformity | Good | Superior |
| Best For | Sterilizing glassware, gentle drying | Precise tests, sensitive samples, curing |
| Cost | Economical | Higher |
Ready to find the perfect laboratory oven for your application?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including a full range of gravity and mechanical convection ovens. Whether you need reliable sterilization, precise drying, or controlled curing processes, our experts can help you select the ideal model for your lab's specific requirements.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and ensure your lab operates with precision and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
People Also Ask
- How does a controlled drying process ensure the quality of radiochromic films? Achieve Precise Dosimetric Results
- What role does a laboratory drying oven play in the processing and chemical analysis of aluminum dross?
- What is the role of a laboratory drying oven in catalyst treatment? Ensure Structural Integrity & High Performance
- Why is a laboratory-grade forced air drying oven required for alloy chip moisture analysis? Ensure Data Precision
- What is the function of a laboratory oven in W18Cr4V steel sample preparation? Expert Microstructural Drying Guide



















