In a technical or industrial setting, atmosphere climate control is the deliberate and precise management of the temperature and chemical composition of the gases within a sealed environment. This is done to create a specific, stable condition required for a scientific or manufacturing process. It is distinct from the Earth's natural climate system, though the principle of an atmosphere acting as a moderating blanket is a useful analogy.
While Earth's atmosphere naturally regulates our planet's climate, technical atmosphere control is an engineered process essential for high-tech manufacturing and science. Its purpose is to create a highly specific and stable gaseous environment to enable outcomes that would be impossible in open air.

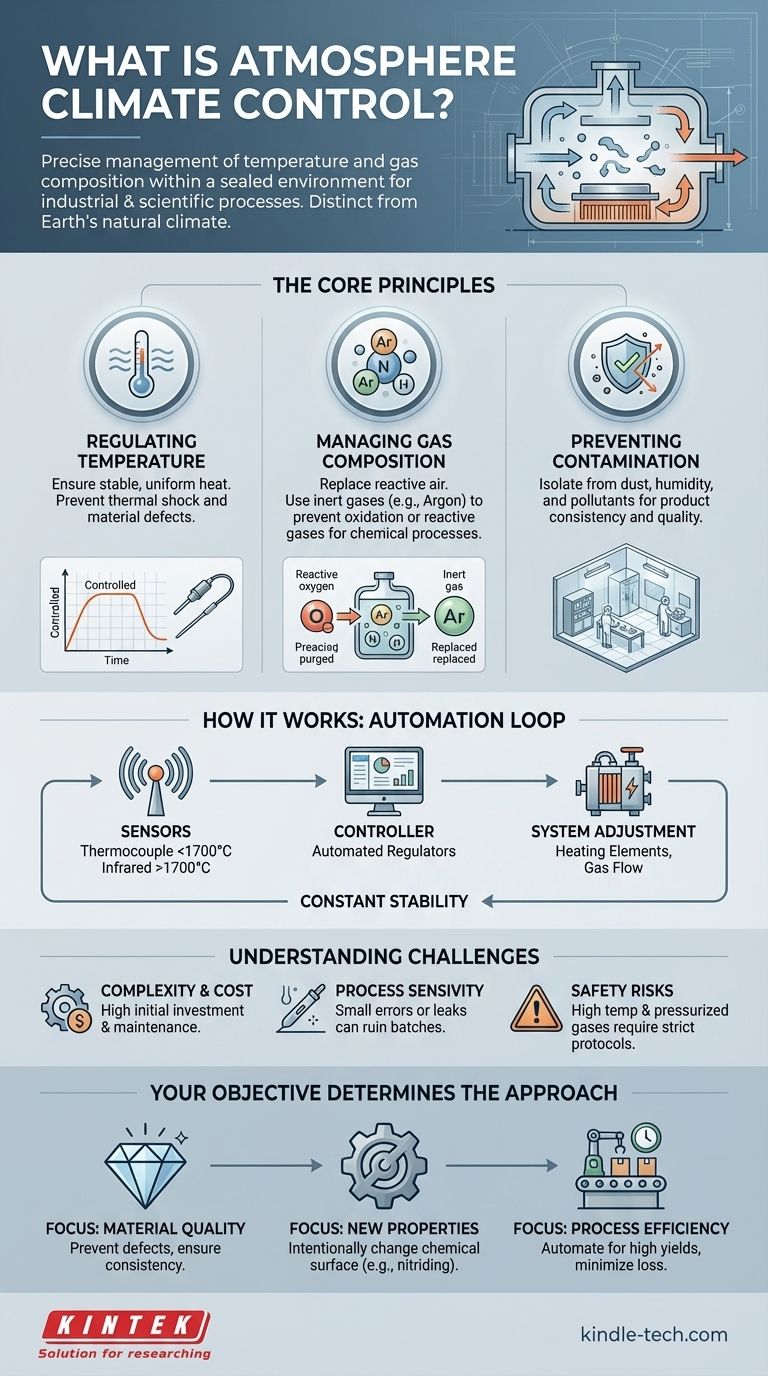
The Core Principles: Why Control an Atmosphere?
The air we breathe is a reactive mix of gases, primarily nitrogen and oxygen. For many sensitive industrial and scientific processes, this open-air environment is a source of contamination and unwanted chemical reactions. Atmosphere control is the solution.
