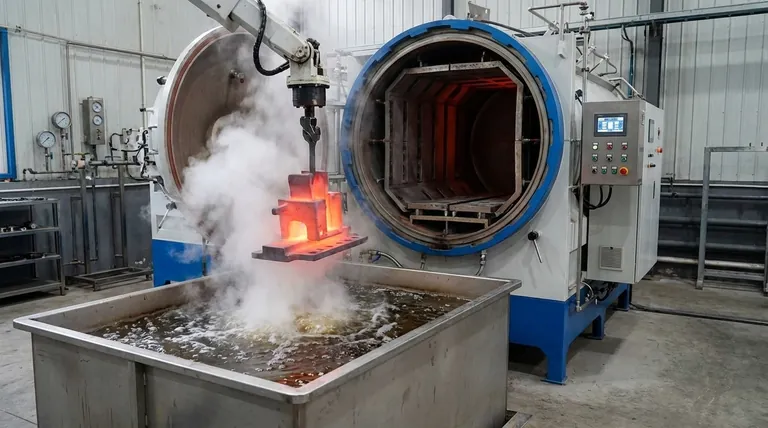
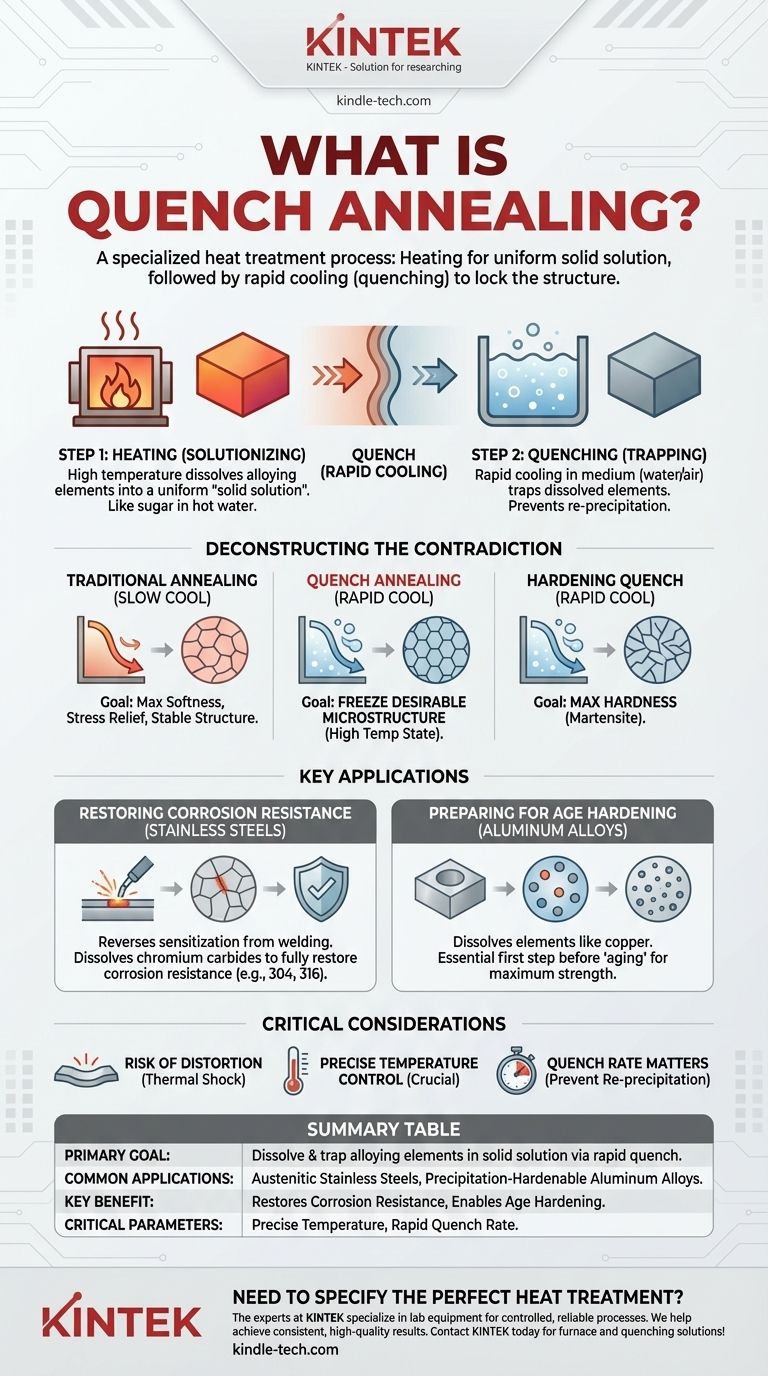
At its core, quench annealing is a specific heat treatment process that involves heating a metal to a high temperature to create a uniform solid solution and then cooling it rapidly, or "quenching," to lock that structure in place. Unlike a traditional anneal which uses slow cooling to achieve maximum softness and stress relief, quench annealing uses rapid cooling to preserve a specific metallurgical state that enhances properties like corrosion resistance or prepares the material for subsequent strengthening.
Quench annealing is a specialized process, most often applied to austenitic stainless steels and certain aluminum alloys. The goal is not simply to soften the metal, but to dissolve and trap specific alloying elements in a solid solution, which is critical for restoring corrosion resistance or enabling age hardening.

Deconstructing the "Contradiction": Annealing vs. Quenching
The term "quench annealing" can seem contradictory. Understanding the distinct goals of its component parts—annealing and quenching—clarifies its unique purpose.
The Goal of Traditional Annealing (Slow Cool)
A standard annealing process, as described in most textbooks, involves heating a material and then cooling it slowly.
