At its core, annealing is a process of controlled relaxation for materials. It is a specific heat treatment that involves heating a material to a designated temperature, holding it there for a period, and then cooling it at a controlled, typically slow, rate. This is done to achieve a softer, more ductile, and internally stable state, making the material easier to work with and more resistant to fracture.
Annealing is not primarily about making a material stronger; it is about making it more workable and stable. By applying heat and then slowly cooling, you are fundamentally resetting the material's internal structure, relieving built-up stresses and removing the brittleness caused by previous manufacturing processes.

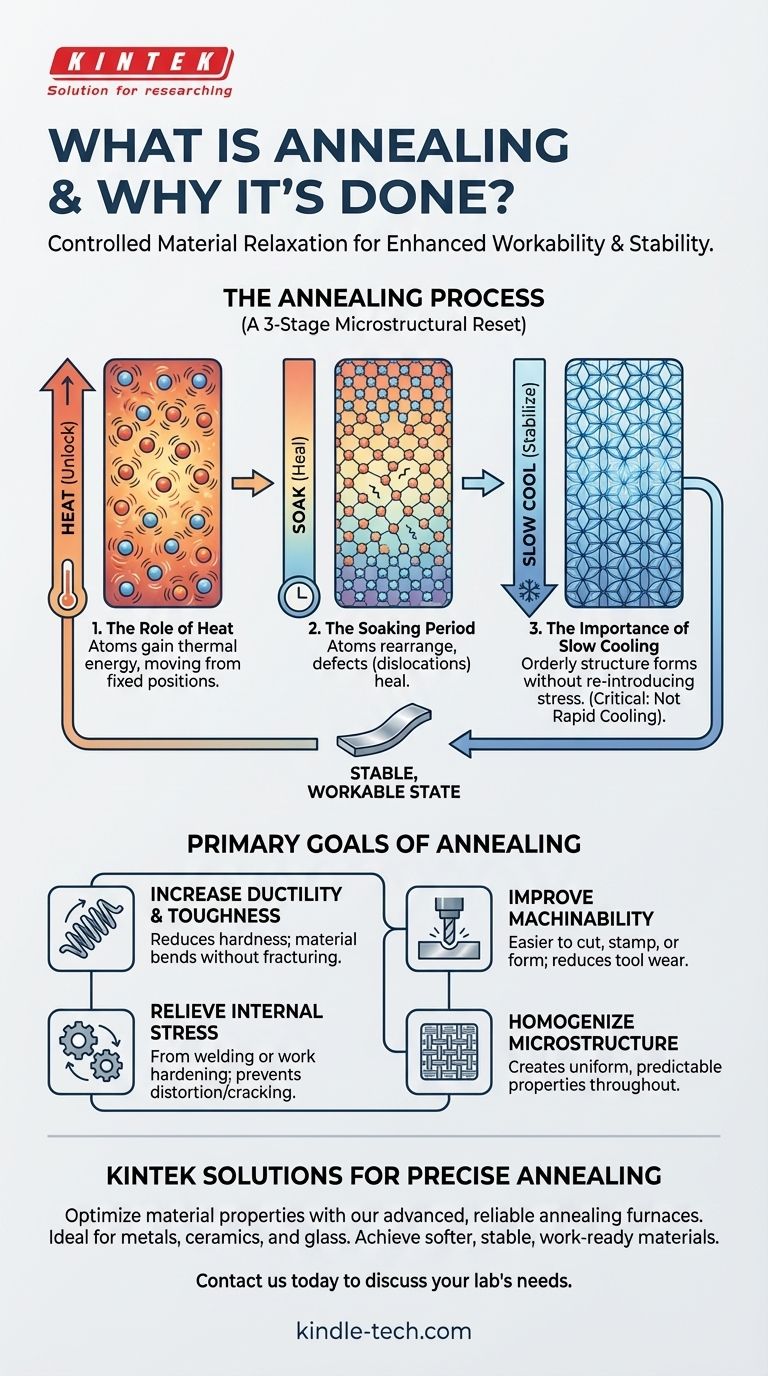
The Mechanics of Annealing: A Microstructural Reset
Annealing is a precise, three-stage process that fundamentally alters a material's internal crystal structure to achieve more desirable properties.
The Role of Heat: Unlocking the Crystalline Structure
When a material is heated during annealing, its atoms gain thermal energy. This energy allows them to vibrate more and move from their fixed positions in the crystal lattice. The temperature is high enough to allow this movement but remains below the material's melting point.
The Soaking Period: Allowing Defects to Heal
The material is then held at this elevated temperature, a stage known as "soaking." During this time, the mobile atoms can rearrange themselves into a more uniform and lower-energy state. This process reduces or eliminates dislocations—defects and irregularities in the crystal structure that are the primary cause of hardness and brittleness.
