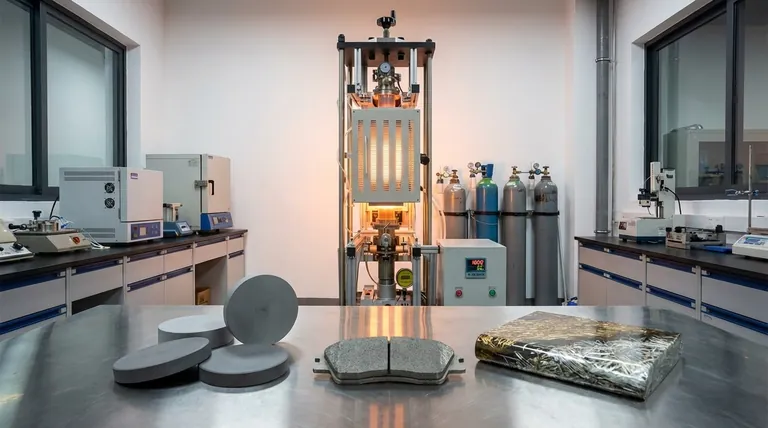
In short, hot pressing is a critical manufacturing technique used to create dense, high-strength materials by applying high temperature and pressure simultaneously. It is most commonly used to fabricate advanced ceramics, high-performance composites, and durable friction components like sintered brake pads for trains and heavy machinery.
The core value of hot pressing is its ability to overcome the limitations of traditional sintering. By combining heat and pressure, it forces powder particles together, eliminating internal voids to produce a fully dense material with a fine-grained structure and superior mechanical properties.

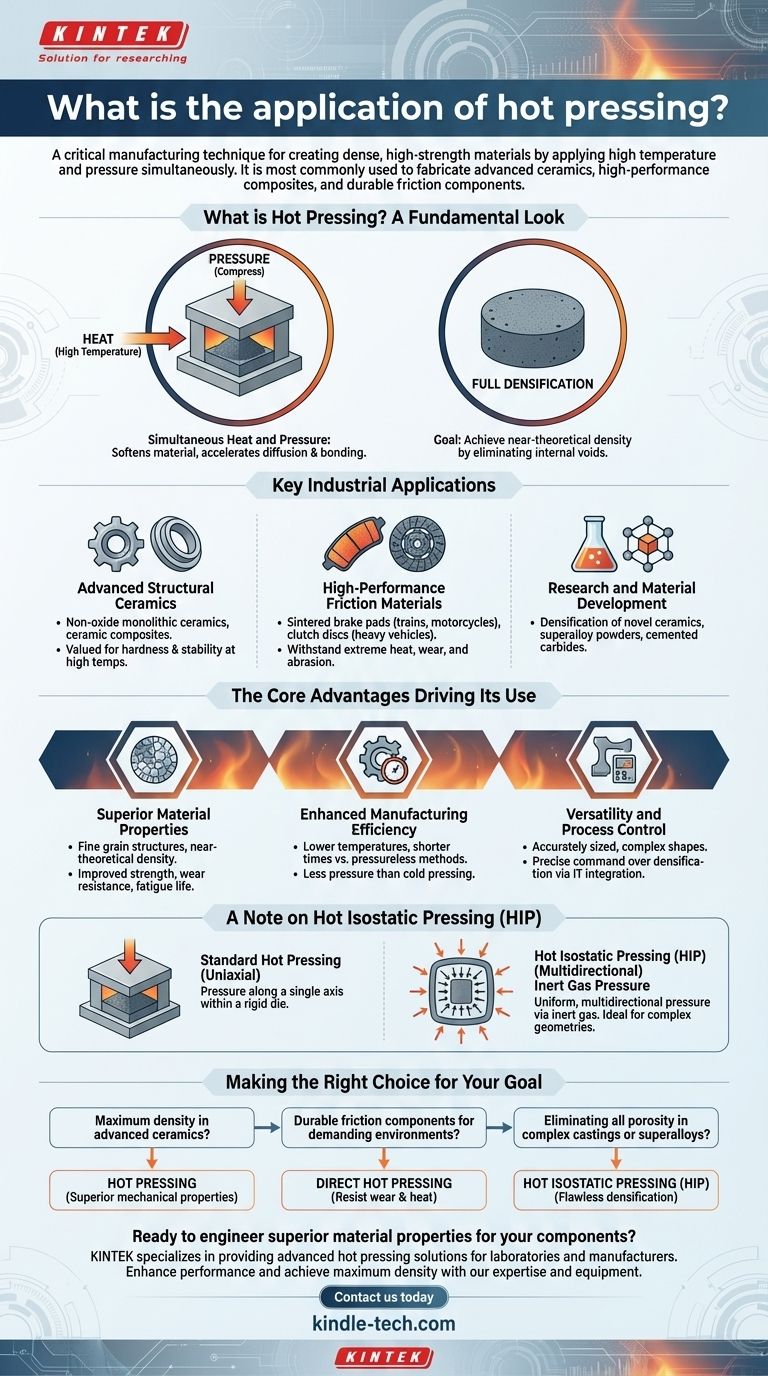
What is Hot Pressing? A Fundamental Look
Simultaneous Heat and Pressure
Hot pressing involves placing a powder compact into a die, which is then heated to a high temperature while simultaneously being compressed.
