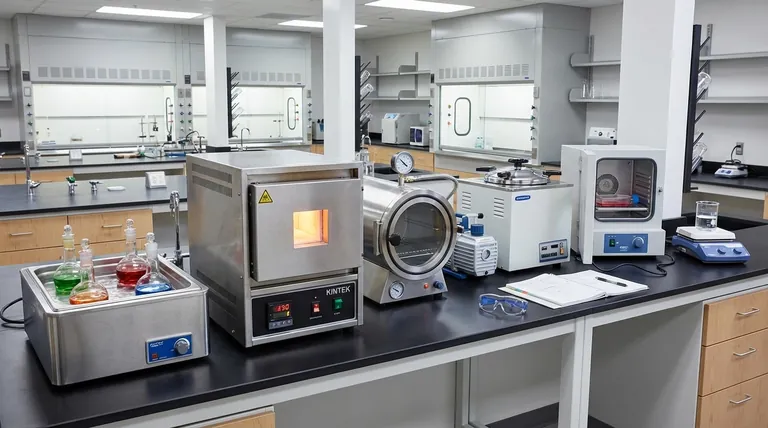
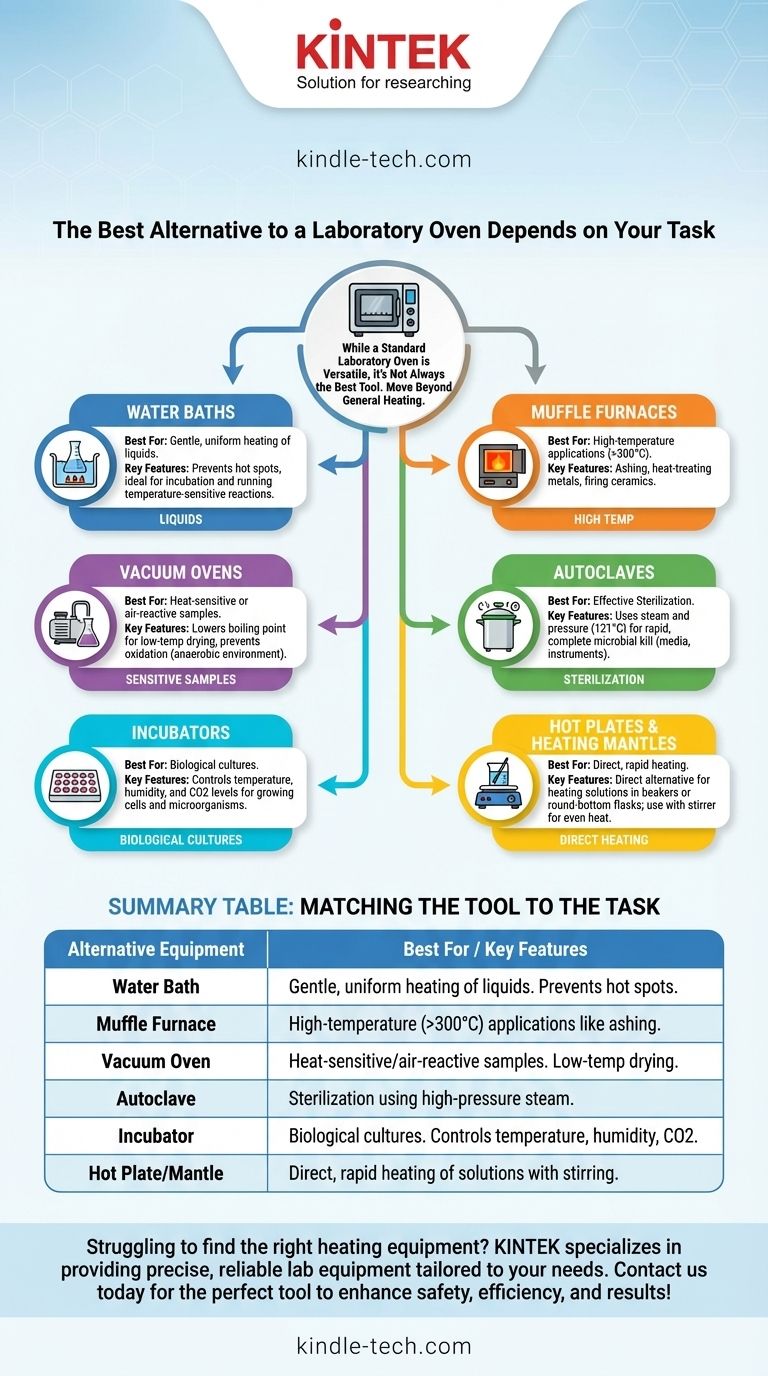
While a standard laboratory oven is a versatile workhorse, it is often not the optimal tool for specialized heating tasks. The best alternative depends entirely on your sample type, temperature requirements, and need for atmospheric control. Key alternatives include water baths for liquids, muffle furnaces for high temperatures, vacuum ovens for sensitive materials, and autoclaves for sterilization.
The central takeaway is to move beyond the general idea of "heating" and define your specific objective. The right tool is determined not by temperature alone, but by the material you are working with (liquid vs. solid), the precision required, and the processing environment (air vs. vacuum vs. steam).

Matching the Tool to the Task
A general-purpose laboratory oven uses convection (circulating hot air) to heat its entire chamber. This is effective for simple tasks like drying glassware but is inefficient and imprecise for many scientific applications. Choosing an alternative is about selecting a method that applies heat in a more targeted and appropriate way.
