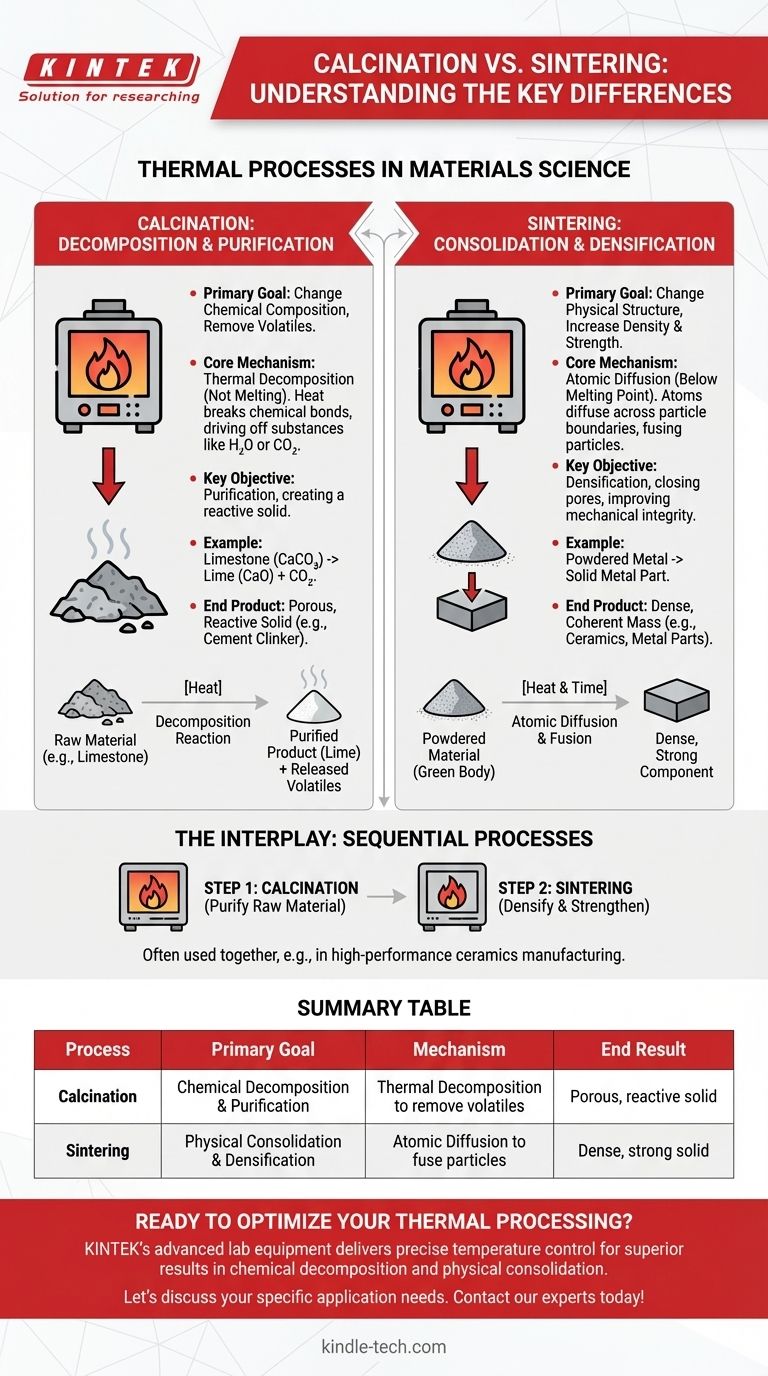
In materials science, calcination and sintering are two distinct thermal processes that, while both involving high heat, serve fundamentally different purposes. Calcination is a process of thermal decomposition designed to change a material's chemical composition by removing volatile components. In contrast, sintering uses heat to fuse particles together into a solid mass, changing the material's physical structure to increase its density and strength.
The essential difference is one of intent. Calcination aims to alter a material's chemical makeup by breaking it down, while sintering aims to alter its physical structure by building it up from a powder.

Deconstructing Calcination: A Process of Decomposition
Calcination uses thermal energy to break chemical bonds within a solid material, driving off volatile substances. It is fundamentally a process of purification or chemical conversion.
The Core Mechanism: Thermal Decomposition
The heat applied during calcination provides the activation energy needed to initiate a decomposition reaction. This is not melting; the material remains in a solid state throughout the process.
Key Objective: Removing Volatiles
The primary goal is to remove specific substances that are chemically bound within the solid. This includes driving off water from hydrates (like in bauxite processing) or removing carbon dioxide from carbonates.
A classic example is the production of lime (calcium oxide) from limestone (calcium carbonate). Heating the limestone forces the release of CO₂, leaving behind the chemically altered lime.
The End Product: A Purified or Reactive Solid
The result of calcination is a solid that has been chemically changed, often becoming more porous and reactive. This product, such as cement clinker or activated alumina, serves as a crucial intermediate for further manufacturing.
Deconstructing Sintering: A Process of Consolidation
Sintering is a method of densification. It uses heat to bond a mass of particles into a coherent, solid object without melting it.
The Core Mechanism: Atomic Diffusion
At temperatures below the melting point, atoms at the contact points between particles become mobile. They diffuse across the particle boundaries, causing the particles to fuse together and the voids between them to shrink or close.
Key Objective: Increasing Strength and Density
The main purpose of sintering is to transform a loosely packed powder into a strong, dense component. This process drastically reduces the material's porosity and increases its mechanical integrity.
This is the core process used in powdered metallurgy to create metal parts and is essential for manufacturing almost all high-strength ceramics.
The End Product: A Dense, Coherent Mass
The result of sintering is a physically robust object with a fine-grained microstructure. The chemical composition of the material remains largely unchanged, but its physical form and properties are dramatically improved.
The Interplay: How the Processes Work Together
In many industrial applications, particularly in ceramics manufacturing, calcination and sintering are not mutually exclusive. Instead, they are often sequential steps in a larger process.
Step 1: Calcination for Purity
A raw material mixture is first calcined to decompose precursors and form a pure, homogenous, and reactive powder with the desired chemical composition.
Step 2: Sintering for Strength
This purified powder is then compacted into a desired shape (a "green body") and sintered at a high temperature. The sintering step provides the final density and strength required for the finished product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice between these processes depends entirely on the transformation you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is chemical purification or decomposition: Calcination is the correct process to remove bound water, CO₂, or other volatile substances from a solid.
- If your primary focus is creating a strong, dense part from a powder: Sintering is the method used to fuse particles, reduce porosity, and achieve mechanical strength.
- If your primary focus is producing a high-performance ceramic or metal component from raw chemicals: You will likely need a multi-step process involving calcination first, followed by sintering.
Understanding this distinction between chemical decomposition and physical consolidation is the key to mastering thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Mechanism | End Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcination | Chemical decomposition and purification | Thermal decomposition to remove volatiles | Porous, reactive solid (e.g., lime from limestone) |
| Sintering | Physical consolidation and densification | Atomic diffusion to fuse particles | Dense, strong solid (e.g., ceramics, metal parts) |
Ready to Optimize Your Thermal Processing?
Whether you're purifying raw materials with calcination or creating high-strength components through sintering, KINTEK's advanced lab equipment delivers precise temperature control and unmatched reliability. Our furnaces and kilns are engineered to meet the exacting demands of materials science, helping you achieve superior results in chemical decomposition and physical consolidation.
Let's discuss your specific application needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect thermal processing solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do tube furnaces or muffle furnaces ensure stoichiometric accuracy during synthesis? Mastering Li4GeO4 & Li4VO4
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data
- What is a rotary retort furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision



















