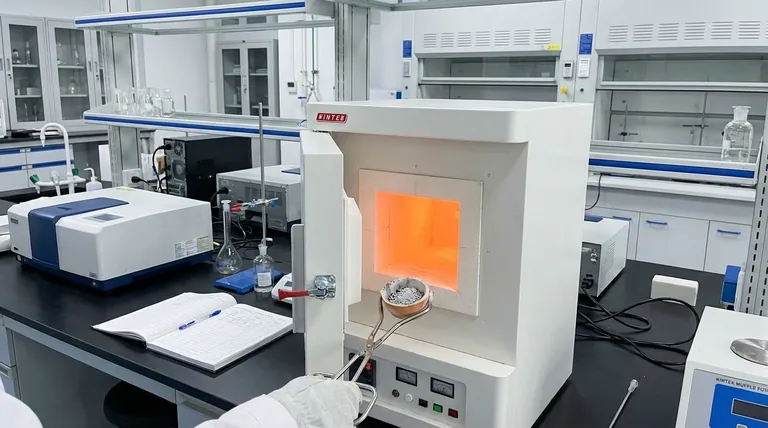
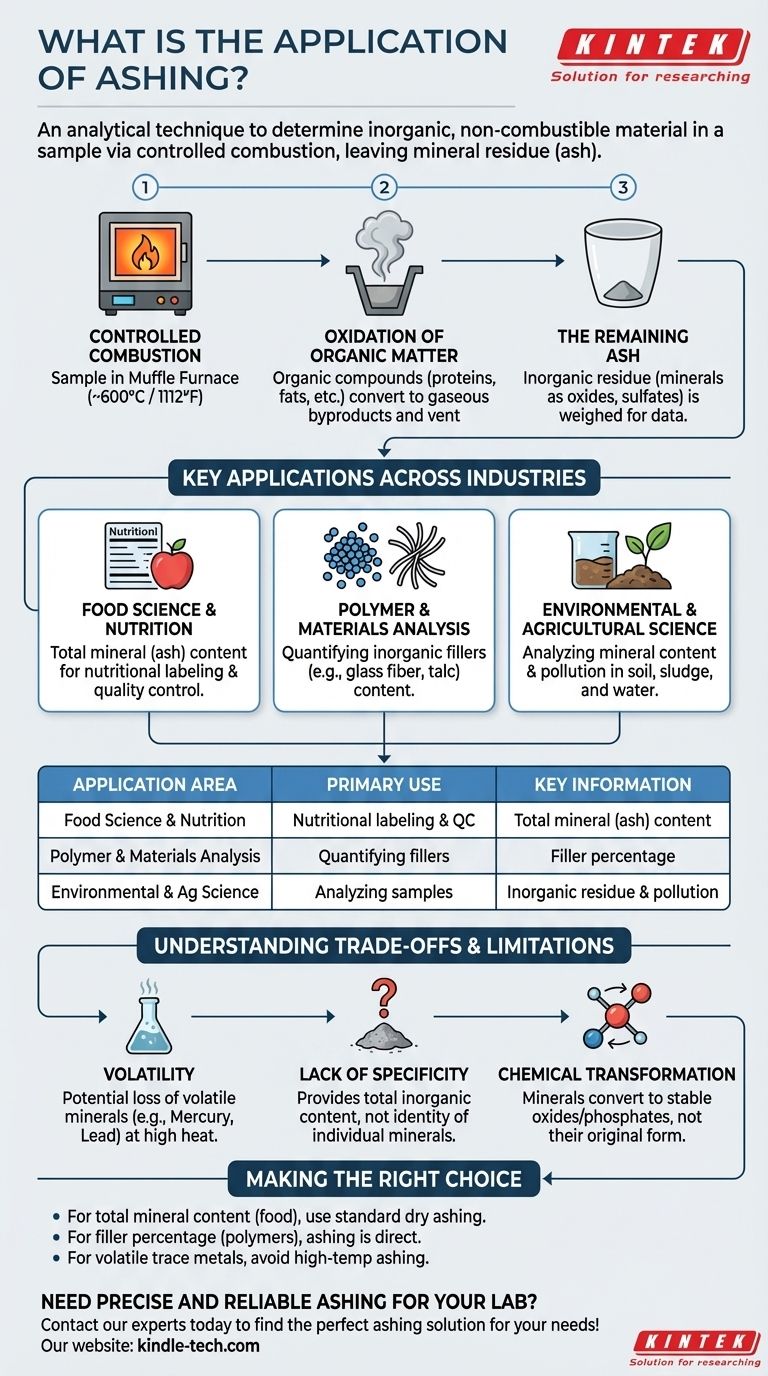
At its core, ashing is an analytical technique used to determine the amount of inorganic, non-combustible material in a sample. It is a process of controlled combustion where all organic substances are burned away, leaving behind only the mineral residue, or "ash." This is widely used in the food industry to quantify the total mineral content of foodstuffs.
