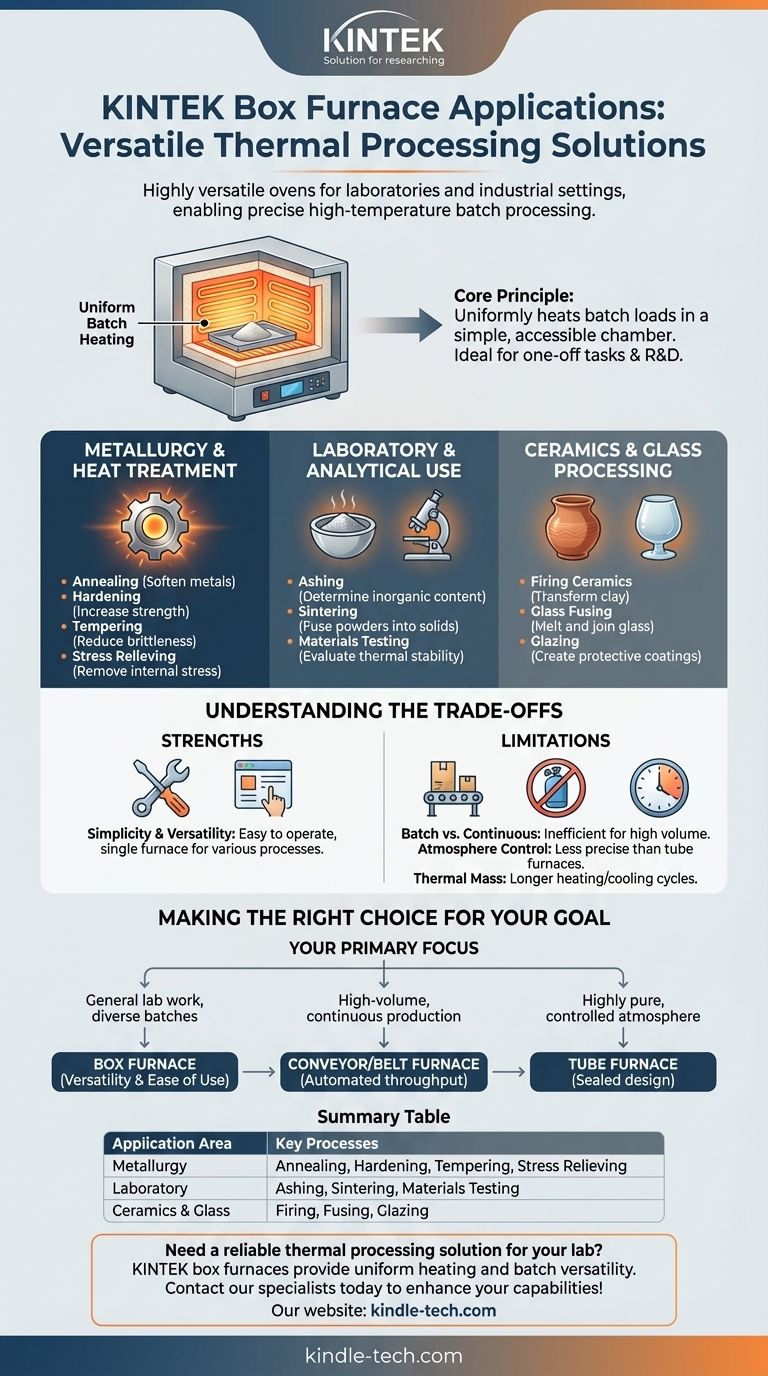
In essence, a box furnace is a highly versatile oven used for high-temperature thermal processing across laboratories and industrial settings. Its primary applications include heat-treating metals to alter their properties, ashing samples to determine their inorganic content, and conducting research on advanced materials that require precise thermal cycling.
The core value of a box furnace lies in its ability to uniformly heat batch loads of materials in a simple, accessible chamber. It is the default choice for a wide range of thermal processes that do not require the complexity or throughput of a continuous-feed system.
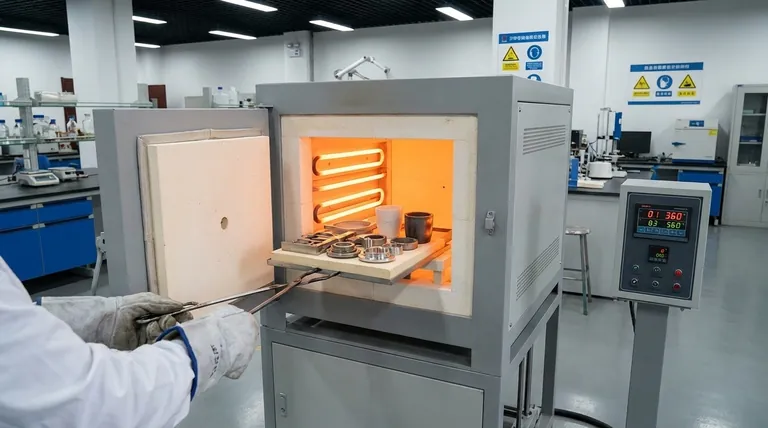

How a Box Furnace Achieves Its Purpose
To understand its applications, you must first understand its fundamental design. Its "box" shape is not merely descriptive; it is central to its function.
