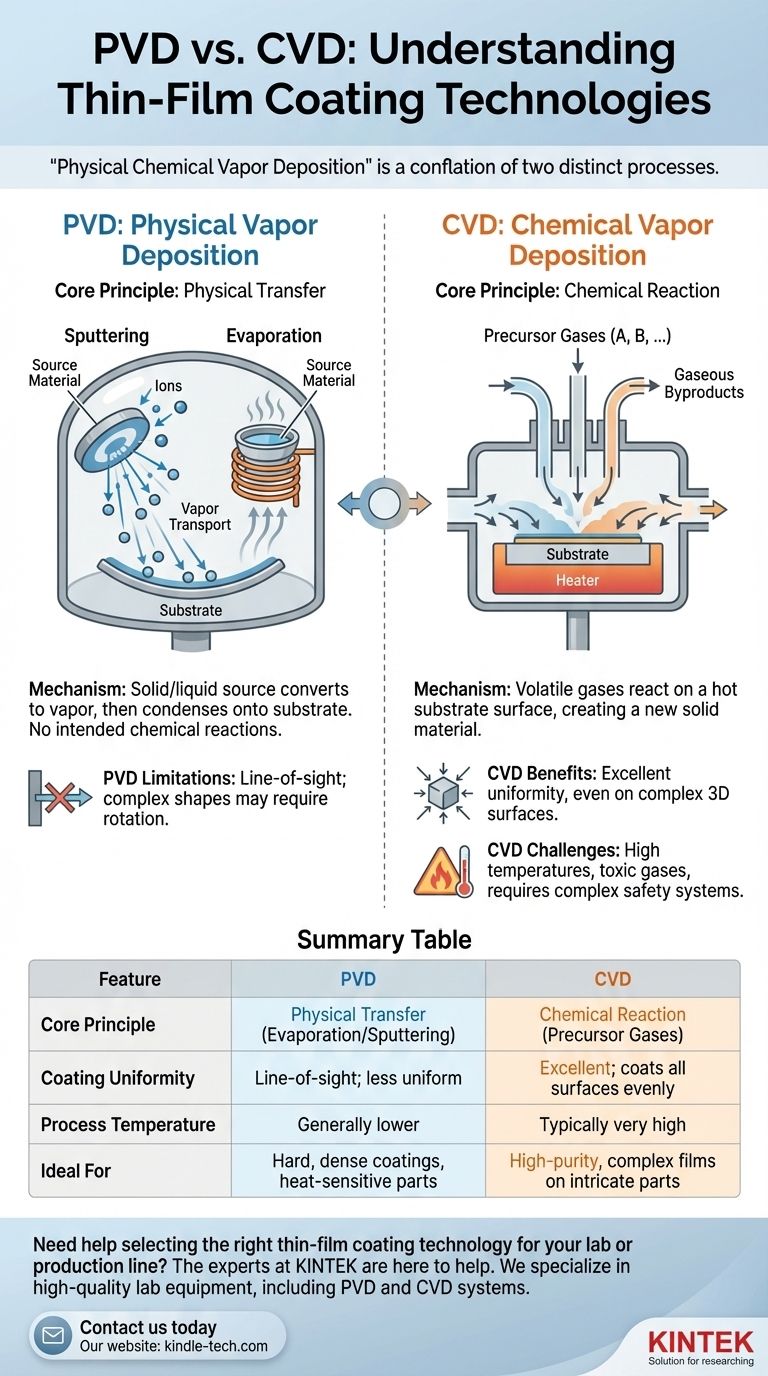
Notably, the term "physical chemical vapor deposition" is not a standard industry classification. It appears to be a conflation of two distinct and fundamental thin-film coating technologies: Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). PVD uses physical processes like evaporation or sputtering to transfer a material from a source to a substrate, while CVD uses chemical reactions between precursor gases to grow a new material directly on the substrate's surface.
The core difference is simple: PVD physically moves a material from a source to a target, while CVD creates an entirely new material on the target's surface through a chemical reaction. Your choice between them hinges on the required material, the shape of the part, and the process conditions the part can withstand.

