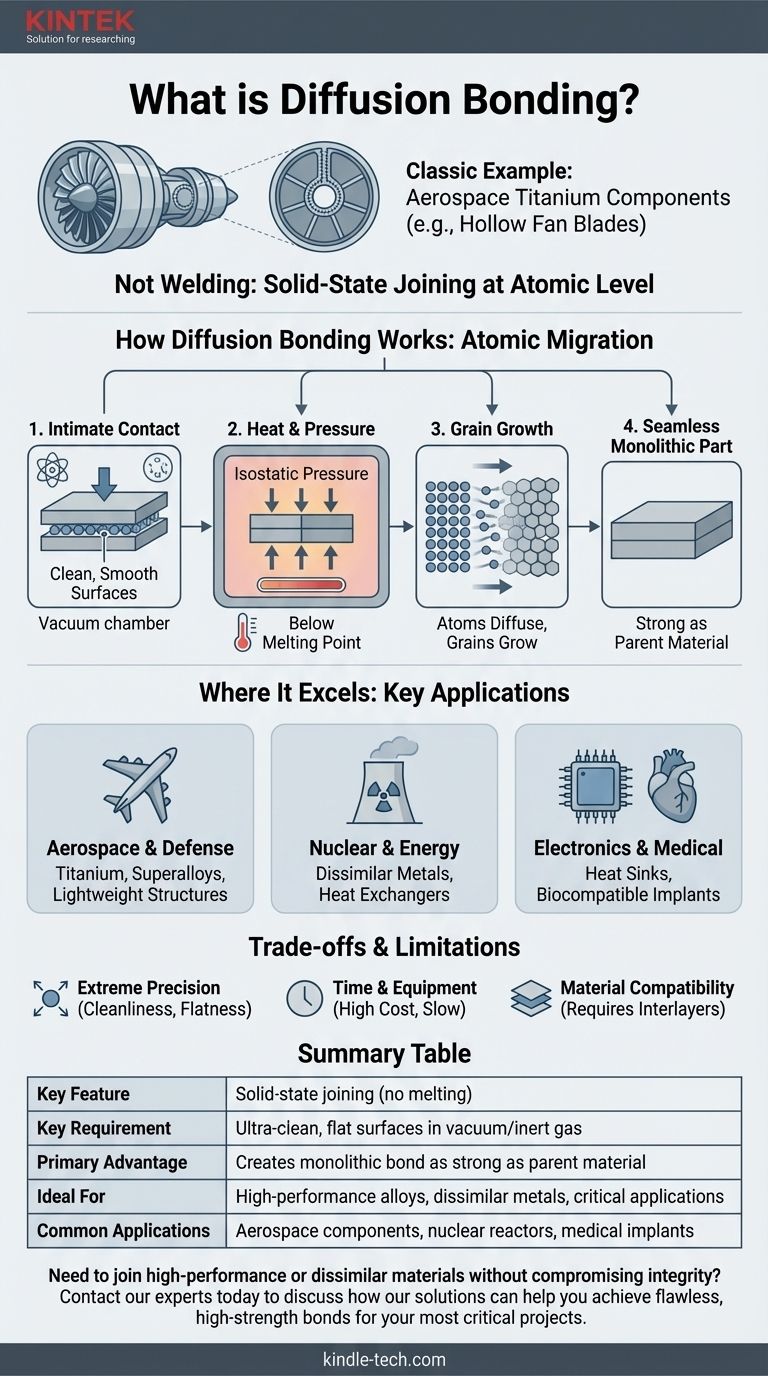
A classic example of diffusion bonding is the fabrication of high-performance titanium alloy components for the aerospace industry, such as multi-layered structural panels or hollow fan blades for jet engines. In this process, multiple sheets of titanium are stacked, heated to a high temperature (well below their melting point), and subjected to immense pressure in a vacuum, causing the atoms at the surface of each sheet to intermingle and form a single, monolithic part.
The core principle to understand is that diffusion bonding is not welding. It is a solid-state joining process that merges materials at an atomic level, creating a seamless bond that is often as strong as the parent material itself.

How Diffusion Bonding Actually Works
To grasp why this process is so unique, we need to look at what happens on a microscopic scale. It's a deliberate, controlled merging of materials.
The Principle: Atomic Migration
At its heart, diffusion bonding relies on the natural tendency of atoms to move, or diffuse. By applying heat, we give atoms the energy they need to migrate across the boundary between two separate pieces of material.
The process is analogous to two dense, orderly crowds of people standing face-to-face. Over time, individuals from each crowd begin to wander into the other, eventually blurring the line until the two groups have merged into one.
