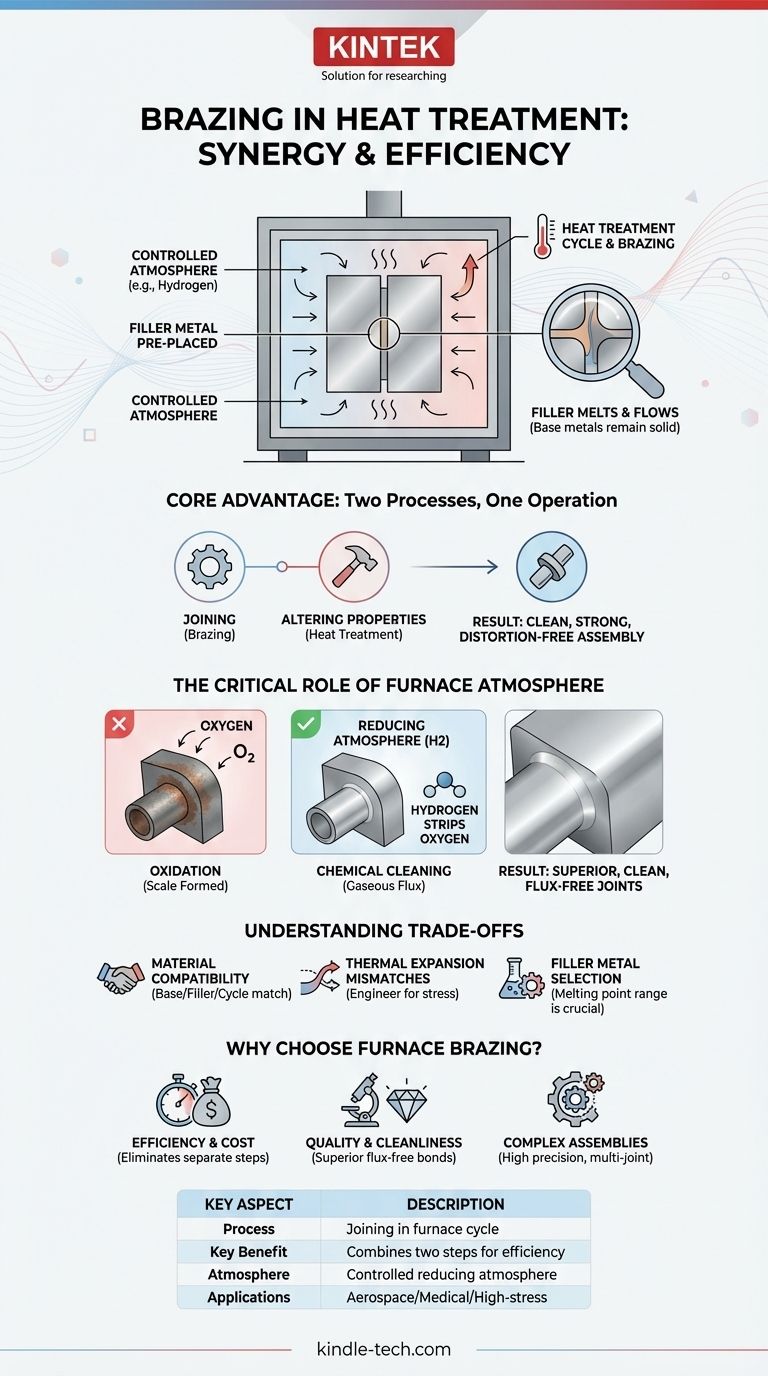
In the context of heat treatment, brazing is a specialized joining process where metal components are bonded together inside a controlled-atmosphere furnace. The heat required for the treatment cycle simultaneously melts a filler metal, which flows between the parts and solidifies to create a strong joint. This method effectively combines two manufacturing steps into one highly efficient operation.
The core advantage of brazing within heat treatment is efficiency and quality. By using the furnace's heat and protective atmosphere, you can join components while simultaneously altering their material properties, resulting in a clean, strong, and distortion-free final assembly.

