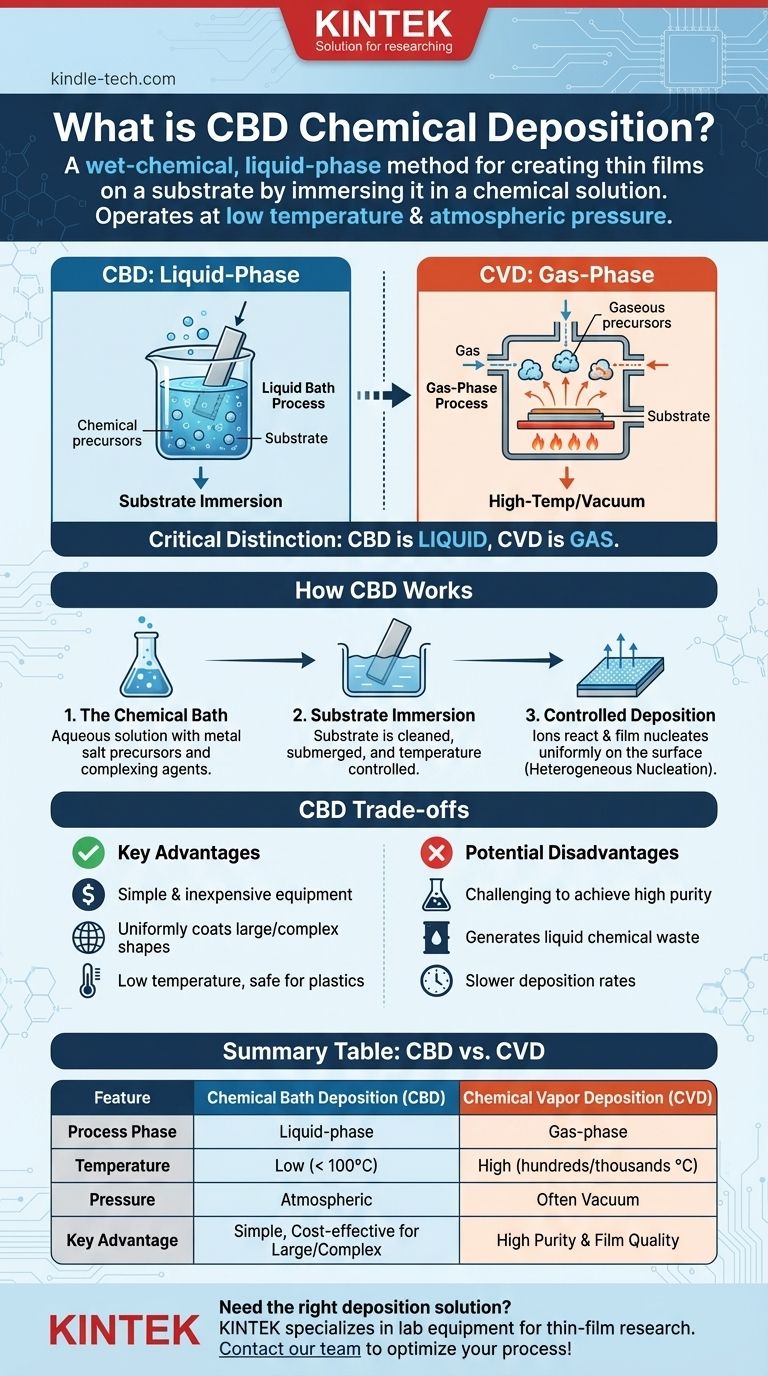
In technical terms, Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD) is a method for creating a thin, solid film on a substrate by immersing it in a liquid chemical solution. Unlike processes that use gases or vacuums, CBD operates at or near atmospheric pressure and uses a controlled chemical reaction within a liquid bath to gradually "grow" the desired material onto the surface.
The most critical distinction to understand is that Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD) is a wet-chemical, solution-based process, while the more commonly known Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a gas-phase process. Confusing the two can lead to fundamental misunderstandings of how a thin film is created.

