In essence, sintering is a thermal process used to transform a loosely packed ceramic powder into a solid, dense, and strong object. By applying heat below the material's melting point, individual powder particles fuse together, reducing the empty space between them and creating a cohesive, polycrystalline material.
The core purpose of sintering is not to melt the ceramic, but to use heat as a catalyst for atomic diffusion. This process eliminates porosity and bonds the particles, fundamentally converting a fragile powder compact into a robust, engineered component with specific mechanical and thermal properties.

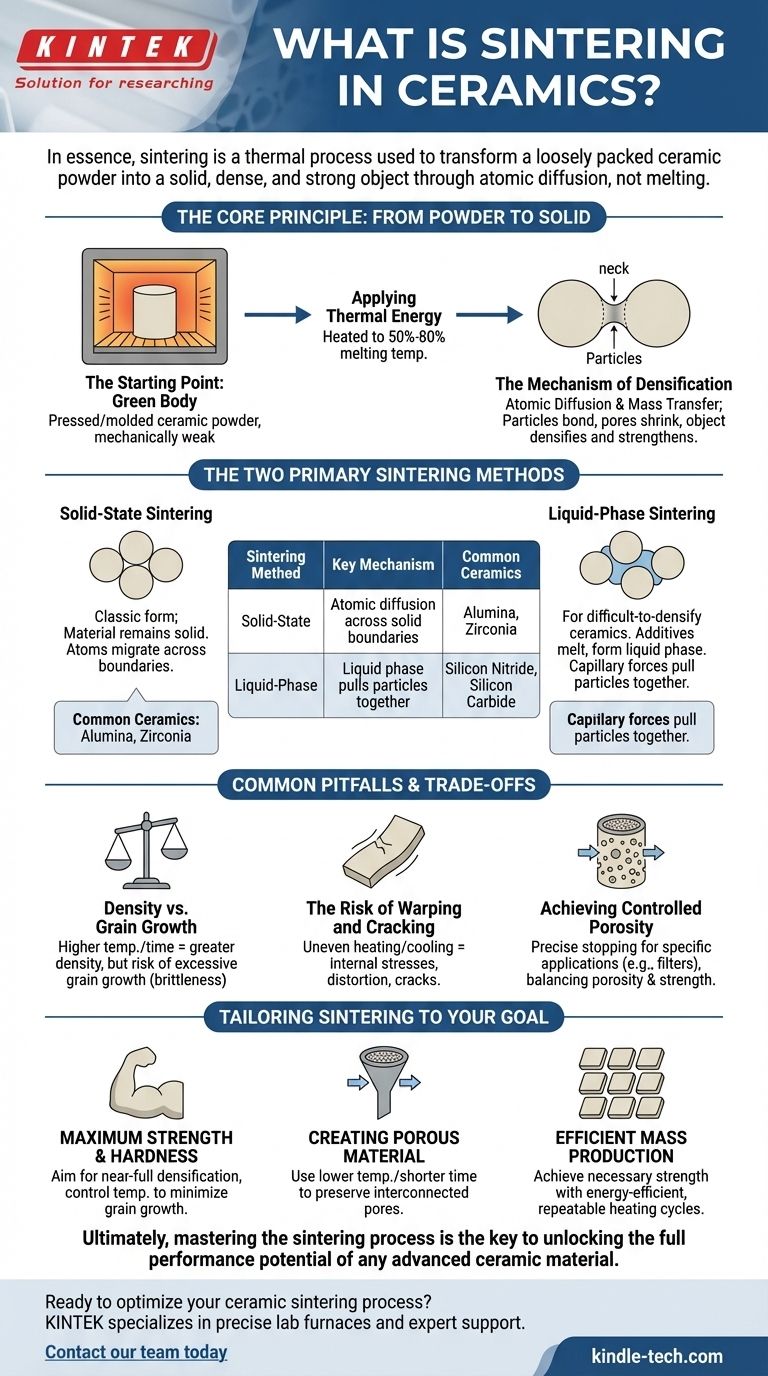
The Core Principle: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is the most important step in the fabrication of advanced ceramics. It is a process of controlled transformation that dictates the final performance of the component.
