A sieve test, also known as a sieve analysis, is a fundamental and widely used method for determining the particle size distribution of a granular material. The process involves passing a measured sample through a series of stacked screens, or sieves, each with a precisely sized wire mesh. By agitating this stack, the material is physically separated by size, allowing for a quantitative analysis of the proportion of particles within specific size ranges.
A sieve test is a core quality control technique that translates the physical act of sorting particles by size into a precise dataset known as a particle size distribution. This data is critical for ensuring material consistency, meeting industry standards, and predicting a material's performance.

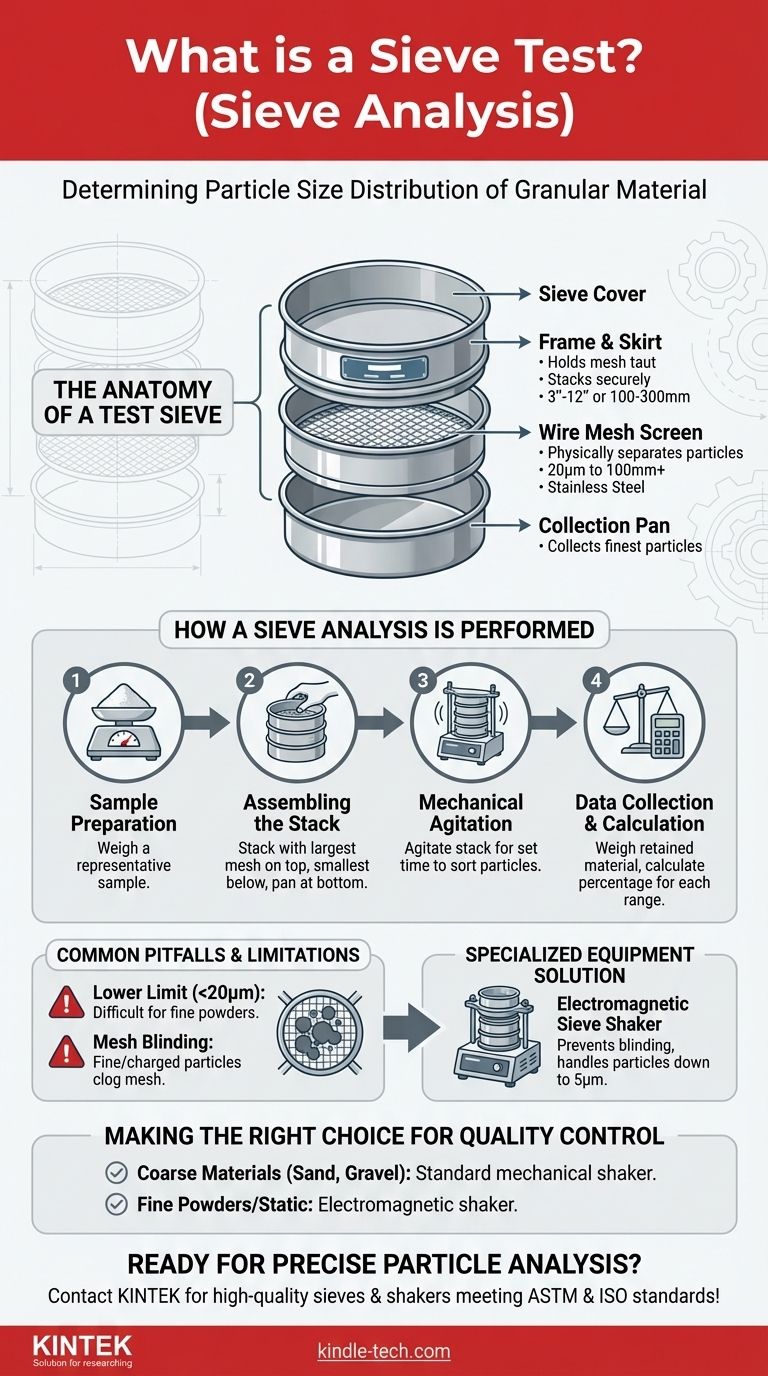
The Anatomy of a Test Sieve
Understanding the instrument is the first step to understanding the process. A standard test sieve is a simple but precise tool composed of several key parts that work together to ensure repeatable, accurate results.
The Wire Mesh Screen
This is the most technical and critical component of the sieve. It is a woven wire cloth, typically made of stainless steel, with openings of a uniform and exact size.
