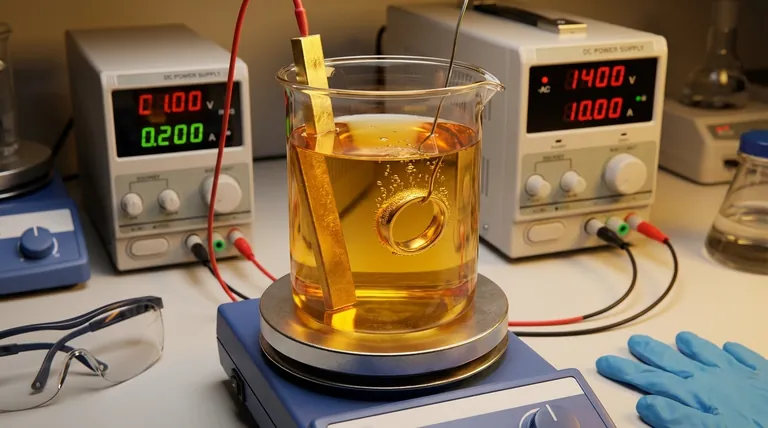
A classic example of electrodeposition is the process of gold plating jewelry. In this application, an electric current is used to move gold ions from a solution onto the surface of a less expensive metal, creating a thin, durable, and lustrous layer of gold. This same fundamental technique is used for everything from chrome-plating car bumpers to fabricating microscopic copper wiring in computer chips.
Electrodeposition is essentially an electrically-driven painting process. It uses a controlled electric current to precisely transfer metal ions through a liquid solution (an electrolyte) and deposit them as a thin, solid film onto a conductive object.

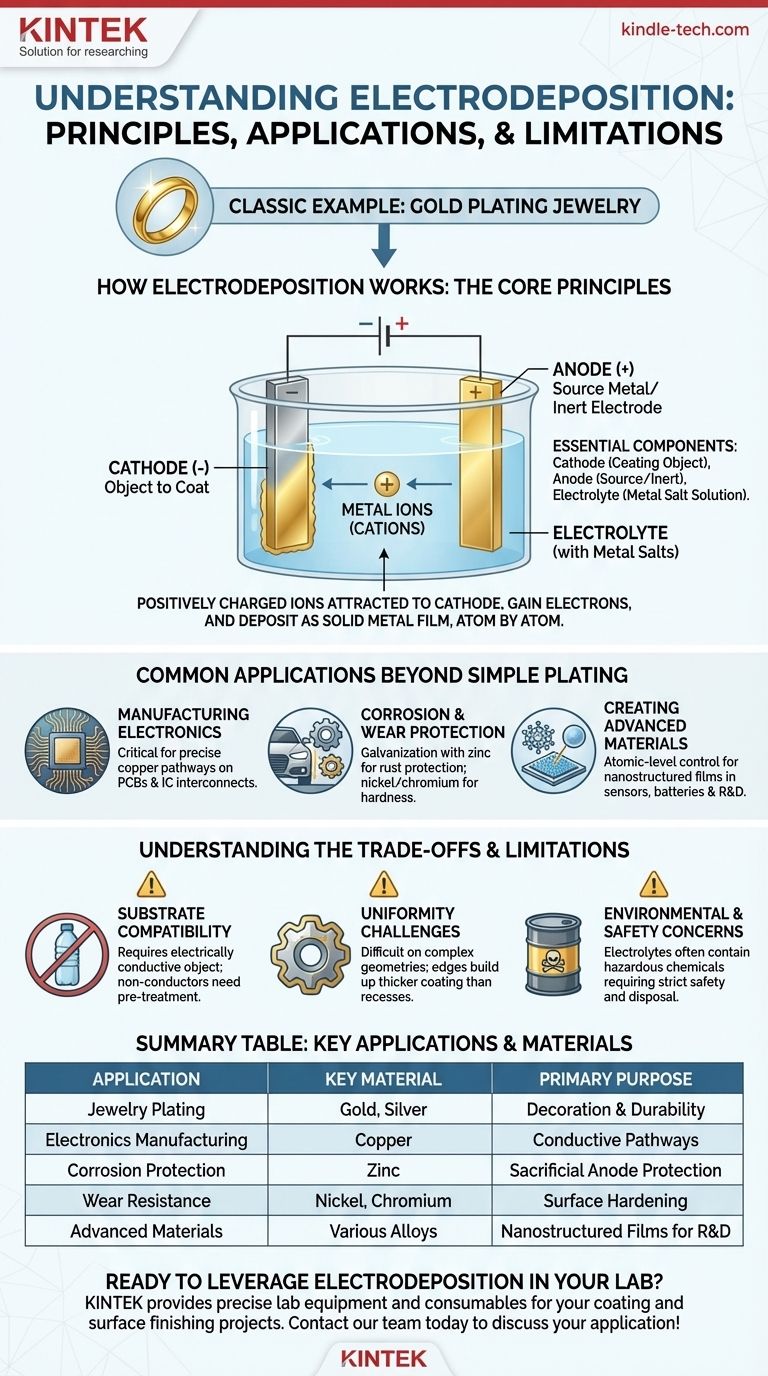
How Electrodeposition Works: The Core Principles
To understand electrodeposition, you need to visualize three key components working together in an electrochemical cell.
