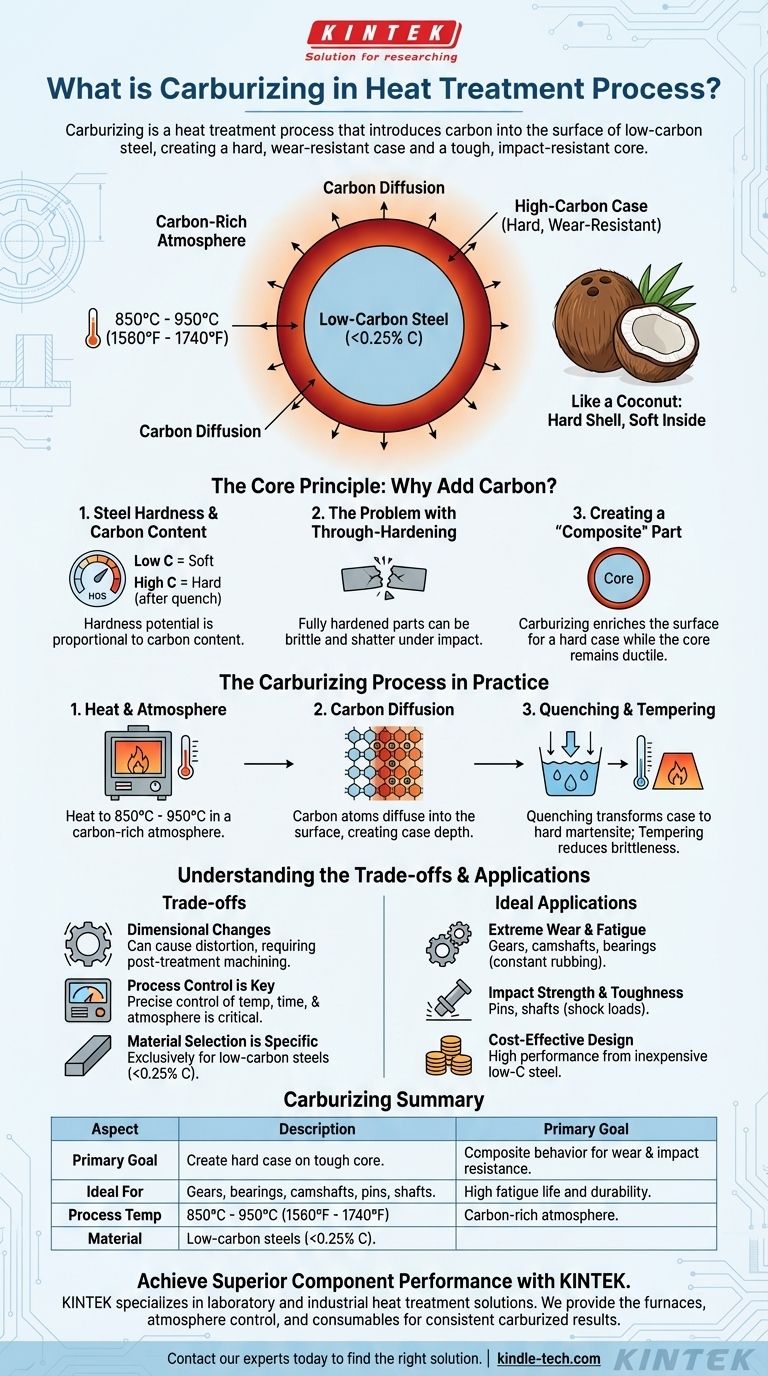
In short, carburizing is a heat treatment process that introduces carbon into the surface of low-carbon steel. By heating the metal in a carbon-rich environment, it creates a part with a very hard, wear-resistant outer layer, or "case," while the interior, or "core," remains soft and tough.
The central purpose of carburizing is not simply to make steel harder, but to create a composite part from a single piece of metal: a hard, wear-resistant surface fused to a tough, impact-resistant core.

The Core Principle: Why Add Carbon?
Carburizing is a specific type of case-hardening process. Its value is rooted in the fundamental relationship between carbon content and the properties of steel.