For Gentle, Uniform Heating of Liquids: Water Baths
A water bath provides exceptionally uniform and gentle heating for samples in flasks or beakers. By immersing the vessel in heated water, it eliminates the hot spots common with hot plates.
This method is ideal for incubating samples at a consistent temperature, dissolving compounds, or running temperature-sensitive reactions. An oil bath can be used for similar purposes at temperatures above the boiling point of water.
For High-Temperature Applications: Muffle Furnaces
When you need temperatures exceeding 300°C (572°F), a muffle furnace is the necessary tool. Standard lab ovens typically cannot reach these temperatures safely or consistently.
Furnaces are used for processes like ashing (burning off organic material to leave inorganic residue), heat-treating metals, or firing ceramics. Their insulated chambers are designed for extreme heat.
For Heat-Sensitive or Air-Reactive Samples: Vacuum Ovens
A vacuum oven allows you to dry samples at a much lower temperature than would be required in open air. By removing atmospheric pressure, it lowers the boiling point of solvents, protecting heat-sensitive compounds from thermal degradation.
It is also essential for materials that react with oxygen. By creating a vacuum or backfilling with an inert gas like nitrogen, a vacuum oven provides an anaerobic environment, preventing oxidation during heating.
For Biological Cultures: Incubators
While an incubator may look like a low-temperature oven, its function is fundamentally different. An incubator is designed to provide a stable, controlled environment for growing and maintaining cell cultures and microorganisms.
They offer superior temperature precision and uniformity, often within a fraction of a degree. Many models also control humidity and CO2 levels, which are critical for cell viability but irrelevant for a standard oven.
For Effective Sterilization: Autoclaves
Dry heat from an oven can sterilize, but it is slow and requires very high temperatures. An autoclave is the gold standard for sterilization in biological and medical labs.
It uses high-pressure steam and pressure (typically at 121°C) to kill all microorganisms, including resilient bacterial spores, far more effectively and quickly than dry heat. It is used for sterilizing media, instruments, and lab waste.
For Direct, Rapid Heating: Hot Plates & Heating Mantles
For simply heating a solution in a beaker, a hot plate is the most direct alternative. When paired with a magnetic stirrer, it ensures even heat distribution throughout a liquid.
A heating mantle is a more specialized device that wraps around a round-bottom flask. It provides intimate, uniform heating, which is ideal for organic synthesis and distillation procedures.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety
Choosing the right equipment also means understanding its limitations and inherent risks. A powerful tool used for the wrong purpose can lead to failed experiments or safety hazards.
The Limits of Hot Plates
Hot plates are convenient but can create dangerous hot spots, leading to bumping in boiling liquids or cracking glassware. They provide poor temperature control without an external probe and are unsuitable for unattended or sensitive reactions.
The Dangers of Muffle Furnaces
The extreme temperatures of a muffle furnace present a significant burn risk. They require specialized personal protective equipment (PPE), such as heat-resistant gloves and face shields, and should never be opened while hot.
The Specificity of Autoclaves
An autoclave is a sterilizer, not a dryer or a general-purpose oven. Attempting to dry glassware in one will leave it wet. Furthermore, never autoclave flammable or reactive chemicals, as this can lead to an explosion.
The Inefficiency of Ovens for Liquids
Heating liquids in an open beaker inside a laboratory oven is inefficient and unsafe. The risk of spilling is high, and the evaporation creates vapors that can be hazardous or damage the oven's electronics.
Selecting the Right Alternative for Your Goal
Base your decision on the specific outcome you need to achieve for your sample.
- If your primary focus is drying simple glassware or warming solids: The standard laboratory oven is likely sufficient.
- If your primary focus is gently heating a liquid solution to a precise temperature: Use a water bath or a stirred hot plate with an external temperature probe.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing media, instruments, or waste: An autoclave is the only appropriate choice for reliable results.
- If your primary focus is growing and maintaining biological cell cultures: An incubator with temperature, and possibly CO2, control is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is drying a compound that is sensitive to heat or air: A vacuum oven is the correct and necessary tool.
- If your primary focus is combusting a sample for analysis or heat-treating materials: You require a high-temperature muffle furnace.
By precisely defining your heating objective, you can select a tool that delivers safety, efficiency, and reliable results.
Summary Table:
| Alternative Equipment | Best For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Water Bath | Gentle, uniform heating of liquids | Prevents hot spots, ideal for incubation |
| Muffle Furnace | High-temperature applications (>300°C) | Ashing, heat-treating, firing ceramics |
| Vacuum Oven | Heat-sensitive or air-reactive samples | Lowers boiling point, prevents oxidation |
| Autoclave | Sterilization | Uses steam and pressure for effective microbial kill |
| Incubator | Biological cultures | Controls temperature, humidity, and CO2 |
| Hot Plate / Heating Mantle | Direct, rapid heating of solutions | Even heat distribution with stirring capability |
Struggling to find the right heating equipment for your specific lab application? KINTEK specializes in providing precise, reliable lab equipment and consumables tailored to your unique needs. Whether you require the gentle uniformity of a water bath, the high-temperature capabilities of a muffle furnace, or the sterile environment of an autoclave, our experts can help you select the perfect tool to enhance safety, efficiency, and results in your laboratory. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How is melting point affected by heating rate? Avoid Inaccurate Measurements in Your Lab
- What temperature does molten steel melt? Understand the Melting Range, Not a Single Point
- What should be considered when performing melting point determination? Ensure Accurate Compound Identification and Purity Assessment
- What affects melting range? Understand the Critical Role of Purity and Structure
- How hot can metal get? From Melting Points to Plasma Temperatures



















