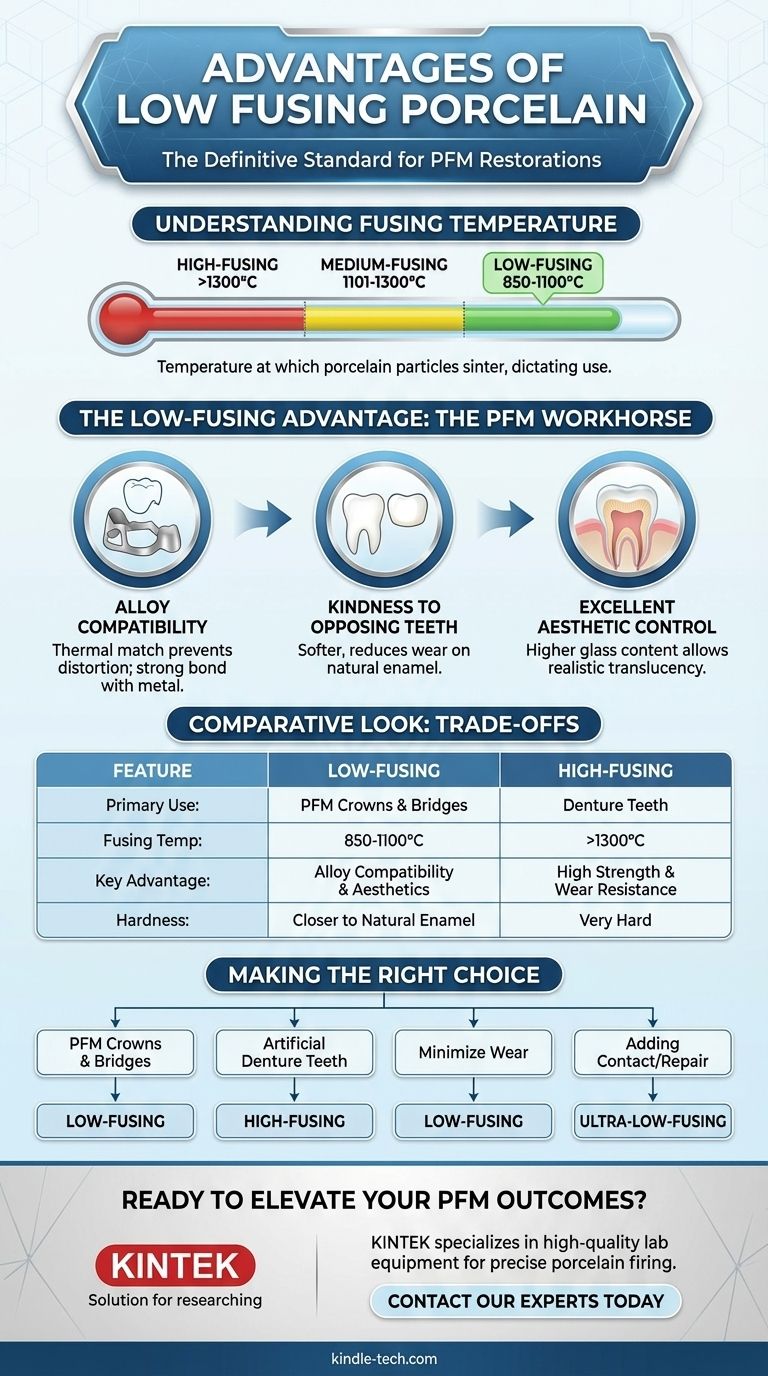
The primary advantage of low-fusing porcelain is its chemical and thermal compatibility with the dental alloys used for crown and bridge substructures. Its lower melting range (typically 850°C - 1050°C) allows it to be fired onto a metal framework without distorting or melting the underlying alloy. This ensures a strong, stable bond and precise fit, making it the definitive standard for porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) restorations.
The choice between high, medium, and low-fusing porcelain is not a matter of quality, but of application. Fusing temperature is a direct indicator of a porcelain's composition and physical properties, dictating its specific use case—from high-strength denture teeth to aesthetically versatile PFM crowns.

The Role of Fusing Temperature in Dental Porcelain
To understand the advantages of any one type, you must first understand what "fusing temperature" signifies. It dictates the material's entire profile, from where it can be used to how it will perform in the mouth.
What "Fusing Temperature" Means
The fusing temperature is the point at which porcelain particles sinter—they coalesce and densify into a solid mass without fully liquefying. This process, known as firing, is what transforms the powdered porcelain into a hard, glass-like structure.
The Three Main Classifications
Dental porcelains are categorized by the temperature at which this sintering occurs:
- High-Fusing: >1300°C (2372°F)
- Medium-Fusing: 1101–1300°C (2013–2372°F)
- Low-Fusing: 850–1100°C (1562–2012°F)
An additional category, ultra-low-fusing (<850°C), also exists, primarily for corrections and certain all-ceramic systems.