Steel Hardness and Carbon Content
The ability of steel to become hard when quenched (rapidly cooled) is directly proportional to its carbon content. Low-carbon steels, while tough and easily formed, cannot be significantly hardened on their own.
The Problem with Through-Hardening
Simply using a high-carbon steel to make a part hard all the way through is often a poor solution. A fully hardened component can become brittle, making it susceptible to shattering under sharp impacts or stress.
Creating a "Composite" Part
Carburizing solves this dilemma. It enriches only the surface of a low-carbon steel part with additional carbon. This creates two distinct zones: a high-carbon case with the potential for high hardness, and a low-carbon core that retains its inherent toughness and ductility.
This is analogous to a coconut: a hard, protective outer shell protecting the softer material inside.
The Carburizing Process in Practice
The process involves two critical stages: enriching the surface with carbon and then locking in the hardness.
The Critical Ingredients: Temperature and Atmosphere
The steel component is heated to a high temperature, typically between 850°C and 950°C (1560°F and 1740°F), well below its melting point. It is held at this temperature inside a sealed furnace with a controlled, carbon-rich atmosphere.
Carbon Diffusion
At this elevated temperature, the steel's crystal structure is open, allowing carbon atoms from the atmosphere to diffuse into the surface. The depth of this carbon penetration, known as the case depth, is controlled by the time and temperature of the process.
The Essential Final Step: Quenching and Tempering
Adding carbon only provides the potential for hardness. To achieve the final properties, the part must be quenched from the high temperature. This rapid cooling transforms the high-carbon case into a very hard structure (martensite), while the low-carbon core becomes a much tougher, more ductile structure. A final, low-temperature tempering treatment is often performed to reduce brittleness in the case.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, carburizing is a complex metallurgical process with critical variables that must be controlled.
Dimensional Changes
The intense heating and rapid quenching inherent in the process can cause the component to distort or change dimensions. This must be anticipated in the design, often requiring post-treatment grinding or machining to achieve final tolerances.
Process Control is Key
The effectiveness of carburizing depends entirely on precise control over temperature, time, and atmospheric composition. Inconsistent process control can lead to a case that is too shallow, too deep, or has an incorrect carbon level, resulting in component failure.
Material Selection is Specific
This process is designed exclusively for low-carbon steels (typically with less than 0.25% carbon). Applying it to medium or high-carbon steels is unnecessary and can create an extremely brittle surface prone to cracking.
When to Specify Carburizing
Choosing this process is an engineering decision driven by the component's required performance characteristics.
- If your primary focus is extreme wear resistance and fatigue life: Carburizing is ideal for parts like gears, camshafts, and bearings that experience constant rubbing and cyclic loading.
- If your primary focus is impact strength and toughness: Carburizing is the standard for components like pins and shafts that must withstand shock loads without fracturing, relying on the tough core to absorb energy.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective design: Carburizing allows you to use inexpensive, easily machinable low-carbon steel to create a component with the high-performance surface of a more expensive alloy.
By understanding carburizing, you can intentionally design components that possess the ideal combination of surface hardness and core toughness for their specific application.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Create a hard, wear-resistant surface (case) on a tough, ductile core from a single piece of low-carbon steel. |
| Key Benefit | Achieves a "composite" material behavior: excellent surface hardness for wear resistance combined with core toughness for impact resistance. |
| Ideal For | Gears, bearings, camshafts, pins, and shafts that require high fatigue life and durability. |
| Process Temp | 850°C - 950°C (1560°F - 1740°F) in a carbon-rich atmosphere. |
| Material | Specifically for low-carbon steels (<0.25% carbon). |
Achieve Superior Component Performance with KINTEK
Does your application demand the unique combination of a hard, wear-resistant surface and a tough, impact-resistant core? The carburizing process is a precise science that requires expert knowledge and reliable equipment to control temperature, atmosphere, and quenching perfectly.
KINTEK specializes in laboratory and industrial heat treatment solutions. We provide the furnaces, atmosphere control systems, and consumables necessary to achieve consistent, high-quality carburized results. Whether you are developing new gears, bearings, or other critical components, our expertise ensures your materials meet the highest standards for durability and performance.
Let's discuss how we can support your heat treatment needs. Contact our experts today to find the right solution for your lab or production line.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control



