This slow cooling allows the metal's internal structure to reorganize into its most stable, lowest-energy state. The primary outcomes are reduced hardness, increased ductility, and the relief of internal stresses.
The Goal of Hardening Quench (Rapid Cool)
In contrast, quenching is synonymous with rapid cooling. When applied to medium- or high-carbon steels, this extreme cooling rate traps carbon to form a very hard, brittle structure called martensite. Here, the quench is a tool for maximizing hardness.
How Quench Annealing Bridges the Gap
Quench annealing borrows the high-temperature heating from annealing and the rapid cooling from quenching, but for an entirely different reason.
It doesn't aim for the absolute softness of a full anneal or the extreme hardness of a martensitic quench. Instead, it uses the quench to freeze a desirable microstructure that is only stable at high temperatures.
The Core Mechanism: Creating and Trapping a Solid Solution
The effectiveness of quench annealing hinges on controlling the behavior of alloying elements within the metal's crystal lattice. The process has two critical steps.
Step 1: Heating to Dissolve Elements (Solutionizing)
The material is heated to a specific temperature where certain alloying elements or phases (like chromium carbides in stainless steel) dissolve completely into the base metal.
This creates a homogeneous, single-phase structure known as a solid solution. Think of it like dissolving sugar completely in hot water—at that temperature, everything is one uniform liquid.
Step 2: Quenching to Trap the Solution
By cooling rapidly in a medium like water or forced air, the dissolved elements are given no time to precipitate back out of the solution.
They become trapped, or "supersaturated," within the metal's crystal structure at room temperature. This preserves the uniform chemical composition achieved during the heating stage, preventing the formation of undesirable phases.
Key Applications and Their "Why"
Quench annealing is not a general-purpose process. It is applied to specific alloy families to solve distinct problems.
Restoring Corrosion Resistance in Stainless Steels
This is the most common application. During welding or other high-temperature fabrication of austenitic stainless steels (e.g., 304, 316), chromium can combine with carbon at grain boundaries. This process, called sensitization, depletes the surrounding area of chromium and makes the steel vulnerable to corrosion.
Quench annealing (often called solution annealing in this context) reheats the steel to dissolve these harmful chromium carbides. The quench then prevents them from re-forming, fully restoring the material's corrosion resistance.
Preparing Aluminum Alloys for Age Hardening
For certain aluminum alloys, quench annealing is the first of a two-stage strengthening process. It dissolves alloying elements like copper into a solid solution.
The quench traps these elements in a supersaturated state. A second, lower-temperature heating process, called aging, then allows these elements to precipitate out as microscopic particles that dramatically increase the alloy's strength and hardness.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Parameters
While powerful, quench annealing requires precise control and is not without risks.
Risk of Distortion
Rapid cooling from a high temperature is a thermal shock. This can introduce significant internal stress, leading to warping or distortion, especially in thin or complex-shaped parts. Fixturing may be required to maintain dimensional stability.
Temperature Control is Crucial
The solutionizing temperature must be exact. If it's too low, the undesirable phases won't fully dissolve. If it's too high, the metal's grains can grow excessively large, which degrades its mechanical properties.
Quench Rate Matters
The cooling must be fast enough to prevent re-precipitation of the unwanted phases. The choice of quenching medium—water, polymer, or air—depends on the alloy's thickness and its specific metallurgical requirements. An insufficient quench rate will negate the entire purpose of the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal process depends entirely on your material and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is restoring corrosion resistance in a fabricated austenitic stainless steel part: Quench annealing (solution treatment) is the correct and necessary process to reverse sensitization.
- If your primary focus is preparing a precipitation-hardenable aluminum alloy for maximum strength: Quench annealing is the essential first step before the final aging treatment.
- If your primary focus is simply to soften a standard steel, improve its machinability, and relieve stress: A traditional, slow-cool anneal is the appropriate choice, not quench annealing.
Ultimately, choosing the right heat treatment is about manipulating a material's internal structure to achieve a specific engineering purpose.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Dissolve & trap alloying elements in a solid solution via rapid cooling (quenching). |
| Common Applications | Austenitic stainless steels (e.g., 304, 316), precipitation-hardenable aluminum alloys. |
| Key Benefit | Restores corrosion resistance, prevents sensitization, enables subsequent age hardening. |
| Critical Parameters | Precise solutionizing temperature, rapid quench rate (water, polymer, or air). |
| Common Alternative | Traditional annealing (slow cool for softness and stress relief). |
Need to specify the perfect heat treatment for your materials?
Quench annealing is a precise process critical for achieving optimal material properties like corrosion resistance and strength. The experts at KINTEK specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables necessary for controlled, reliable heat treatment processes.
We help laboratories like yours achieve consistent, high-quality results. Let us assist you in selecting the right furnace and quenching solutions for your specific alloy and application.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your lab's heat treatment needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the importance of a laboratory vacuum oven for SrFeO3 nanocrystals? Protect Your Nanomaterial Integrity
- What is the purpose of flux in brazing? Ensure Strong, Clean Joints Every Time
- Which type of furnace can be used at high temperature? Choose the Right Tool for Your Process
- What keeps the mould together in vacuum casting? Harness Atmospheric Pressure for Perfect Casts
- How do you prevent vacuum leaks? A Proactive Strategy for System Integrity
- Why is a vacuum welding system used for sealing zirconium alloy cladding? Ensure Precise Surface Oxidation Results
- What role do high-temperature vacuum or atmosphere furnaces play in the solution treatment of 17-4 PH steel?
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Hot Zone Materials and Processed Metals



