Regulating Temperature with Precision
The most fundamental parameter to control is temperature. Many processes, from growing crystals to heat-treating metal alloys, require not just high heat, but exceptionally stable and uniform heat.
Sudden temperature changes can introduce stress, cracks, or other defects into a material. Atmosphere control systems prevent this by creating a thermal buffer, ensuring the product is heated and cooled at a precisely managed rate.
Managing Atmospheric Composition
Beyond temperature, the gases themselves are critical. Oxygen, for example, is highly reactive at high temperatures and causes oxidation (like rust), which can ruin sensitive electronics or weaken metal parts.
Controlled atmospheres replace reactive air with specific gases. This can be an inert gas like argon or nitrogen to prevent all reactions, or a reactive gas like hydrogen to actively remove oxides or participate in a chemical process.
Preventing Contamination
The goal is to create a pure, predictable environment. Atmosphere control isolates the process from airborne dust, humidity, and other contaminants that could compromise the final product, ensuring consistency and quality from batch to batch.
How It Works: Sensors and Control Systems
Achieving this level of control requires a sophisticated system of sensors and automated regulators working in a constant feedback loop.
Sensing Temperature: Thermocouples and Infrared
Accurate measurement is the first step. Different tools are used for different temperature ranges, as accuracy varies with heat.
- A thermocouple is a robust sensor used for most industrial heat ranges, typically for temperatures below 1700°C. It measures temperature based on a voltage change between two different metals.
- An infrared instrument (pyrometer) is used for extreme temperatures above 1700°C. It measures the thermal radiation emitted by a hot object without needing to make physical contact.
The Control Loop: Automation and Stability
The sensor data is fed to a controller. The operator sets a desired temperature, and the system automates the rest.
The controller constantly compares the measured temperature to the setpoint. It then adjusts the power to the heating elements to either raise or lower the heat, preventing the sudden spikes or drops that would occur without this feedback. This same principle applies to regulating gas flow and pressure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Implementing atmosphere control is not a simple task and involves significant considerations.
Complexity and Cost
Systems for controlling high-temperature atmospheres are expensive to build and maintain. They require specialized furnaces, vacuum-tight seals, gas delivery plumbing, and sophisticated electronic controllers, all of which represent a major investment.
Process Sensitivity
These are high-precision processes. A small leak admitting oxygen, a faulty sensor, or an incorrect gas mixture can ruin an entire production batch, leading to wasted time and materials. Constant monitoring and calibration are essential.
Safety Risks
Working with high temperatures and compressed gases, some of which may be flammable (like hydrogen) or pose an asphyxiation risk (like nitrogen and argon), requires strict safety protocols and operator training.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
How you approach atmosphere control depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is material quality: Your goal is to use a specific atmosphere (e.g., inert argon) to prevent defects like oxidation and ensure perfectly consistent, repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is creating new material properties: You will use a reactive atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen in a process called nitriding) to intentionally change the chemical surface of a material to make it harder.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: You should leverage fully automated control systems to maintain a stable process window, minimize human error, and achieve high yields with minimal product loss.
Ultimately, mastering atmosphere control is about creating the perfect, isolated environment to achieve a specific scientific or industrial outcome.
Summary Table:
| Aspect of Control | Purpose | Key Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Ensure stable, uniform heating/cooling to prevent material defects. | Thermocouples (<1700°C), Infrared Pyrometers (>1700°C), Automated Controllers |
| Gas Composition | Prevent oxidation or enable specific chemical reactions. | Inert Gases (Argon, Nitrogen), Reactive Gases (Hydrogen), Gas Delivery Systems |
| Contamination | Isolate process from dust, humidity, and airborne pollutants. | Vacuum-tight Seals, Purge Systems, Cleanroom-grade Components |
Ready to achieve flawless results in your lab or production line?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust lab equipment and consumables for precise atmosphere control. Whether you need to prevent oxidation in metal heat treatment, grow perfect crystals, or ensure contamination-free processing, our solutions deliver the stable, pure environments your work demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you optimize your process efficiency, improve material quality, and achieve consistent, repeatable outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2
- What is the purpose of inert atmosphere? A Guide to Protecting Your Materials and Processes
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- What is the role of an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace in Cu-Mo sintering? Achieve High-Purity Densification
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety



