The Link Between Temperature and Composition
The fusing temperature is determined by the porcelain's composition, specifically the ratio of glass (fluxes like sodium or potassium) to refractory crystals (like quartz or alumina).
Higher fusing temperatures indicate a more crystalline structure, resulting in higher strength and stability. Lower fusing temperatures indicate a higher concentration of glass, which lowers the melting point.
Low-Fusing Porcelain: The PFM Workhorse
Low-fusing porcelain dominates the market for PFM restorations for several clear and compelling reasons that directly address the challenges of bonding ceramic to metal.
The Critical Advantage: Alloy Compatibility
This is the single most important factor. The metal alloys used for crowns (e.g., high noble, noble, base metal) would warp, sag, or even melt at the temperatures required to fire high-fusing porcelain.
Low-fusing porcelains are specifically engineered to have a coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) that is compatible with these alloys. Upon cooling, the porcelain must contract slightly less than the metal, placing it under beneficial compression and creating a durable, fracture-resistant bond.
Kindness to Opposing Teeth
A significant clinical advantage of low-fusing porcelain is its relative softness compared to high-fusing types. Its hardness is much closer to that of natural tooth enamel.
This means a crown made from low-fusing porcelain is less likely to cause excessive wear on the opposing natural teeth over time, a major consideration for long-term oral health.
Excellent Aesthetic Control
Modern low-fusing porcelains have a higher glass content, which can be leveraged to create highly aesthetic and translucent restorations. This allows skilled technicians to mimic the natural vitality, opalescence, and color gradations of a real tooth with remarkable accuracy.
Understanding the Trade-offs: A Comparative Look
No material is perfect for every situation. The strength of high-fusing porcelain is a disadvantage in a PFM context, just as the lower fusing temperature of PFM porcelain makes it unsuitable for denture teeth.
High-Fusing Porcelain: Strength and Stability
The primary application for high-fusing porcelain is the fabrication of prefabricated denture teeth.
Its high strength, density, and wear resistance make it ideal for this purpose. However, its extreme firing temperature makes it completely incompatible with any metal casting alloy used for crowns.
Medium-Fusing Porcelain: The Diminishing Middle Ground
Historically, medium-fusing porcelains were used for certain all-ceramic jacket crowns and pontics. They offered a balance of aesthetics and strength.
Today, their use has largely been superseded by advanced low-fusing materials and high-strength pressed or milled all-ceramic systems (like lithium disilicate or zirconia), which offer superior outcomes.
The Sintering Shrinkage Problem
All porcelains shrink during firing, typically by 15-20% by volume. This is a fundamental challenge for the dental technician, who must build up the porcelain in layers and anticipate this shrinkage to achieve the correct final shape and fit. The specific handling characteristics can vary between material types.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your material selection should be dictated entirely by the clinical or technical objective. There is no single "best" porcelain, only the correct one for the task.
- If your primary focus is creating PFM crowns and bridges: Low-fusing porcelain is the industry standard due to its essential thermal and chemical compatibility with dental alloys.
- If your primary focus is fabricating artificial denture teeth: High-fusing porcelain provides the necessary strength, stain resistance, and durability for this application.
- If your primary focus is minimizing wear on opposing natural teeth: Low-fusing porcelain is the superior choice as its hardness is closer to that of natural enamel.
- If your primary focus is adding a contact or repairing a chip: An ultra-low-fusing correction porcelain is required to avoid reflowing the entire underlying restoration.
Understanding these material properties empowers you to select the precise tool needed to achieve predictable, durable, and aesthetic clinical outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Low-Fusing Porcelain | High-Fusing Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | PFM Crowns & Bridges | Denture Teeth |
| Fusing Temperature | 850°C - 1100°C | >1300°C |
| Key Advantage | Alloy Compatibility & Aesthetics | High Strength & Wear Resistance |
| Hardness | Closer to Natural Enamel | Very Hard |
Ready to elevate your dental lab's PFM outcomes?
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables your dental laboratory needs for precise and reliable porcelain firing. Our solutions help you achieve the perfect bond and stunning aesthetics that low-fusing porcelain is known for.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and help you deliver superior restorations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the main difference between soldering and brazing? Choose the Right Metal Joining Method
- What is the advantage of firing porcelain in a vacuum? Achieve Denser, Stronger, and More Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- Why are porcelain fired under vacuum? To Eliminate Porosity for Superior Strength & Translucency
- How does precision temperature control impact TiAl alloy sintering? Master Microstructure Development
- What is the function of a porcelain furnace? Precision Firing for Lifelike Dental Restorations



















