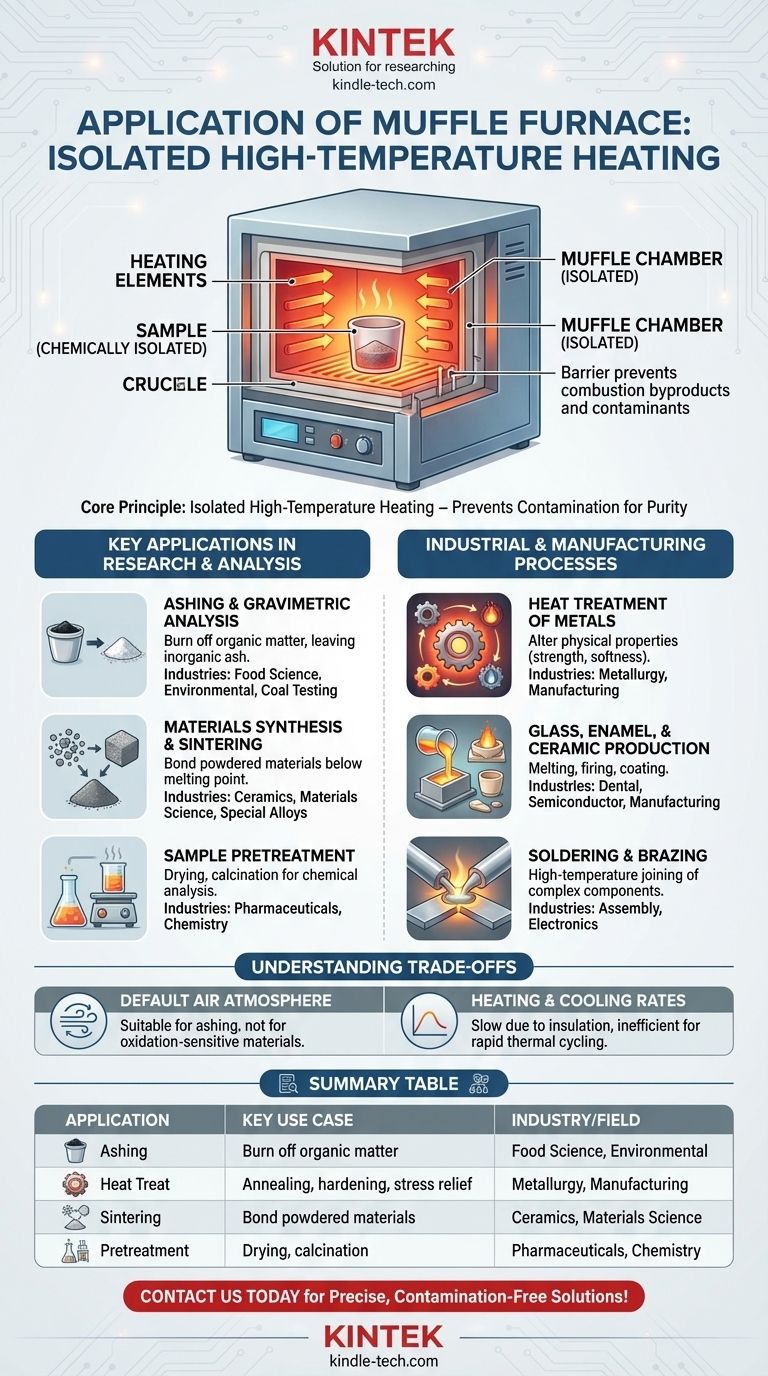
At its core, a muffle furnace is used for high-temperature processes that require a sample to be heated in a controlled, insulated environment. Its key applications include ashing, heat-treating metals, sintering materials like ceramics, and preparing samples for chemical analysis across various industries. The furnace's defining feature is that it isolates the material being heated from the heating elements and any combustion byproducts, preventing contamination.
The essential value of a muffle furnace is not just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its capacity to do so while keeping the sample chemically isolated. This ensures that the process itself—whether it's burning off organic matter or altering a metal's structure—is the only thing affecting the material.

The Core Principle: Isolated High-Temperature Heating
A muffle furnace is fundamentally a thermally insulated chamber. The name comes from the "muffle," which is the inner chamber that contains the sample and separates it from the actual heating coils or flames.
