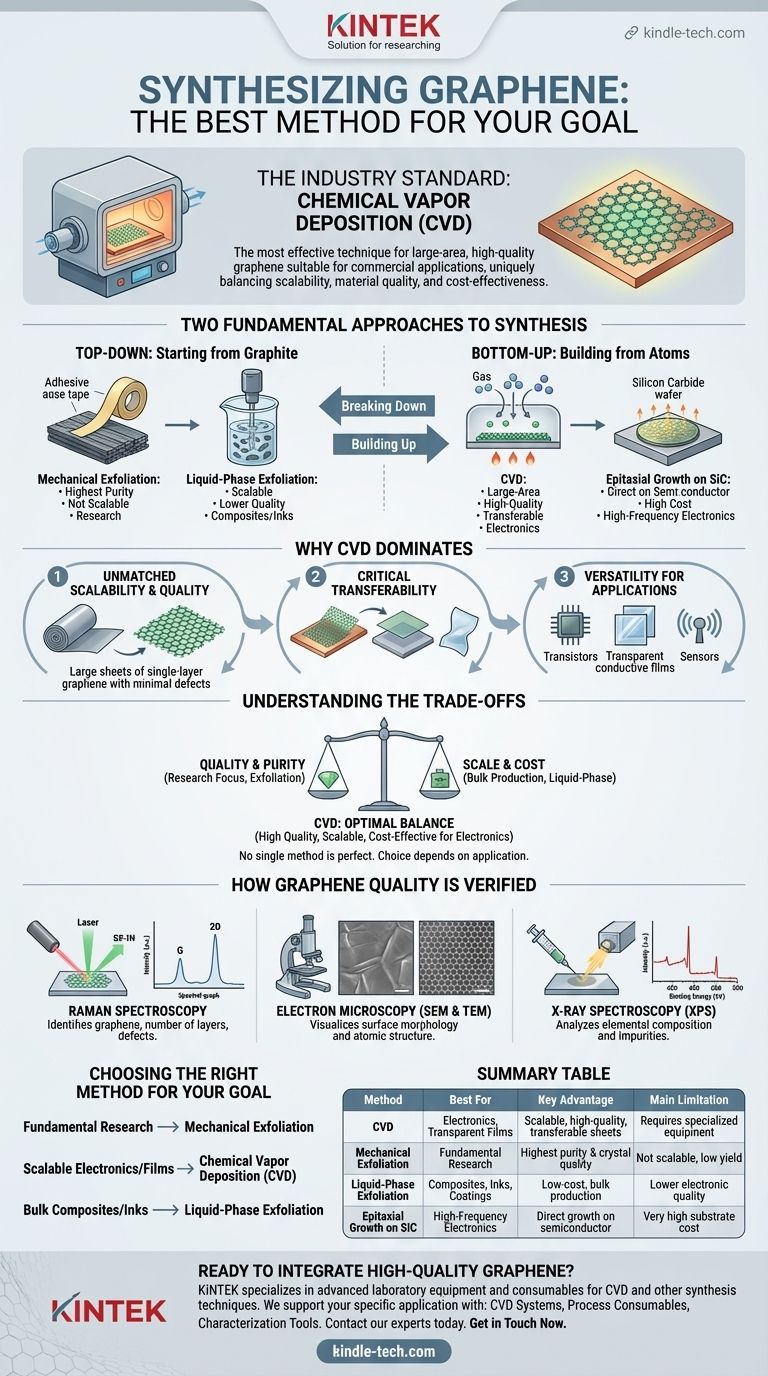
While several methods exist, the most effective and widely adopted technique for producing large-area, high-quality graphene suitable for commercial applications is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). It has become the industry standard because it uniquely balances scalability, material quality, and cost-effectiveness, particularly for applications in electronics.
The "best" method for synthesizing graphene is not a single answer but a choice dictated by your end goal. While mechanical exfoliation produces the highest purity samples for research, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) offers the best combination of quality, scale, and transferability needed for most technological and industrial advancements.

The Two Fundamental Approaches to Graphene Synthesis
To understand why CVD is preferred, it's helpful to categorize synthesis methods into two fundamental strategies: building up from atoms or breaking down from a larger source.
H3: Top-Down Methods: Starting from Graphite
Top-down methods begin with graphite—essentially a thick stack of graphene layers—and separate those layers.
Mechanical exfoliation is the original method, famously using adhesive tape to peel away layers until a single atomic sheet remains. It produces exceptionally high-quality, pristine graphene flakes, but it is not scalable and is primarily used for fundamental scientific research.
Liquid-phase exfoliation is a more scalable top-down approach where graphite is dispersed in a liquid and broken apart using energy, often from sonication. This can produce large quantities of graphene flakes for use in composites, coatings, and inks, but the electrical quality is typically lower than other methods.