Understanding Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
The Core Principle: A Physical Transition
Physical Vapor Deposition is fundamentally a phase-change process. A solid or liquid source material is converted into a vapor phase and then transported in a vacuum environment, where it condenses back into a thin, solid film on the surface of the object you are coating (the substrate).
No chemical reactions are intended to occur. The deposited film has the same basic chemical composition as the source material.
Key PVD Methods
The process is defined by how the source material is vaporized. The two primary methods are sputtering and evaporation.
Sputtering involves bombarding a solid target of the coating material with high-energy ions, which physically knock atoms off the target's surface. These ejected atoms then travel and deposit onto the substrate.
Evaporation uses heat to raise the temperature of the source material in a high vacuum until it boils or sublimates, creating a vapor that then condenses onto the cooler substrate.
Common PVD Applications
PVD is prized for producing dense, hard, and adherent coatings.
It is widely used for applying temperature-resistant coatings to aerospace components, hard and corrosion-resistant layers on cutting tools, and thin optical or conductive films for semiconductors and solar panels.
Understanding Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
The Core Principle: A Chemical Reaction
Chemical Vapor Deposition is a chemical process. Instead of physically moving a material, CVD introduces one or more volatile precursor gases into a reaction chamber containing the substrate.
These gases decompose or react with each other on the hot substrate surface, leaving behind a solid film of a new material. The excess gaseous byproducts are pumped out of the chamber.
How CVD Works
The part to be coated is placed inside a reaction chamber, which is often under vacuum. Precursor gases are introduced, and energy (usually heat) is applied to the substrate.
This energy drives a chemical reaction on the surface, which "grows" the desired film. The process continues until the film reaches the required thickness.
Common CVD Applications
CVD is essential for creating extremely high-purity and high-performance films.
It is a cornerstone of the semiconductor industry for creating the complex layered structures in microchips. It is also used to produce wear-resistant coatings on tools, grow carbon nanotubes, and deposit photovoltaic materials for thin-film solar cells.
Understanding the Trade-offs
PVD Limitations: Line of Sight
Most PVD processes are "line-of-sight," meaning the coating material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate.
This can make it difficult to achieve a uniform coating on parts with complex geometries, such as those with deep recesses or hidden surfaces. Parts often need to be rotated and repositioned to ensure even coverage.
CVD Challenges: High Temperatures and Complexity
CVD often requires very high substrate temperatures to initiate the necessary chemical reactions. This can limit the types of materials that can be coated without being damaged.
Furthermore, the precursor gases used can be highly toxic, corrosive, or pyrophoric (igniting in air), requiring sophisticated handling and safety systems. The references note that CVD often requires a high level of operator skill.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct technology requires understanding your material and geometric constraints.
- If your primary focus is a dense, hard coating on a relatively simple shape: PVD is often the more direct and cost-effective solution, noted for its excellent adhesion.
- If your primary focus is a highly pure, uniform coating on a complex 3D surface: CVD is the superior method, as the gaseous precursors can reach all exposed surfaces.
- If your primary focus is creating a compound material from different elements: CVD is the natural choice, as its entire basis is forming new materials through chemical reactions.
- If your primary focus is coating a heat-sensitive substrate like plastic: Certain low-temperature PVD processes are often more suitable than traditional high-temperature CVD.
Ultimately, understanding the core mechanism—a physical transfer versus a chemical reaction—is the key to selecting the ideal technology for your application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Physical transfer of material (evaporation/sputtering) | Chemical reaction of precursor gases on the substrate |
| Coating Uniformity | Line-of-sight; less uniform on complex shapes | Excellent; gases coat all exposed surfaces evenly |
| Process Temperature | Generally lower | Typically very high |
| Ideal For | Hard, dense coatings on simpler shapes; heat-sensitive substrates | High-purity, complex compound films on intricate parts |
Need help selecting the right thin-film coating technology for your lab or production line? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including PVD and CVD systems, tailored to your specific application requirements.
Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how our solutions can enhance your coating process, improve material performance, and drive your research or manufacturing forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application



















