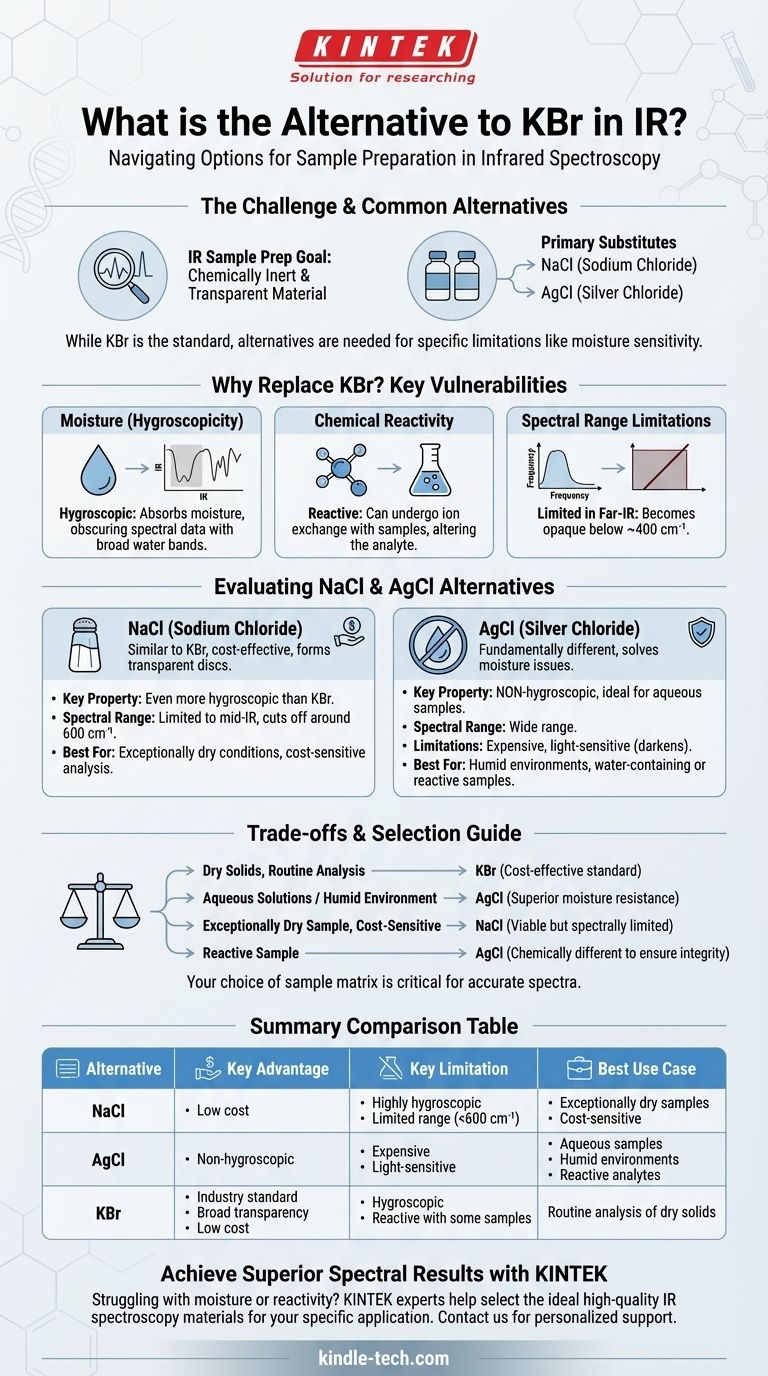
For infrared (IR) spectroscopy, the most common alternatives to Potassium Bromide (KBr) for creating sample pellets are other salts that are also transparent to IR radiation. The primary substitutes are Sodium Chloride (NaCl) and Silver Chloride (AgCl), each chosen to overcome specific limitations of KBr, such as its tendency to absorb water.
The core challenge in IR sample preparation is finding a material that is chemically inert and transparent in the spectral region of interest. While KBr is the standard, its sensitivity to moisture often necessitates alternatives like AgCl for aqueous samples or NaCl for cost-sensitive applications.

Why We Need an Alternative to KBr
KBr is the default choice for a reason: it's generally effective and inexpensive. However, it has key vulnerabilities that can compromise the quality of your spectral data.
The Problem with Moisture (Hygroscopicity)
KBr is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the air and from the sample itself.