This combined action softens the material, making it easier to deform and bond. It drastically accelerates the diffusion and mass transfer processes that are essential for creating a solid, cohesive part.
The Goal: Full Densification
The primary objective of hot pressing is to achieve a final product with a density that is very close to its theoretical maximum.
By physically forcing the particles together, the process squeezes out the pores and voids that are often left behind in conventional sintering methods, resulting in a stronger, more reliable component.
Key Industrial Applications
Advanced Structural Ceramics
Hot pressing is the most common technique for producing dense, non-oxide monolithic ceramics and ceramic composites. These materials are valued for their hardness and stability at high temperatures but are notoriously difficult to densify without applied pressure.
High-Performance Friction Materials
The technique is essential in the friction material industry. It's used to produce sintered brake pads for high-speed trains, motorcycles, and industrial equipment, as well as sintered clutch discs for heavy trucks, tractors, and marine vessels.
These applications demand components that can withstand extreme heat, wear, and abrasion, properties directly enhanced by the hot pressing process.
Research and Material Development
Smaller hot pressing units are standard in research settings for developing new materials. This includes the densification of novel ceramics, the consolidation of superalloy powders for aerospace, and the fabrication of cemented carbides for cutting tools.
The Core Advantages Driving Its Use
Superior Material Properties
The process produces parts with fine grain structures and near-theoretical density. This directly translates to significantly improved mechanical and electrical properties, including higher strength, wear resistance, and fatigue life.
Enhanced Manufacturing Efficiency
Because the applied pressure aids the sintering process, hot pressing can be performed at lower temperatures and for shorter times compared to pressureless methods. The thermoplastic state of the heated powder also means it requires significantly less pressure than cold pressing.
Versatility and Process Control
Modern hot pressing allows for the production of accurately sized, complex shapes and large-diameter materials. The integration of IT for measurement and control gives manufacturers precise command over the densification process, ensuring consistent quality and performance.
A Note on Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
Uniaxial vs. Multidirectional Pressure
Standard hot pressing is uniaxial, meaning pressure is applied along a single axis within a rigid die.
A related technology, Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), places the component in a high-pressure vessel and uses an inert gas to apply uniform, multidirectional pressure.
When to Use HIP
HIP is exceptionally effective at completely removing residual porosity in parts, especially in complex castings or consolidated superalloy powders. It ensures that pressure is applied evenly to all surfaces, making it ideal for components with intricate geometries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is maximum density in advanced ceramics: Hot pressing is the industry-standard method for achieving superior mechanical properties that pressureless sintering cannot match.
- If your primary focus is durable friction components for demanding environments: Direct hot pressing is the ideal choice for creating sintered brake pads and clutches that resist wear and heat.
- If your primary focus is eliminating all porosity in complex castings or superalloys: Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is the superior variant for applying uniform pressure to achieve flawless densification.
Ultimately, choosing the right thermal-mechanical process allows you to engineer material properties from the ground up, ensuring the final component meets its performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Materials | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Structural Ceramics | Non-oxide ceramics, composites | Superior hardness & high-temperature stability |
| High-Performance Friction Materials | Sintered brake pads, clutch discs | Extreme wear & heat resistance |
| Research & Material Development | Superalloys, cemented carbides | Accelerated development of novel materials |
Ready to engineer superior material properties for your components?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced hot pressing solutions for laboratories and manufacturers. Whether you're developing next-generation ceramics, durable friction materials, or researching new alloys, our expertise and equipment can help you achieve maximum density and enhanced performance.
Contact us today to discuss how our lab equipment and consumables can optimize your hot pressing process and bring your material goals to life.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is the use of a vacuum hot pressing furnace essential for CrFeMoNbZr targets? Ensure Full Density & Chemical Purity
- What role does the Laboratory Vacuum Hot Press Furnace play in the production of ZnS ceramics? Unlock Optical Excellence
- Why increase the temperature when forging? Achieve Superior Strength and Formability
- What function does the pressure applied by a vacuum hot press furnace serve? Enhance Ti-Al3Ti Composite Sintering
- What are the benefits of a vacuum hot press for yttrium oxide? Achieve High-Density, Transparent Ceramics



