The Core Components
A box furnace consists of a heavily insulated chamber with a door on one side for access. Inside, heating elements, typically made of materials like Kanthal (for up to ~1200°C) or silicon carbide (for higher temperatures), are arranged to radiate heat evenly throughout the chamber.
This design creates a stable, uniform thermal environment, which is critical for consistent results.
The Principle of Batch Processing
Unlike continuous or conveyor furnaces, a box furnace operates on a batch basis. An operator places a part or a tray of material inside, closes the door, runs a pre-programmed temperature cycle, and then removes the finished batch.
This simple workflow makes it ideal for one-off tasks, research and development, or low-to-medium volume production where each batch may have unique requirements.
Key Applications Across Industries
The combination of uniform heating and batch flexibility makes the box furnace a staple in several key fields.
Metallurgy and Heat Treatment
This is a primary industrial application. Specific processes include:
- Annealing: Heating and slowly cooling metal to make it softer and more ductile.
- Hardening: Heating steel to a critical temperature and then rapidly cooling (quenching) it to increase hardness.
- Tempering: Re-heating a hardened part to a lower temperature to reduce brittleness.
- Stress Relieving: Heating a welded or machined part to remove internal stresses built up during fabrication.
Laboratory and Analytical Use
In research and quality control labs, box furnaces are indispensable tools for:
- Ashing: Burning off all organic material in a sample at a controlled temperature to precisely measure the weight of the remaining inorganic ash. This is common in food science, environmental analysis, and plastics testing.
- Sintering: Heating compacted powders below their melting point to fuse them into a solid, coherent mass. This is fundamental to creating many ceramic and metallic parts.
- Materials Testing: Subjecting materials to high temperatures to evaluate their stability, degradation, or performance under thermal stress.
Ceramics and Glass Processing
The excellent temperature uniformity is critical for artists and manufacturers working with ceramics and glass.
- Firing Ceramics: Transforming clay into a hard, durable ceramic object.
- Glass Fusing: Heating pieces of glass until they melt and fuse together.
- Glazing: Firing a ceramic piece a second time after applying a glaze to create a vitreous, protective coating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly versatile, a box furnace is not the right solution for every thermal processing need. Objectively weighing its strengths and limitations is key.
Strength: Simplicity and Versatility
Its straightforward design makes it easy to operate and maintain. A single furnace can be used for a wide variety of materials and processes simply by changing the temperature program.
Limitation: Batch vs. Continuous Processing
The furnace's greatest strength is also its main limitation. It is inherently inefficient for high-volume, automated production lines where parts must be processed continuously. For this, a conveyor furnace is required.
Limitation: Atmosphere Control
A standard box furnace operates in ambient air. While some models can be equipped with ports for introducing an inert gas like nitrogen or argon, they are not as well-sealed as a tube furnace. A tube furnace is superior for processes that demand a highly pure, controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation.
Limitation: Thermal Mass and Cycle Time
The heavy insulation required for high temperatures and uniformity gives the furnace significant thermal mass. This means it can take a considerable amount of time to heat up and cool down, making it less suitable for applications requiring extremely rapid thermal cycling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct type of furnace depends entirely on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab work or heat treating diverse parts in batches: A box furnace offers unmatched versatility and ease of use.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production of similar parts: You should investigate a conveyor or belt furnace designed for automated throughput.
- If your primary focus is processing samples under a highly pure and controlled gas atmosphere: A tube furnace is almost always the superior choice due to its sealed design.
Understanding these core principles allows you to select not just a tool, but the right thermal processing solution for your specific objective.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes |
|---|---|
| Metallurgy | Annealing, Hardening, Tempering, Stress Relieving |
| Laboratory | Ashing, Sintering, Materials Testing |
| Ceramics & Glass | Firing, Fusing, Glazing |
Need a reliable thermal processing solution for your lab? A KINTEK box furnace provides the uniform heating and batch-processing versatility essential for consistent results in heat treatment, ashing, and materials research. Our expertise in lab equipment ensures you get the right tool for your specific application. Contact our specialists today to discuss your requirements and enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Which metals cannot be hardened by heat treatment? Understand the limits of thermal hardening.
- Which type of material is used in a muffle furnace? A Guide to Its High-Temperature Construction
- What is the condition of a muffle furnace? Ensuring Clean, Controlled Heat for Your Lab
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a blast furnace? Precision vs. Production
- Why is it important to hardening a steel? To Achieve Superior Strength and Wear Resistance



