Water has very strong, broad absorption bands in the infrared spectrum. This absorbed moisture can easily obscure the peaks from your actual sample, leading to inaccurate or uninterpretable results.
Potential for Chemical Reactivity
As an alkali halide salt, KBr can undergo ion exchange with certain samples. This reaction alters the chemical nature of your analyte, meaning the spectrum you record is not of your original material.
Limitations in Spectral Range
While KBr offers a wide transparent window, it becomes opaque in the far-infrared region (typically below 400 cm⁻¹). If you need to analyze vibrations at these very low frequencies, KBr is unsuitable.
Evaluating the Common Alternatives
The best alternative depends entirely on your sample, your environment, and your analytical goals.
Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
Often thought of as a direct substitute for KBr, NaCl shares many of its properties. It is an alkali halide that becomes plastic under pressure, forming a transparent disc.
It is very cost-effective, but it is even more hygroscopic than KBr. Furthermore, its useful spectral range is more limited, cutting off around 600 cm⁻¹. It is only a viable alternative in very dry conditions for mid-IR analysis.
Silver Chloride (AgCl)
AgCl is a fundamentally different type of material and solves the primary problem with KBr and NaCl.
Its most significant advantage is that it is not hygroscopic. This makes it the ideal choice for analyzing samples that contain water or for working in humid laboratory environments without a glovebox. However, AgCl is significantly more expensive and is sensitive to light, which can cause it to darken over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sample preparation material is a balancing act. There is no single "best" option for every scenario.
Cost vs. Performance
KBr and NaCl are inexpensive and widely available. Specialized materials like AgCl solve critical problems (like water contamination) but come at a much higher price point.
Inertness vs. Environment
The most critical factor is ensuring the matrix material does not react with your sample. If KBr or NaCl is reactive, you must switch to a more inert, albeit more expensive, alternative.
Spectral Range vs. Usability
You must ensure your chosen material is transparent in the frequency range you need to measure. NaCl's higher-frequency cutoff makes it unsuitable for analyzing certain vibrations that KBr could capture.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Select your material based on the specific demands of your experiment.
- If your primary focus is routine analysis of dry solids: KBr remains the cost-effective industry standard due to its broad transparency and low cost.
- If you are working with aqueous solutions or in a humid environment: Silver Chloride (AgCl) is the superior choice to avoid spectral contamination from water.
- If cost is the main driver and your sample is exceptionally dry: Sodium Chloride (NaCl) can serve as a viable, though spectrally more limited, alternative to KBr.
- If you suspect your sample is reacting with an alkali halide: You must use a chemically different material like AgCl to ensure the integrity of your analysis.
Ultimately, your choice of sample matrix is as critical as the spectrometer itself for obtaining a clean and accurate spectrum.
Summary Table:
| Alternative | Key Advantage | Key Limitation | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium Chloride (NaCl) | Low cost | Highly hygroscopic, limited spectral range (<600 cm⁻¹) | Exceptionally dry samples, cost-sensitive mid-IR analysis |
| Silver Chloride (AgCl) | Non-hygroscopic, ideal for aqueous samples | Expensive, light-sensitive | Humid environments, water-containing samples, reactive analytes |
| Potassium Bromide (KBr) | Industry standard, broad transparency, low cost | Hygroscopic, can react with samples | Routine analysis of dry solids |
Struggling with moisture interference or sample reactivity in your IR analysis? The right sample preparation matrix is critical for obtaining clean, accurate spectra. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables, including a full range of IR spectroscopy materials. Our experts can help you select the ideal matrix for your specific application—whether you're working with aqueous solutions, sensitive compounds, or need cost-effective solutions. Let us help you achieve superior spectral results. Contact our team today for personalized support and discover how KINTEK's products can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and data quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Barium Fluoride BaF2 Substrate Window
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer CaF2 Substrate Window Lens
- Infrared High Resistance Single Crystal Silicon Lens
- CF Ultra-High Vacuum Observation Window Window Flange High Borosilicate Glass Sight Glass
People Also Ask
- How does potassium bromide affect humans? A Look at Its Risks and Obsolete Medical Use
- Why is KBr used for IR? Create Transparent Pellets for Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- Why you should avoid water contamination when performing FTIR measurements using NaCl or KBr plates? Protect Your Equipment & Data Integrity
- What are the factors affecting optical properties? Master the Atomic and Microstructural Influences
- What is the primary function of a sapphire glass window? Optimizing High-Throughput IR Thermography Reactors







