In simple terms, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a high-tech vacuum coating process that applies an extremely thin but incredibly durable layer of material onto the surface of an object. Think of it as a sophisticated method for bonding a new, high-performance "skin" to an item, fundamentally changing its properties like color, hardness, and resistance to wear.
PVD is not a material itself, but an advanced process that vaporizes a solid material in a vacuum and deposits it, atom by atom, onto a target surface. This creates a bonded, high-performance film that is far superior to traditional painting or plating.

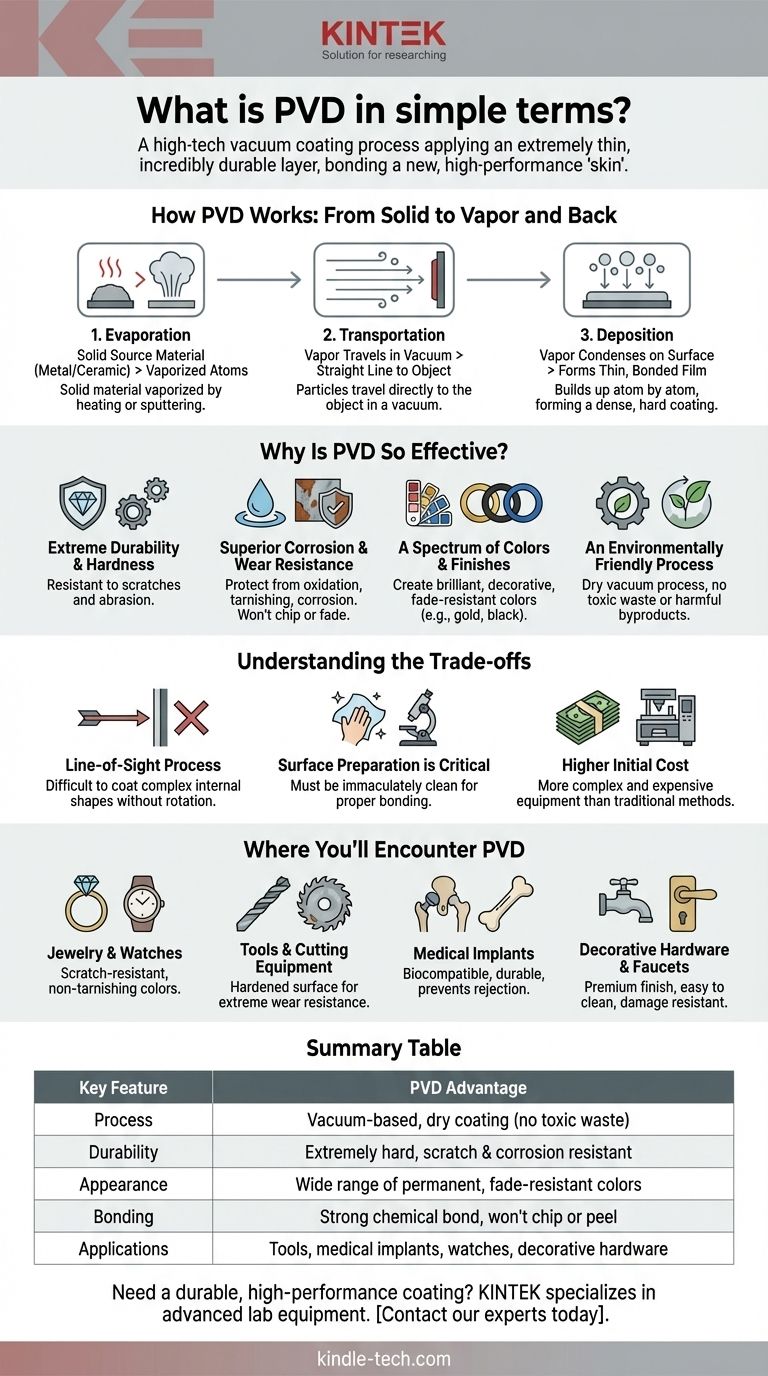
How PVD Works: From Solid to Vapor and Back
The entire PVD process happens inside a high-vacuum chamber. The vacuum is critical because it ensures the coating particles don't collide with air molecules, allowing them to travel directly to the object being coated. The process can be broken down into three fundamental stages.
