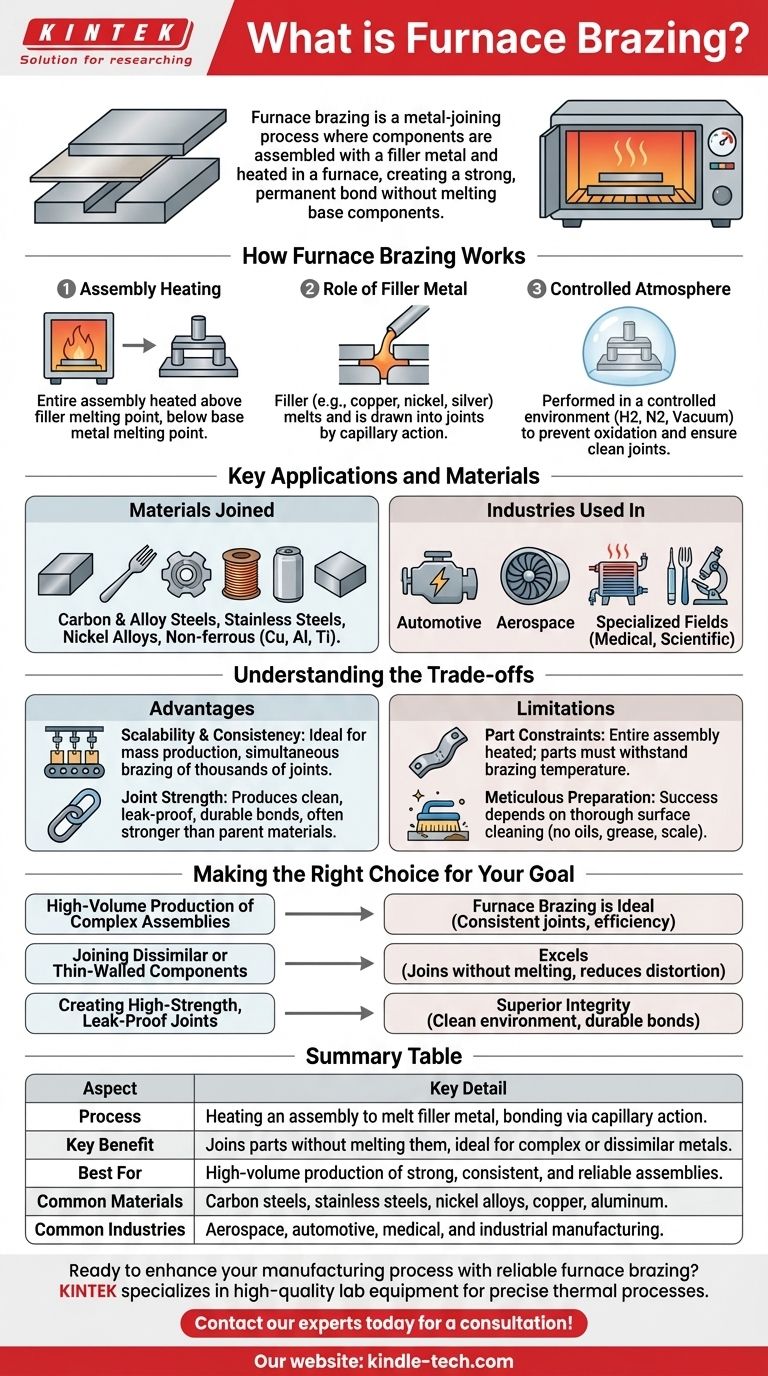
Furnace brazing is a metal-joining process where components are assembled with a filler metal and heated in a furnace. The temperature is raised just enough to melt the filler metal, which flows into the gaps between the parts through capillary action. Upon cooling, the filler solidifies, creating a strong, permanent bond without melting the base components themselves.
At its core, furnace brazing is not just a joining technique; it is a highly efficient manufacturing method for creating strong, complex, and consistent assemblies at scale by heating the entire part in a controlled environment.

How Furnace Brazing Works
Furnace brazing transforms separate components into a single, integrated assembly with high precision and reliability. The process relies on a few fundamental principles.