The Starting Point: The "Green" Body
The process begins with a ceramic powder that has been pressed or molded into the desired shape. This initial object, known as a "green" body, is chalk-like and mechanically very weak.
Applying Thermal Energy
The green body is placed in a furnace and heated to a high temperature, typically between 50% and 80% of its absolute melting temperature. This thermal energy activates the atoms and enables the process of densification.
The Mechanism of Densification
At the sintering temperature, atoms begin to move. This atomic diffusion and mass transfer allows particles to bond at their points of contact. As these "necks" between particles grow, the pores and voids shrink, pulling the particles closer together and causing the entire object to densify and strengthen.
The Two Primary Sintering Methods
The specific mechanism for densification depends on the material. The two most common methods are solid-state and liquid-phase sintering.
Solid-State Sintering
This is the classic form of sintering, where the material remains entirely solid throughout the process. Atoms migrate across the boundaries of the solid particles to fill in the gaps.
This method is commonly used for ceramics like alumina and zirconia, which can densify effectively through diffusion alone.
Liquid-Phase Sintering
For ceramics that are very difficult to densify, such as silicon nitride and silicon carbide, a different approach is needed. Additives are mixed with the initial powder.
At the sintering temperature, these additives melt and form a small amount of liquid. This liquid phase wets the ceramic particles and pulls them together through capillary forces, dramatically speeding up the rearrangement and densification process.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
Controlling the sintering process is critical because it involves a delicate balance of competing factors. Simply using more heat is rarely the best solution.
Density vs. Grain Growth
Higher temperatures and longer times increase density, which is often desirable. However, this can also lead to excessive grain growth, where smaller crystal grains merge into larger ones. Overly large grains can make the final ceramic brittle and reduce its strength.
The Risk of Warping and Cracking
As the component shrinks during densification, any unevenness in heating, cooling, or initial powder packing can create internal stresses. These stresses can cause the part to warp, distort, or even crack.
Achieving Controlled Porosity
While the goal is often full densification, some applications like filters require a specific level of porosity. Achieving this requires carefully stopping the sintering process before all pores are eliminated, which can be challenging to do while still ensuring adequate mechanical strength.
Tailoring Sintering to Your Goal
The ideal sintering parameters are entirely dependent on the desired outcome for the final product. Understanding your primary goal is the key to controlling the process correctly.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and hardness: You will aim for near-full densification, carefully controlling the temperature profile to minimize grain growth.
- If your primary focus is creating a porous material (like a filter): You will use lower temperatures or shorter sintering times to deliberately preserve an interconnected network of pores while still bonding the particles.
- If your primary focus is mass production of reliable parts (like tiles): Your goal is to achieve the necessary strength and stability using the most energy-efficient and repeatable heating cycle possible.
Ultimately, mastering the sintering process is the key to unlocking the full performance potential of any advanced ceramic material.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Method | Key Mechanism | Common Ceramics |
|---|---|---|
| Solid-State Sintering | Atomic diffusion across solid particle boundaries | Alumina, Zirconia |
| Liquid-Phase Sintering | Liquid phase from additives pulls particles together | Silicon Nitride, Silicon Carbide |
Ready to optimize your ceramic sintering process for maximum strength, controlled porosity, or efficient production? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab furnaces and expert support needed to achieve your specific material goals. Contact our team today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities and ensure reliable, high-performance results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Does a muffle furnace need to be vented? Essential Safety and Performance Guide
- What are the factors that affect melting? Master Temperature, Pressure & Chemistry for High-Quality Results
- How hot does a furnace get in Celsius? From 1100°C to 1800°C for Your Lab Needs
- What is ramp rate and how does that affect a melting point measurement? Master the Key to Accurate Thermal Analysis
- What is the purpose of a muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free High-Temperature Heating



