How Chemical Bath Deposition Works
CBD is fundamentally a process of controlled precipitation from a solution onto a surface. It is valued for its simplicity and ability to coat large or complex shapes uniformly.
The Chemical Solution (The "Bath")
The process begins with an aqueous solution containing the chemical precursors for the final film. These are typically soluble metal salts.
A complexing agent, such as thioglycolic acid as mentioned for tin oxide, is often added. This agent temporarily binds to the metal ions, preventing them from precipitating out of the solution too quickly.
The Substrate and Immersion
The object to be coated, known as the substrate, is cleaned and then submerged in the chemical bath.
The temperature of the bath is then carefully controlled, often raised slightly, to initiate the chemical reaction.
Controlled Reaction and Deposition
As the bath is heated, the complexing agent slowly releases the metal ions. These ions then react with other chemicals in the solution to form the desired insoluble compound (e.g., an oxide or sulfide).
Instead of forming particles randomly in the liquid, the reaction is controlled so that this new solid material preferentially forms and adheres to the surface of the substrate, a process called heterogeneous nucleation. The film slowly grows thicker as the immersion continues.
Clarifying a Common Confusion: CBD vs. CVD
The provided references primarily describe Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), a very different technique. Understanding the distinction is crucial.
The Core Difference: Liquid vs. Gas
CBD is a liquid-phase technique. The substrate is physically dipped into a chemical bath.
CVD is a gas-phase technique. The substrate is placed in a chamber, and gaseous precursor chemicals are introduced, which then react on the hot surface to form a film.
Process Conditions
CBD typically operates at low temperatures (often below 100°C) and at normal atmospheric pressure.
CVD almost always requires high temperatures (hundreds or thousands of degrees Celsius) and often a vacuum chamber to control the atmosphere and deliver the reactive gases.
Applications and Materials
CBD is excellent for materials like cadmium sulfide (CdS) or tin oxide (SnOₓ) and is widely used for creating specific layers in thin-film solar cells.
CVD is used for a wider range of high-performance materials, including creating ultra-pure silicon films for electronics, hard coatings for cutting tools, and advanced materials like carbon nanotubes.
Understanding the Trade-offs of CBD
Like any engineering process, CBD has a specific set of advantages and limitations that make it suitable for some applications but not others.
Key Advantages
The equipment for CBD is simple and inexpensive, as it does not require high-vacuum chambers or high-temperature power sources.
Because it involves simple immersion, it's an excellent method for uniformly coating large surface areas or objects with complex, non-flat shapes.
The low operating temperature makes it compatible with temperature-sensitive substrates, such as plastics.
Potential Disadvantages
Achieving high film purity can be challenging, as impurities from the chemical bath can be incorporated into the growing film.
The chemical bath has a finite life and generates liquid chemical waste, which requires proper and often costly disposal.
Compared to vapor-based methods, CBD can have slower deposition rates, making it less suitable for applications requiring very thick films to be grown quickly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The choice between CBD and another method like CVD depends entirely on the material requirements, substrate, and budget for your project.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective deposition over large areas or complex shapes: CBD is often superior due to its simple equipment and uniform coating ability.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible purity and crystalline quality for advanced electronics: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is generally the preferred method, despite its higher cost and complexity.
- If you are working with temperature-sensitive substrates like plastics: CBD's low-temperature process makes it a viable option where high-temperature CVD would damage the material.
Understanding the fundamental difference between liquid-phase and gas-phase deposition is the key to selecting the right tool for your specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD) | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Phase | Liquid-phase (solution) | Gas-phase (vapor) |
| Temperature | Low (< 100°C) | High (hundreds/thousands °C) |
| Pressure | Atmospheric | Often requires vacuum |
| Key Advantage | Simple, cost-effective for large/complex shapes | High purity and film quality |
Need to select the right deposition method for your materials? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for all your thin-film research and production needs. Whether you're exploring CBD for large-area coatings or require high-purity CVD systems, our experts can help you choose the right solution. Contact our team today to discuss your project and optimize your deposition process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Research and Development
People Also Ask
- What are the drawbacks of PECVD? Understanding the Trade-offs of Low-Temperature Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials

