Ashing's primary purpose is to isolate and quantify the inorganic components of a material. By removing all organic matter through high-temperature oxidation, it provides a direct measure of the total mineral content, a critical parameter in quality control and nutritional analysis.

The Fundamental Principle of Ashing
To understand its application, you must first understand how ashing works. It is a process of thermal decomposition that leverages the different properties of organic and inorganic compounds.
Controlled Combustion
The process is typically performed in a high-temperature muffle furnace. A pre-weighed sample is placed inside and heated in the presence of air, usually to a temperature around 600°C (1112°F).
Oxidation of Organic Matter
At this high temperature, the organic components of the sample (like proteins, fats, and carbohydrates) react with oxygen and combust. They are converted into gaseous byproducts like carbon dioxide and water vapor, which are then vented from the furnace.
The Remaining Ash
The material left behind is the inorganic residue. These non-combustible substances, primarily minerals, are converted into more stable forms like oxides, sulfates, and phosphates. The weight of this ash is what provides the key analytical data.
Key Applications Across Industries
While its use in food science is prominent, the principle of ashing is applied across various fields for quality control and material characterization.
Food Science and Nutrition
This is the most common application. The total ash content is a required parameter on many nutritional labels as it represents the total amount of minerals. It's a quick, effective way to measure the non-organic nutritional value of a food product.
Polymer and Materials Analysis
In the plastics and composites industry, ashing is used to determine the content of inorganic fillers. Materials like glass fiber, talc, or calcium carbonate are often added to polymers to enhance their properties. Ashing burns off the polymer matrix, leaving the filler behind to be weighed.
Environmental and Agricultural Science
Ashing is used to analyze the mineral content of soil, the inorganic residue in sludge, or the particulate matter collected from water samples. This helps in assessing soil quality, pollution levels, and environmental composition.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Ashing is a powerful tool, but it is a destructive and somewhat blunt instrument. Understanding its limitations is crucial for accurate interpretation of results.
The Problem of Volatility
A significant drawback is the potential loss of volatile minerals. Certain elements and their compounds (like mercury, lead, and some halides) can vaporize and be lost at the high temperatures used in dry ashing. This can lead to an underestimation of the true mineral content.
Lack of Specificity
A standard ashing test provides the total inorganic content, not the identity or quantity of individual minerals. It tells you how much ash there is, but not what that ash is made of. Subsequent analytical techniques, like spectroscopy, are required to identify specific elements.
Chemical Transformation
The high heat fundamentally changes the chemical form of the minerals. What you are weighing are primarily oxides and phosphates, not the minerals as they originally existed in the sample. This is an important distinction for advanced chemical analysis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying ashing effectively depends entirely on what you need to measure.
- If your primary focus is total mineral content for nutritional labeling: Standard dry ashing is an efficient, industry-accepted method for this purpose.
- If your primary focus is determining the filler percentage in a polymer: Ashing is an excellent and direct method for quantifying the inorganic filler load.
- If your primary focus is analyzing for specific, potentially volatile trace metals: You should avoid high-temperature ashing and instead use wet ashing or direct spectroscopic methods.
Understanding both the purpose and the limitations of ashing is the key to leveraging it as an effective analytical tool.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Primary Use of Ashing | Key Information Obtained |
|---|---|---|
| Food Science & Nutrition | Nutritional labeling & quality control | Total mineral (ash) content |
| Polymer & Materials Analysis | Quantifying inorganic fillers (e.g., glass fiber) | Filler percentage in a material |
| Environmental & Agricultural Science | Analyzing soil, sludge, and water samples | Inorganic residue and pollution levels |
Need precise and reliable ashing for your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment, including muffle furnaces essential for accurate ashing procedures. Whether you're in food science, materials testing, or environmental analysis, our solutions help you achieve consistent, dependable results for your quality control and research.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect ashing solution for your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between muffle furnace and tubular furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right Lab Furnace
- What is the most common metal used for blacksmithing? Start with Mild Steel for Forging Success
- What is muffle furnace principle and procedure? Master Safe, Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What are the 4 types of heat treatment steel undergoes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening & Tempering
- What temperature should a furnace run at? From Home Comfort to Industrial Processes



















