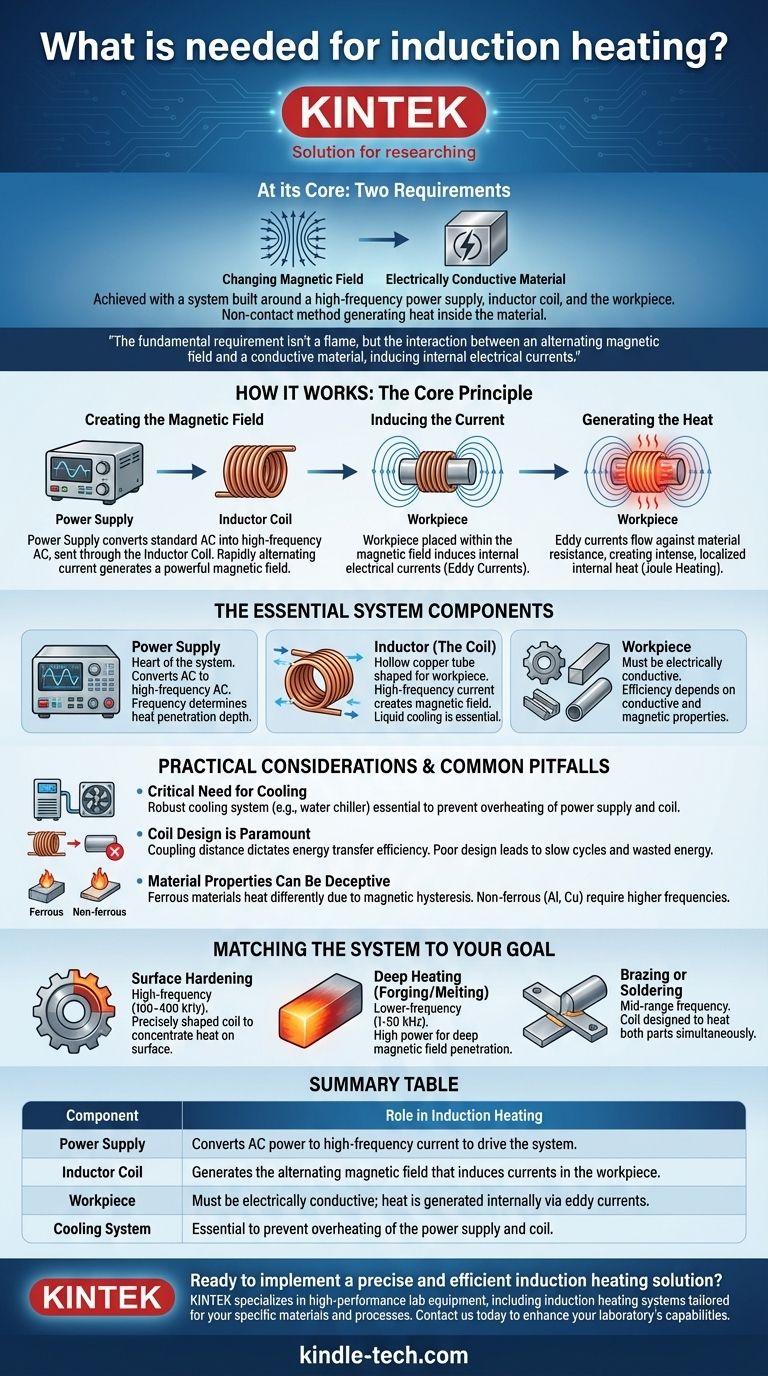
At its core, induction heating requires two things: a changing magnetic field and an electrically conductive material placed within it. This is achieved with a system built around a high-frequency power supply, an inductor coil, and the workpiece you intend to heat. The process is a non-contact method that uses electromagnetic principles to generate heat directly inside the material itself.
The fundamental requirement for induction heating isn't a flame or external element, but rather the interaction between an alternating magnetic field and a conductive material. This interaction induces internal electrical currents, and the material's own resistance to this current flow is what creates the heat.

The Core Principle: How It Works
To understand the components, you must first understand the underlying physics. Induction is a clean, fast, and highly controllable heating method that relies on a few key steps.