Step 1: Evaporation (Creating the Vapor)
First, a solid source material—often a metal or ceramic like titanium, zirconium, or chromium—is placed inside the chamber. This material is then vaporized into its individual atoms or molecules. This is typically done by heating it to a high temperature or by bombarding it with high-energy ions in a process called sputtering.
Step 2: Transportation (Moving Through the Vacuum)
Once vaporized, these particles travel in a straight line through the vacuum chamber from the source to the target object. The parts being coated are often placed on a rotating fixture to ensure all surfaces are evenly exposed to the vapor stream.
Step 3: Deposition (Building the Film)
When the vapor particles reach the surface of the object (known as the substrate), they condense and form a thin, highly-adherent film. This layer builds up atom by atom, creating a very dense, uniform, and hard coating that is chemically bonded to the surface.
Why Is PVD So Effective?
PVD coatings are widely used because they offer significant performance advantages over traditional finishes like electroplating, painting, or powder coating.
Extreme Durability and Hardness
The resulting film is often much harder than the substrate material itself. This makes PVD-coated items, such as tools and watch casings, exceptionally resistant to scratches and abrasion.
Superior Corrosion and Wear Resistance
The coating creates a chemically inert barrier that protects the object from oxidation, tarnishing, and corrosion. The bond is so strong that the coating won't chip, fade, or peel.
A Spectrum of Colors and Finishes
PVD can create a wide range of brilliant, decorative finishes. By precisely introducing certain gases like nitrogen or methane during the deposition process, materials like titanium can be made to form compounds that produce colors like gold, rose gold, black, and blue. These colors are part of the coating itself and are extremely resistant to fading.
An Environmentally Friendly Process
Unlike electroplating, which involves wet chemistry with hazardous acids and toxic waste products, PVD is a dry vacuum process. It produces no harmful byproducts, making it a much cleaner and more environmentally responsible technology.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PVD is not the solution for every application. It's important to understand its limitations.
It's a "Line-of-Sight" Process
The coating material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate. This means it can be difficult to uniformly coat complex internal shapes or deeply recessed areas without sophisticated part rotation.
Surface Preparation is Critical
The substrate must be immaculately clean before entering the vacuum chamber. Any dust, oil, or microscopic contaminants will prevent the coating from bonding correctly, potentially causing it to fail.
Higher Initial Cost
PVD equipment and the process itself are more complex and expensive than simple painting or plating. This can make it less cost-effective for very low-value items or extremely small production runs.
Where You'll Encounter PVD
Understanding the goal of the coating helps you recognize its value in different products.
- If you see it on jewelry or watches: It means the color and finish are highly scratch-resistant and will not tarnish or fade like traditional plating.
- If you see it on tools or cutting equipment: It indicates a hardened surface designed for extreme wear resistance and reduced friction, leading to longer tool life and better performance.
- If you see it on medical implants: This refers to a biocompatible and inert coating that enhances durability and prevents the body from rejecting the implant.
- If you see it on decorative hardware or faucets: It signifies a premium finish that is easy to clean and will resist the damage caused by cleaning products and daily use.
Recognizing the term PVD allows you to identify a product built with a focus on superior durability, performance, and modern manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | PVD Advantage |
|---|---|
| Process | Vacuum-based, dry coating (no toxic waste) |
| Durability | Extremely hard, scratch & corrosion resistant |
| Appearance | Wide range of permanent, fade-resistant colors |
| Bonding | Strong chemical bond, won't chip or peel |
| Applications | Tools, medical implants, watches, decorative hardware |
Need a durable, high-performance coating for your lab equipment or components? The PVD process described is key to creating long-lasting, wear-resistant surfaces. KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance the durability and performance of your products.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