The Importance of Slow Cooling: Locking in Stability
Finally, the material is cooled slowly. This slow rate is critical because it allows the new, more orderly crystalline structure to form without re-introducing internal stresses. A rapid cool (quenching) would trap the material in a disordered state, making it hard and brittle—the exact opposite of annealing's goal.
The Primary Goals of Annealing
Engineers and manufacturers perform annealing to solve specific problems and prepare materials for subsequent operations.
Reducing Hardness and Increasing Ductility
The most common reason for annealing is to soften a material. By reducing crystal dislocations, annealing increases ductility (the ability to be drawn into a wire or deformed without fracturing) and toughness, making the material less prone to cracking under stress.
Relieving Internal Stress
Processes like welding, casting, or work hardening (e.g., bending or hammering) create immense internal stresses within a material's structure. These stresses can lead to premature failure or dimensional distortion over time. Annealing provides a controlled way to release this stored energy, creating a more stable and predictable component.
Improving Machinability and Formability
A softer, more ductile material is significantly easier to machine, cut, stamp, or bend. Annealing a workpiece before these operations reduces tool wear, improves surface finish, and allows for more aggressive cold working without the risk of the material cracking.
Homogenizing the Microstructure
Annealing refines the grain structure of the material, making it more uniform and consistent throughout. This homogenization ensures that the mechanical properties are predictable across the entire part.
Understanding the Key Variations and Considerations
While the principle is universal, the application of annealing is tailored to specific materials and desired outcomes.
The Trade-off: Hardness vs. Ductility
Annealing is a deliberate choice to sacrifice hardness and tensile strength in exchange for ductility and workability. For applications requiring maximum hardness, a different heat treatment, like quenching and tempering, would be used.
Special Case: Vacuum Annealing
Performing the annealing process inside a vacuum prevents oxidation and surface contamination. This is crucial for materials where surface finish and purity are critical, resulting in a bright, clean part that requires no further cleaning.
Special Case: Low Hydrogen Annealing
Also known as "baking," this is a specific low-temperature anneal designed to remove trapped hydrogen from metals, particularly steel. This process is essential for preventing hydrogen embrittlement, a catastrophic failure mode where hydrogen causes the metal to crack under load.
Beyond Metals: Annealing Ceramics and Glass
The principles of annealing are not limited to metals. Ceramic and glass components are also annealed to relieve internal stresses introduced during manufacturing, which significantly improves their mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right annealing process depends entirely on what you need to achieve with your material.
- If your primary focus is preparing a material for extensive machining or cold forming: Anneal to maximize ductility and reduce hardness, which prevents tool wear and material fracture during processing.
- If your primary focus is ensuring the long-term stability of a welded or heavily worked part: Use a stress-relief anneal to remove internal stresses that could lead to cracking or distortion in service.
- If your primary focus is preventing embrittlement in high-strength steels: Employ a specific low-temperature bake, or 'low hydrogen anneal', to drive out trapped hydrogen without significantly altering the base hardness.
Ultimately, annealing empowers you to reset a material's properties, transforming a brittle, stressed component into a stable and workable foundation.
Summary Table:
| Goal of Annealing | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Reduce Hardness | Increases ductility and toughness |
| Relieve Internal Stress | Prevents cracking and distortion |
| Improve Machinability | Easier to cut, bend, and form |
| Homogenize Microstructure | Creates uniform material properties |
Ready to optimize your material properties with precise annealing?
At KINTEK, we specialize in laboratory equipment and consumables, including advanced annealing furnaces designed for reliability and exact temperature control. Whether you are processing metals, ceramics, or glass, our solutions help you achieve softer, more stable, and work-ready materials—improving your manufacturing outcomes and product performance.
Contact us today via our Contact Form to discuss your specific annealing needs and discover the right equipment for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the lowest possible vacuum pressure? Achieve Pristine Conditions for Your Lab
- What role do industrial vacuum ovens play in LPBF powder pretreatment? Optimize Your Metal Additive Manufacturing
- What are the process advantages of introducing argon gas during magnesium reduction? Enhance Purity and Yield
- What function does a vacuum environment serve in a high-temperature furnace? Protect Fe-Si Alloy Thermal Cycle Tests
- What temperature is a hardening furnace? Achieve Precise Heat Treatment for Superior Metal Hardness
- How does a vertical furnace achieve energy-saving sintering? Harness Internal Energy for Efficient Pellet Treatment
- What is debinding and sintering? Master the Two-Step Process for Dense Metal Parts
- How do high-temperature furnaces affect bio-oil yield? Optimize Pyrolysis with Precision Control



