Creating the Magnetic Field
The process begins with a specialized power supply. This unit converts standard AC line voltage into a high-frequency alternating current.
This high-frequency AC is then sent through an inductor, which is typically a copper coil custom-shaped for the application. As the current alternates rapidly through the coil, it generates a powerful and dynamic magnetic field around it.
Inducing the Current
When an electrically conductive workpiece (like a piece of steel) is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces electrical currents within the workpiece. These are known as eddy currents.
Generating the Heat
These eddy currents flow against the electrical resistivity of the metal. This resistance creates intense, localized heat, a phenomenon known as Joule heating. Heat is generated inside the part, not applied to its surface, which is why the process is so efficient.
The Essential System Components
While the principle is based on physics, a practical induction heating system relies on three primary components working in concert.
The Power Supply
This is the heart of the system. It takes standard electrical power and transforms it into the high-frequency alternating current required to drive the process. The frequency of this current is a critical variable that determines how deeply the heat penetrates the workpiece.
The Inductor (The Coil)
The inductor is almost always a hollow copper tube, formed into a coil or other shape that conforms to the workpiece. The high-frequency current from the power supply flows through this coil, creating the magnetic field. It is hollow to allow for liquid cooling.
The Workpiece
This is the part, material, or object to be heated. The critical requirement is that the workpiece must be electrically conductive. The efficiency of the heating process depends heavily on the material's specific conductive and magnetic properties.
Common Pitfalls and Practical Considerations
Simply having the three core components is often not enough for a reliable, repeatable industrial process. Ancillary systems are almost always required.
The Critical Need for Cooling
The high currents involved in induction heating generate significant waste heat in both the power supply and the inductor coil itself. A robust cooling system, often a water chiller, is essential to prevent the components from overheating and failing.
Coil Design is Paramount
The efficiency of the energy transfer is dictated by the coupling distance, or the gap between the coil and the workpiece. A poorly designed or mismatched coil will lead to inefficient heating, slow cycle times, and wasted energy.
Material Properties Can Be Deceptive
Not all conductive materials heat equally well. Ferrous materials like steel heat very effectively below a certain temperature (the Curie point) due to magnetic hysteresis losses, which adds a secondary heating effect. Non-ferrous materials like aluminum or copper require higher frequencies and more power to heat effectively due to their lower electrical resistance.
Matching the System to Your Goal
Understanding these components allows you to tailor a system to a specific industrial or scientific goal.
- If your primary focus is surface hardening: You need a high-frequency power supply (100-400 kHz) and a precisely shaped coil to concentrate heat on the surface layer.
- If your primary focus is deep heating for forging or melting: You need a lower-frequency (1-50 kHz), high-power system to ensure the magnetic field penetrates deep into the material.
- If your primary focus is brazing or soldering: A mid-range frequency and a coil designed to heat both parts of the joint simultaneously is the most effective approach.
By mastering the relationship between power, frequency, and coil design, you gain precise control over the heating process.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Induction Heating |
|---|---|
| Power Supply | Converts AC power to high-frequency current to drive the system. |
| Inductor Coil | Generates the alternating magnetic field that induces currents in the workpiece. |
| Workpiece | Must be electrically conductive; heat is generated internally via eddy currents. |
| Cooling System | Essential to prevent overheating of the power supply and coil. |
Ready to implement a precise and efficient induction heating solution? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction heating systems tailored for your specific materials and processes. Whether you need surface hardening, deep heating, or brazing, our expertise ensures optimal power, frequency, and coil design for your application. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's capabilities with reliable, custom-engineered solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum hot press (VHP) contribute to the densification of Al-Cu-ZrC composite materials? Key VHP Benefits
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play in the fabrication of CuCrFeMnNi alloys? Achieve High Purity
- Why is the vacuum system of a Vacuum Hot Pressing furnace critical for ODS ferritic stainless steel performance?
- How does a vacuum hot press furnace address structural defects in as-cast CoCrPtB alloy ingots? Optimize Your Density
- How does the mechanical pressure from a vacuum hot-pressing furnace facilitate the densification of B4C/Al composites?












