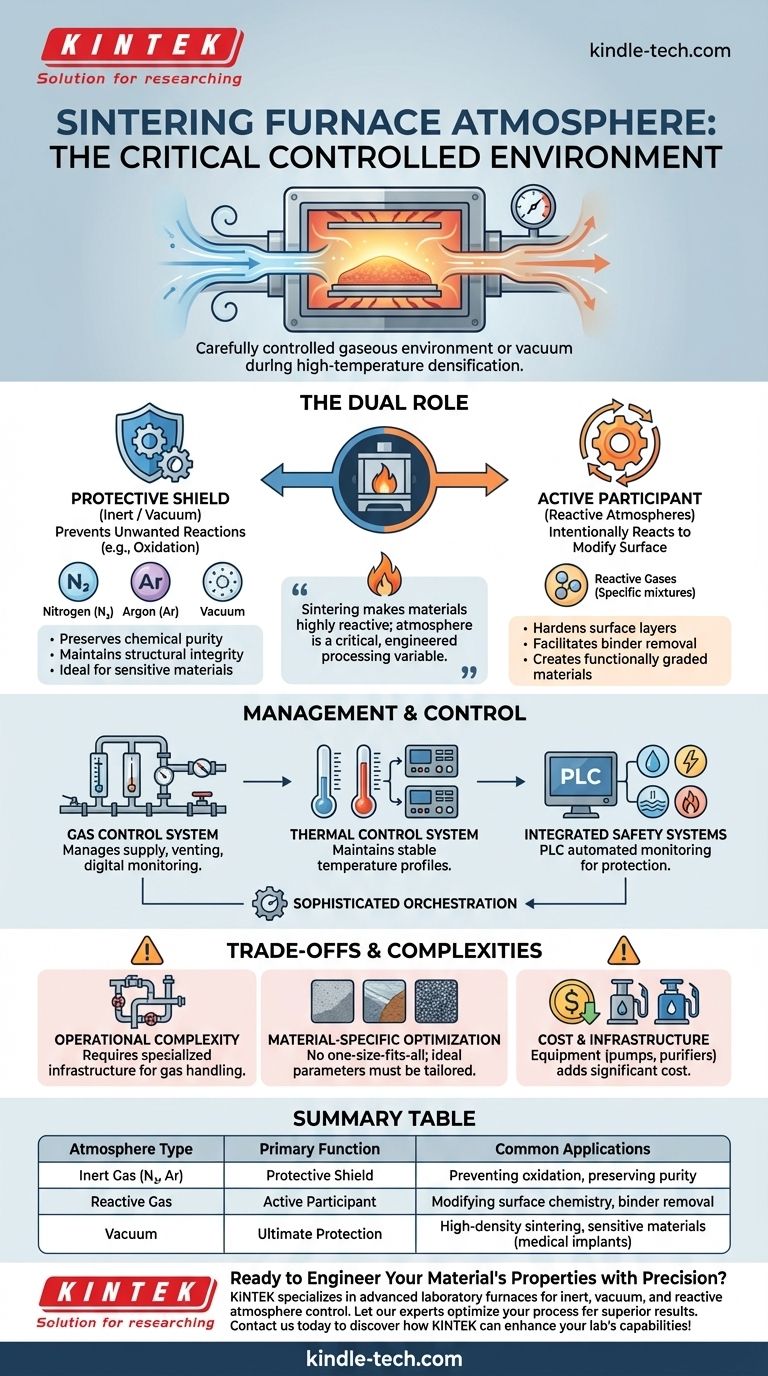
The atmosphere of a sintering furnace is the carefully controlled gaseous environment maintained within the furnace chamber during the high-temperature densification process. This atmosphere is not ambient air but is typically a specific gas—like nitrogen or argon—or a vacuum. Its purpose is to actively control the chemical interactions that occur on the material's surface, either by preventing unwanted reactions like oxidation or by intentionally promoting specific surface changes.
Sintering at extreme temperatures makes materials highly reactive and vulnerable to their surroundings. The furnace atmosphere is therefore not a passive background condition, but a critical processing variable that is deliberately engineered to protect the material or to actively modify its properties.
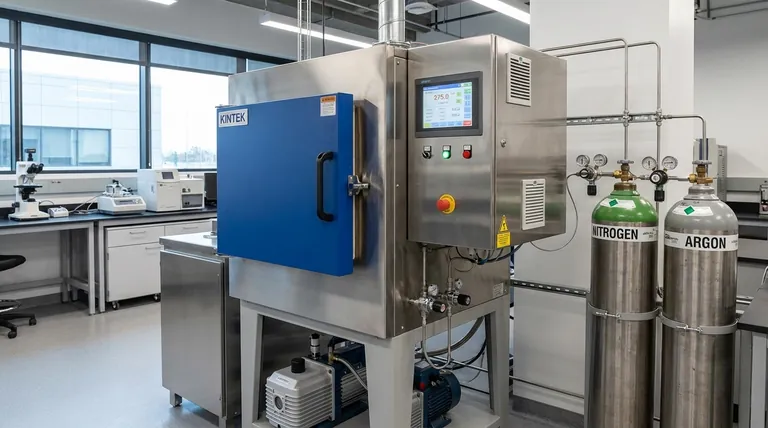

The Dual Role of the Furnace Atmosphere
Controlling the furnace atmosphere serves one of two fundamental purposes: to be chemically protective or to be chemically reactive. The choice between them is dictated entirely by the desired properties of the final component.