The Core Principle: Assembly Heating
The entire assembly—the base metals and the pre-placed filler metal—is loaded into a furnace. The furnace then uniformly heats the assembly to a specific temperature that is above the melting point of the filler metal but below the melting point of the base metals.
The Role of the Filler Metal
The filler metal, often in the form of a paste, wire, or shim, is what creates the bond. Common fillers are based on alloys of copper, nickel, silver, and gold. Once molten, this filler is drawn into the tight-fitting joints, creating a metallurgical bond as it cools and solidifies.
The Importance of a Controlled Atmosphere
Most furnace brazing is performed in a controlled atmosphere (such as hydrogen, nitrogen, or a vacuum). This carefully managed environment prevents the oxidation of the metal surfaces during heating, ensuring a clean, strong joint and often eliminating the need for corrosive chemical fluxes.
Key Applications and Materials
The versatility of furnace brazing allows it to be used across a vast range of industries and materials, from common steels to exotic alloys.
Which Materials Can Be Joined?
Furnace brazing is exceptionally effective for joining a wide variety of metals. This includes carbon and alloy steels, stainless steels, and nickel-based alloys. It is also used for non-ferrous materials like copper, aluminum, and titanium.
Where is Furnace Brazing Used?
The process is critical in manufacturing components where strength and reliability are non-negotiable.
- Automotive: Engine components, hydraulic fittings, and other critical parts.
- Aerospace: Turbine components, fuel systems, and space application hardware.
- Industrial: Heat exchangers, pipe fittings, and machined assemblies.
- Specialized Fields: Medical and scientific equipment, nuclear components, and electronic devices.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, furnace brazing has specific characteristics that make it ideal for some applications but less suitable for others. Understanding these trade-offs is key to leveraging the process effectively.
Advantage: Scalability and Consistency
The primary advantage is its efficiency for mass production. Heating an entire furnace allows for the simultaneous brazing of hundreds or even thousands of joints at once, ensuring high consistency from part to part.
Advantage: Joint Strength and Integrity
Furnace brazing produces clean, strong, and often leak-proof joints. The uniform heating and cooling cycle minimizes internal stresses, resulting in a durable assembly that is often as strong as the parent materials.
Limitation: Part and Process Constraints
Because the entire assembly is heated, the process is best suited for parts that can withstand the brazing temperature without damage or distortion. It is also a batch process, which may be less efficient for one-off repairs or very low-volume production runs.
Prerequisite: Meticulous Surface Preparation
The success of a brazed joint depends entirely on the cleanliness of the surfaces. All parts must be thoroughly cleaned to remove oils, grease, and surface scale before entering the furnace. Failure to do so is a common cause of poor joint quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To decide if furnace brazing is the right solution, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of complex assemblies: Furnace brazing is ideal due to its ability to create many consistent joints simultaneously.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar metals or thin-walled components: This process excels because it joins materials without melting them, reducing the risk of distortion or damage.
- If your primary focus is creating high-strength, leak-proof joints: The clean, controlled environment of furnace brazing produces superior joint integrity for critical applications.
Ultimately, furnace brazing empowers engineers to design and produce robust metal assemblies with unparalleled efficiency and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | Heating an assembly in a furnace to melt a filler metal, which bonds parts via capillary action. |
| Key Benefit | Joins parts without melting them, ideal for complex or dissimilar metals. |
| Best For | High-volume production of strong, consistent, and reliable assemblies. |
| Common Materials | Carbon steels, stainless steels, nickel alloys, copper, and aluminum. |
| Common Industries | Aerospace, automotive, medical, and industrial manufacturing. |
Ready to enhance your manufacturing process with reliable furnace brazing?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables needed for precise thermal processes like furnace brazing. Whether you are in aerospace, automotive, or industrial manufacturing, our solutions help you achieve strong, consistent, and leak-proof joints for your most critical assemblies.
Let's discuss how we can support your production goals. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What are the different types of brazing welding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heat Source
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy



