Preventing Contamination
The muffle design is critical. By shielding the sample, it ensures that byproducts from fuel or oxidation from the heating elements do not interact with and contaminate the material.
This makes it indispensable for applications where the chemical purity and integrity of the sample are paramount.
Key Applications in Research and Analysis
The furnace's ability to provide a clean, high-heat environment makes it a cornerstone of many analytical laboratories.
Ashing and Gravimetric Analysis
Ashing is one of the most common applications. The furnace is used to heat a sample to a temperature high enough to burn off all organic substances, leaving only the non-combustible inorganic material, or ash.
This is crucial in fields like food science, environmental analysis, and coal testing to determine the non-volatile or inorganic content of a sample.
Materials Synthesis and Sintering
In materials science, a muffle furnace is used to create new materials. Sintering, for example, involves heating powdered materials (like ceramics or metals) below their melting point until their particles bond together.
This process is fundamental to producing technical ceramics, special alloys, and other advanced solid materials.
Sample Pretreatment
In chemistry and pharmaceuticals, the furnace is often used for sample pretreatment. This can involve drying, calcination (decomposing a substance by heating), or preparing medical samples for further, more sensitive analysis.
Industrial and Manufacturing Processes
Beyond the lab, muffle furnaces are workhorses in various industrial settings for modifying and creating materials.
Heat Treatment of Metals
The furnace provides the precise thermal environment needed for heat-treating metals and alloys.
Processes like annealing (softening metal), hardening (increasing strength), quenching, and stress relief are all performed to alter the physical and mechanical properties of a workpiece.
Glass, Enamel, and Ceramic Production
The high temperatures achieved are ideal for melting glass, creating durable enamel coatings on metal, and firing technical ceramics used in industries from dental to semiconductor manufacturing.
Soldering and Brazing
The furnace's controlled environment is also used for high-temperature joining processes like soldering and brazing, which are essential for assembling complex components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, a standard muffle furnace is not the right tool for every high-temperature task. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Default Air Atmosphere
A standard muffle furnace operates in a normal air atmosphere. This is ideal for processes like ashing but unsuitable for materials that would readily oxidize or react with air at high temperatures.
Processes requiring an inert or reactive gas atmosphere typically demand a specialized tube furnace or vacuum furnace.
Heating and Cooling Rates
Due to their heavy insulation, muffle furnaces have significant thermal mass. This means they heat up and cool down relatively slowly.
This is not a problem for most batch processes but makes them inefficient for applications requiring rapid thermal cycling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating instrument depends entirely on the material and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is determining inorganic content: A muffle furnace is the standard and ideal tool for ashing organic materials in food, environmental, or fuel analysis.
- If your primary focus is modifying a metal's physical properties: The furnace provides the controlled thermal environment required for heat-treatment processes like annealing, hardening, and stress relief.
- If your primary focus is creating new solid materials: Its clean, high-temperature environment is essential for sintering ceramics, synthesizing novel compounds, and producing special alloys.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is the foundational tool for any high-temperature process where sample purity and a controlled thermal environment are non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Use Case | Industry/Field |
|---|---|---|
| Ashing | Burn off organic matter to analyze inorganic content | Food Science, Environmental, Coal Testing |
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, hardening, stress relief of metals | Metallurgy, Manufacturing |
| Sintering | Bond powdered materials below melting point | Ceramics, Materials Science |
| Sample Pretreatment | Drying, calcination for chemical analysis | Pharmaceuticals, Chemistry |
Need precise, contamination-free high-temperature processing? KINTEK's muffle furnaces are engineered for critical applications like ashing, sintering, and heat treatment, ensuring your samples remain pure and your results are reliable. Our lab equipment is trusted by research and industrial laboratories worldwide. Contact us today to find the perfect muffle furnace for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What type of furnace is a muffle furnace? A Guide to High-Purity, Contamination-Free Heating
- What is the meaning of muffle furnace? The Key to Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- What is the construction of a muffle furnace? Discover the Precision Engineering for Pure, Controlled Heating
- What is the use of muffle furnace in food lab? Essential for Accurate Ash Content Analysis
- What is the use of muffle furnace in chemistry laboratory? Achieve Precise High-Temperature Material Processing



