The Essential Components
The setup consists of two electrodes immersed in a special liquid.
- The Cathode: This is the object you want to coat. It is connected to the negative terminal of a power source.
- The Anode: This is the source metal (or an inert electrode). It is connected to the positive terminal of the power source.
- The Electrolyte: This is a solution, often containing dissolved salts of the metal you want to deposit (e.g., gold salts for gold plating).
The Electrochemical Reaction
When the power is turned on, an electric field is established between the two electrodes. This initiates a controlled chemical reaction.
Positively charged metal ions (cations) floating in the electrolyte are attracted to the negatively charged cathode.
Building the Coating Layer by Layer
As the ions reach the cathode, they gain electrons and are "reduced" back into their solid metallic state, plating onto the surface.
This process builds the coating one atomic layer at a time, resulting in a highly uniform and well-bonded film. Meanwhile, the anode may dissolve to replenish the metal ions in the solution, maintaining the process.
Common Applications Beyond Simple Plating
While decorative coating is a common example, the true power of electrodeposition lies in its precision and versatility for industrial and technological applications.
Manufacturing Electronics
Electrodeposition is critical for creating the intricate copper pathways on printed circuit boards (PCBs) and the interconnects within integrated circuits. Its precision allows for the fabrication of microscopic conductive lines.
Corrosion and Wear Protection
A process called galvanization uses electrodeposition to coat steel with a layer of zinc. The zinc layer corrodes preferentially, sacrificing itself to protect the underlying steel from rust. Nickel and chromium coatings are also used to improve hardness and wear resistance on industrial parts.
Creating Advanced Materials
Because it offers atomic-level control, electrodeposition is used in research and high-tech manufacturing to create nanostructured films. These materials have unique properties and are used in sensors, catalysts, and advanced batteries.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, electrodeposition is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to applying it effectively.
Substrate Compatibility
The primary requirement is that the object being plated (the substrate) must be electrically conductive. Plating on plastics, ceramics, or other insulators requires a complex pre-treatment process to apply a thin conductive seed layer first.
Uniformity Challenges
Achieving a perfectly even coating on objects with complex geometries can be difficult. High-current-density areas, like sharp corners and edges, tend to build up a thicker coating than recessed areas or holes.
Environmental and Safety Concerns
The electrolyte baths used in electroplating often contain acidic, alkaline, or toxic chemicals (like cyanide in some processes). These materials require strict safety protocols for handling and environmentally sound procedures for disposal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your reason for using electrodeposition will determine the material and process parameters you should focus on.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics or decoration: Prioritize materials like gold, silver, rhodium, or chromium for their appearance and durability on consumer goods.
- If your primary focus is engineering and protection: Consider functional coatings like zinc for corrosion resistance, nickel for wear resistance, or copper for conductivity.
- If your primary focus is advanced research or electronics: Explore the precise control of electrodeposition to create alloy films or nanostructures with specific catalytic or electrical properties.
By understanding electrodeposition as a controlled, electrically-driven coating method, you can effectively leverage its power across countless industrial and scientific applications.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Material | Primary Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Jewelry Plating | Gold, Silver | Decoration & Durability |
| Electronics Manufacturing | Copper | Conductive Pathways |
| Corrosion Protection (Galvanization) | Zinc | Sacrificial Anode Protection |
| Wear Resistance | Nickel, Chromium | Surface Hardening |
| Advanced Materials | Various Alloys | Nanostructured Films for R&D |
Ready to leverage electrodeposition in your lab? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for your coating and surface finishing projects. Whether you are developing new materials or scaling up a production process, our expertise can help you achieve superior results. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance



