These openings range from several inches (over 100mm) for coarse materials down to just 20 microns (0.00078 inches) for very fine powders. The precision of this mesh is what guarantees the accuracy of the size separation.
The Frame and Skirt
The frame is the rigid circular metal ring, often made of brass or stainless steel, that holds the wire mesh taut and in place. Standard U.S. frame diameters are typically 3, 8, or 12 inches, while international standards use 100, 200, or 300mm.
The skirt is the edge of the frame designed to fit securely on top of the next sieve in the stack, preventing the assembly from tipping over during agitation.
The Sieve Cover and Pan
A complete stack of sieves is topped with a sieve cover to prevent any loss of the sample during shaking.
At the very bottom of the stack sits a solid collection pan, often called a receiver. This pan collects the finest particles that pass through all the screens in the stack.
How a Sieve Analysis Is Performed
The procedure for conducting a sieve test is straightforward and methodical, designed to ensure the results are both accurate and repeatable. The outcome is not just a pile of sorted material, but a valuable set of data.
Sample Preparation
The process begins with a representative, weighed sample of the material to be analyzed. Using a known starting mass is essential for calculating the final percentages accurately.
Assembling the Sieve Stack
The sieves are stacked in a column, or "nest," with the sieve having the largest mesh openings at the top. Each subsequent sieve placed below it has progressively smaller openings. The collection pan is placed at the very bottom.
Mechanical Agitation
The prepared sample is placed in the top sieve, the cover is secured, and the entire stack is placed in a mechanical shaker. This device agates the stack, usually with a vibrating or tapping motion, for a set period.
This agitation ensures that all particles have an opportunity to pass through the mesh openings until they arrive at a sieve they are too large to pass through.
Data Collection and Calculation
After shaking is complete, the material retained on each individual sieve is carefully removed and weighed.
The mass from each sieve is then divided by the total initial mass of the sample. This calculation determines the percentage of the material that falls within each specific particle size range, creating the particle size distribution.
Common Pitfalls and Limitations
While highly effective, the standard sieve test is not without its limitations. Understanding these is key to interpreting results correctly and knowing when a different method may be required.
The Lower Limit of Particle Size
For extremely fine powders, traditional woven-wire sieves become less effective. Particles smaller than about 20 microns are difficult to measure accurately with this method.
The Risk of Mesh Blinding
Fine or statically-charged particles can clog, or "blind," the openings in the mesh. This blockage prevents other particles from passing through, leading to inaccurate measurements and a skewed distribution.
The Need for Specialized Equipment
To analyze particles finer than 20 microns or those prone to clogging, specialized instruments are required. Electromagnetic sieve shakers, for example, use advanced agitation to keep fine sieves clear, allowing for analysis of particles as small as 5μm.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The purpose of a sieve test is to generate reliable data. The correct approach depends entirely on the material you are analyzing and the standards you must meet.
- If your primary focus is quality control for coarse materials (like sand, gravel, or grains): The standard method using a stack of woven-wire sieves on a mechanical shaker is the proven, industry-standard approach.
- If your primary focus is analyzing fine powders or materials prone to static: You must consider specialized equipment like an electromagnetic shaker to prevent mesh blinding and ensure accurate results for sub-millimeter particles.
- If your primary focus is adhering to a specific industry standard (e.g., ASTM, ISO): The exact sieve sizes, sample weight, and shaking duration are non-negotiable and must be followed precisely as specified by the governing body.
Ultimately, mastering the sieve test empowers you to transform a simple physical sample into the precise data needed for predictable and reliable results.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Purpose | Common Sizes/Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Wire Mesh Screen | Physically separates particles by size | 20μm to 100mm+; Stainless Steel |
| Frame & Skirt | Holds mesh taut; stacks sieves securely | 3", 8", 12" (US); 100, 200, 300mm (Int'l) |
| Cover & Pan | Prevents sample loss; collects finest particles | Metal (Brass, Stainless Steel) |
| Mechanical Shaker | Agitates sieve stack for consistent separation | Various models for different standards |
Ready to achieve precise and reliable particle size analysis in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of test sieves and mechanical or electromagnetic sieve shakers designed to meet ASTM and ISO standards. Whether you're working with coarse aggregates or fine powders, our solutions help you prevent mesh blinding and ensure accurate, repeatable results for superior quality control.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieving solution for your specific material and application needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment



