Step 1: Intimate Contact
The process cannot begin unless the two surfaces are in perfect, atom-to-atom contact. This requires the surfaces to be exceptionally clean and smooth—far beyond what is visible to the naked eye.
Any contaminants, like oxides or oils, act as a barrier that prevents atoms from meeting and bonding. This is why the process is typically done in a vacuum or an inert gas environment.
Step 2: Applying Heat and Pressure
Heat provides the thermal energy for atoms to become mobile. Importantly, the temperature is kept below the material's melting point. This prevents the undesirable effects of melting and solidification found in welding, such as distortion or weakened zones.
Simultaneously, high isostatic pressure (equal pressure from all sides) is applied. This forces the two surfaces together, crushing any microscopic high points (asperities) and closing the tiny voids between them.
Step 3: Grain Growth Across the Interface
Over a period of hours, atoms diffuse across the original boundary. The material's crystalline structures, known as grains, begin to grow across this interface.
Ultimately, the original boundary line completely disappears. The result is a single, continuous piece of material with a joint that is virtually undetectable, both visually and mechanically.
Where Diffusion Bonding Excels: Key Applications
Diffusion bonding is a specialized, high-cost process reserved for applications where component failure is not an option and traditional methods are insufficient.
Aerospace and Defense
This is the most common application. It is used to join titanium alloys, superalloys, and metal matrix composites for airframe structures, landing gear components, and hollow turbine blades that are both lightweight and incredibly strong.
Nuclear and Energy
The ability to join dissimilar metals is a key advantage. For example, diffusion bonding can join stainless steel to copper for components in nuclear reactors or high-performance heat exchangers, where different thermal and structural properties are required in the same part.
Electronics and Medical
In high-power electronics, diffusion bonding is used to attach heat sinks to semiconductor devices without the thermal stress of welding or soldering. In the medical field, it joins biocompatible metals like titanium for implants, ensuring a perfect, crevice-free bond that won't harbor bacteria.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, diffusion bonding is not a universal solution. Its demanding nature creates significant limitations.
The Need for Extreme Precision
The requirement for ultra-clean, perfectly flat surfaces cannot be overstated. Surface preparation is meticulous, complex, and a primary driver of the overall cost. Any failure in preparation will result in a failed bond.
The Time and Equipment Investment
This is not a fast process. Bond cycles often take several hours to complete. It also requires highly specialized and expensive equipment, such as a Hot Isostatic Press (HIP) or vacuum furnaces capable of exerting high pressures at high temperatures.
Material Compatibility
Not all materials are easily diffusion bonded. The process works best with materials that have similar crystal structures and atomic properties. Bonding vastly different materials often requires a thin interlayer of a compatible third material to act as a "bridge" between the two.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting diffusion bonding requires a clear understanding of your non-negotiable requirements.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials without melting: Diffusion bonding is an unparalleled choice, especially for high-consequence applications in the nuclear, electronic, or energy sectors.
- If your primary focus is creating the strongest possible joint in high-performance alloys: Diffusion bonding creates a bond with properties nearly identical to the parent material, making it ideal for critical aerospace and defense components.
- If your primary focus is speed and cost for general fabrication: A more conventional joining process like welding, brazing, or even mechanical fastening will almost always be the more practical and economical solution.
Ultimately, diffusion bonding empowers engineers to create components that would be impossible to manufacture by any other method.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Solid-state joining (no melting) |
| Key Requirement | Ultra-clean, flat surfaces in a vacuum/inert gas |
| Primary Advantage | Creates a monolithic bond as strong as the parent material |
| Ideal For | High-performance alloys, dissimilar metals, critical applications |
| Common Applications | Aerospace components, nuclear reactors, medical implants |
Need to join high-performance or dissimilar materials without compromising their integrity?
Diffusion bonding is a specialized solution for creating components where failure is not an option. KINTEK specializes in the advanced equipment and consumables required for this precise process, serving the exacting needs of aerospace, medical, and energy laboratories.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve flawless, high-strength bonds for your most critical projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play in the fabrication of CuCrFeMnNi alloys? Achieve High Purity
- How does the degassing stage in a vacuum hot press (VHP) optimize diamond/aluminum composite performance?
- How does the vacuum hot pressing process affect the properties of finished materials? Maximize Density and Performance
- What are the advantages of using a Vacuum Hot-Pressing Furnace for Ti-6Al-4V? Achieve Forged-Like Strength & Purity
- How does the pressure loading system of a vacuum hot press furnace regulate CoCrCuFeNi alloy microstructure?



