The Synergy of Brazing and Heat Treatment
Combining these processes is a deliberate engineering choice designed to optimize manufacturing. It leverages the inherent conditions of a heat treatment cycle to produce superior joints.
What is Brazing?
Brazing is a metal-joining technique that uses a filler metal with a lower melting point than the base metals being joined. The filler metal is heated above its melting point (specifically, above 450°C or 842°F), flows into the gap between the parts through capillary action, and then cools to form the bond.
Crucially, the base metals themselves never melt. This is the key distinction between brazing and welding.
What is Heat Treatment?
Heat treatment is a broad group of processes involving the controlled heating and cooling of metals to alter their physical and mechanical properties. This can be done to make a material harder, softer, or more resistant to wear.
Combining the Processes
Furnace brazing integrates these two operations. An assembly of parts, with the filler metal pre-placed at the joints, is loaded into a heat treatment furnace. As the furnace executes a specific heating and cooling profile to treat the material (e.g., for hardening), it also provides the thermal energy needed to melt the brazing filler.
The Critical Role of the Furnace Atmosphere
The environment inside the furnace is not just incidental; it is essential for the success of the process. Brazing without a controlled atmosphere at high temperatures would fail.
Preventing Oxidation
When metals are heated in the presence of oxygen, they form oxides, or scale, on their surface. This oxide layer acts as a barrier, preventing the molten filler metal from wetting the base material and forming a proper metallurgical bond.
The Function of a Reducing Atmosphere
Heat treatment furnaces for brazing are typically filled with a controlled, oxygen-free atmosphere, often containing gases like hydrogen. As a powerful reducing agent, hydrogen actively strips oxygen from the metal surfaces by reacting with any existing oxides.
This chemical cleaning action essentially functions as a "gaseous flux," preparing the surfaces to be perfectly clean at the exact moment the filler metal melts.
The Result: Clean and Strong Assemblies
Because no flux is used and oxidation is prevented, the resulting assembly is exceptionally clean and free of residue. The bond is strong, continuous, and suitable for high-stress and high-purity applications, such as in the aerospace or medical industries.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, this combined process requires careful planning and is not universally applicable.
Material Compatibility
The base metals, filler metal, and the required heat treatment cycle must all be compatible. For example, the temperature required to achieve the desired hardness in the base metal must align with the melting range of the filler metal.
Thermal Expansion Mismatches
When joining dissimilar materials, their different rates of thermal expansion can induce stress in the joint as the assembly cools. This must be carefully engineered to prevent distortion or joint failure.
Filler Metal Selection is Crucial
Choosing the right filler metal is paramount. Its melting point must be low enough to not damage the base materials but high enough to occur at the correct point in the heat treatment cycle.
Is Furnace Brazing Right for Your Application?
Choosing this process depends entirely on your project's goals.
- If your primary focus is efficiency and cost reduction: Combining processes into a single furnace run eliminates separate joining operations, saving significant time, labor, and handling.
- If your primary focus is joint quality and cleanliness: The controlled, reducing atmosphere of the furnace creates superior, flux-free joints that are often impossible to achieve otherwise.
- If your primary focus is complex or multi-joint assemblies: Furnace brazing allows you to join multiple, intricate, or internal joints simultaneously with high precision and repeatability.
By integrating brazing into the heat treatment cycle, you transform two separate manufacturing steps into a single, highly controlled, and value-added process.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Joining metals using a filler metal within a heat treatment furnace cycle. |
| Key Benefit | Combines two manufacturing steps into one for efficiency and superior joint quality. |
| Atmosphere | Controlled reducing atmosphere (e.g., hydrogen) prevents oxidation and cleans surfaces. |
| Applications | Ideal for aerospace, medical, and high-stress assemblies requiring precision and cleanliness. |
Ready to enhance your manufacturing process with integrated brazing and heat treatment? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions for precise thermal processing. Our expertise ensures you achieve strong, clean joints while optimizing efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory needs and deliver reliable performance for your critical applications. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing



