A Protective Shield (Inert Atmospheres)
The most common function of a furnace atmosphere is to be chemically inert, acting as a protective shield for the material being sintered.
At high temperatures, most materials are prone to reacting with oxygen and other elements in the air. This can lead to oxidation, contamination, and a degradation of mechanical or electrical properties.
By filling the furnace with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon, these unwanted reactions are prevented. This preserves the chemical purity and structural integrity of the material as it densifies.
An Active Participant (Reactive Atmospheres)
In some advanced processes, the atmosphere is designed to be chemically active, meaning it intentionally reacts with the material's surface.
This allows for the modification of the component's surface chemistry to achieve specific properties. For example, a particular gas might be introduced to create a hardened surface layer or to facilitate the removal of binder materials in a controlled way.
This transforms the sintering furnace from a simple oven into a thermochemical reactor, enabling the creation of functionally graded or composite materials.
The Absence of Atmosphere (Vacuum)
A vacuum is the ultimate protective environment. By pumping the air out of the furnace chamber, virtually all reactive gas molecules are removed.
Vacuum sintering is critical for materials that are extremely sensitive to oxidation or contamination, such as certain rare earth magnets or medical implants. It also excels at removing trapped gases from the material, aiding in the elimination of pores and achieving maximum density.
How the Atmosphere is Managed and Controlled
Maintaining a precise atmosphere requires a sophisticated system of hardware and software working in concert with the heating elements.
The Gas Control System
Atmosphere furnaces require a dedicated gas control system. This manages the supply of specific gases into the furnace and the safe treatment and venting of exhaust gases. Digital flow monitoring systems ensure the correct volume and pressure of gas are maintained throughout the sintering cycle.
Temperature and Process Stability
A thermal control system, consisting of temperature sensors and intelligent controllers, works to maintain a stable temperature profile. This system must work alongside the gas control system to ensure the atmospheric conditions are optimal and consistent for every stage of the process—from heating up to holding at temperature and cooling down.
Integrated Safety Systems
Given the extremely high temperatures, high electrical currents, and use of pressurized gases, safety is the most important feature of a sintering furnace. Modern furnaces use a comprehensive PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) to automatically monitor and control water cooling, electrical systems, and the gas or vacuum environment, protecting both the equipment and personnel.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Complexities
While essential, creating a controlled atmosphere introduces significant challenges compared to sintering in open air.
Operational Complexity
Using specific gases increases the complexity of the entire operation. It requires specialized infrastructure for gas storage and supply, as well as systems for handling exhaust emissions.
Material-Specific Optimization
There is no one-size-fits-all atmosphere. The ideal gas composition, pressure, and flow rate must be carefully optimized for different materials to achieve the desired results, making process development more demanding.
Cost and Infrastructure
The equipment needed for atmosphere control—such as vacuum pumps, gas purifiers, and advanced control systems—adds significant cost and complexity to the furnace. The ongoing cost of high-purity gases also contributes to higher operational expenses.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of a furnace atmosphere is a critical decision based on the material being processed and the end goal of the application.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation and preserving material purity: An inert atmosphere like argon or nitrogen, or a high vacuum, is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible density for sensitive materials: A vacuum furnace provides the most effective environment by removing nearly all reactive and trapped gases.
- If your primary focus is altering the surface chemistry of a component: A carefully selected reactive atmosphere is required to drive the desired chemical changes during the sintering cycle.
Ultimately, controlling the furnace atmosphere is what transforms a simple heating process into a precise materials engineering tool.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Primary Function | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Gas (N₂, Ar) | Protective Shield | Preventing oxidation, preserving material purity |
| Reactive Gas | Active Participant | Modifying surface chemistry, binder removal |
| Vacuum | Ultimate Protection | High-density sintering, sensitive materials (e.g., medical implants) |
Ready to Engineer Your Material's Properties with Precision?
Choosing the right sintering furnace atmosphere is critical to achieving your material's desired density, purity, and performance. At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced laboratory furnaces and consumables, providing tailored solutions for your specific sintering needs—whether you require inert gas, vacuum, or reactive atmosphere control.
Let our experts help you optimize your process for superior results. Contact us today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK can enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab
- What is the role of an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace in Cu-Mo sintering? Achieve High-Purity Densification
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained



