H3: Bottom-Up Methods: Building from Atoms
Bottom-up methods construct the graphene lattice atom by atom on a substrate. This provides precise control over the final structure.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the leading bottom-up technique. It involves growing graphene directly onto a catalytic metal substrate from a carbon-containing gas.
Epitaxial growth on silicon carbide (SiC) is another method, where heating a SiC wafer causes silicon to sublimate, leaving behind a layer of graphene. While it produces high-quality graphene directly on a semiconducting wafer, the high cost of SiC substrates limits its widespread use.
Why Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) Dominates
CVD has emerged as the most promising synthesis route because it solves the critical challenges of scale and quality simultaneously.
H3: The CVD Process Explained
The CVD process for graphene is conceptually straightforward. A metal foil, typically copper (Cu), is heated in a vacuum furnace. A carbon-containing gas, such as methane (CH4), is introduced. At high temperatures, the methane decomposes, and carbon atoms arrange themselves into the hexagonal graphene lattice on the surface of the copper foil.
H3: Unmatched Scalability and Quality
The primary advantage of CVD is its ability to produce large, continuous sheets of single-layer graphene. This is a prerequisite for creating electronic devices like transistors, transparent conductive films, and sensors. The process can be scaled to produce graphene films measured in square meters.
H3: Critical Transferability and Versatility
A key feature of CVD is that the graphene film can be easily transferred from its growth substrate (the copper foil) onto virtually any other material, such as silicon wafers, glass, or flexible plastics. This versatility is what makes CVD-grown graphene ideal for integration into a vast range of technological applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single method is perfect for every scenario. Choosing the right one requires understanding the inherent compromises between quality, cost, and scale.
H3: Quality vs. Cost
Mechanical exfoliation offers the highest possible crystal quality but is prohibitively expensive and slow for any commercial volume. Liquid-phase exfoliation is the cheapest for bulk production, but the material quality is insufficient for high-performance electronics. CVD strikes a crucial balance, offering high quality at a cost-effective price point for large areas.
H3: Scale vs. Purity
While CVD produces excellent, large-area films, the process can introduce minor defects, grain boundaries, or impurities not found in the pristine flakes from mechanical exfoliation. For most applications, this trade-off is acceptable, but for fundamental physics research, exfoliated flakes are often still preferred.
H3: Process Complexity
CVD requires specialized equipment, including high-temperature furnaces, vacuum systems, and controlled gas flow. Furthermore, the post-growth transfer process adds steps and requires careful handling to avoid damaging the delicate atomic-scale film.
How Graphene Quality is Verified
Regardless of the synthesis method, the resulting material must be analyzed to confirm its properties. Professionals rely on a standard set of characterization techniques.
H3: Raman Spectroscopy
This is the most important and widely used technique. It can definitively identify graphene, determine the number of layers (single, double, or multi-layer), and assess its structural quality by detecting defects.
H3: Electron Microscopy (SEM & TEM)
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) is used to examine the surface and topography of the graphene film, revealing wrinkles, folds, or tears. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) provides high-resolution images of the atomic lattice itself, confirming the hexagonal structure.
H3: X-ray Spectroscopy (XPS)
X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy characterizes the chemical state and elemental composition of the sample, helping to identify any unwanted impurities or functional groups attached to the graphene sheet.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Goal
Your application dictates the optimal synthesis method.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research on pristine material: Mechanical exfoliation remains the gold standard for producing the highest-quality, defect-free samples for scientific discovery.
- If your primary focus is scalable electronics or transparent conductors: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the only viable method for creating the large, high-quality, and transferable films required.
- If your primary focus is bulk production for composites, paints, or inks: Liquid-phase exfoliation offers the best route for producing large volumes of graphene flakes where pristine electronic quality is not the main concern.
Understanding these critical trade-offs empowers you to select the synthesis method that directly aligns with your technical and commercial objectives.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Advantage | Main Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Electronics, Transparent Films | Scalable, high-quality, transferable sheets | Requires specialized equipment |
| Mechanical Exfoliation | Fundamental Research | Highest purity & crystal quality | Not scalable, low yield |
| Liquid-Phase Exfoliation | Composites, Inks, Coatings | Low-cost, bulk production | Lower electronic quality |
| Epitaxial Growth on SiC | High-Frequency Electronics | Direct growth on semiconductor | Very high substrate cost |
Ready to Integrate High-Quality Graphene into Your Research or Product?
Choosing the right synthesis method is just the first step. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced laboratory equipment and consumables needed to successfully implement these techniques, particularly Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
We understand that your success depends on reliable, precise tools. Whether you are developing next-generation electronics, advanced composites, or breakthrough materials, our expertise and products are designed to help you achieve superior results.
Let's discuss how we can support your specific application:
- CVD Systems: Scale your graphene production with robust and controllable systems.
- Process Consumables: Ensure consistent quality with high-purity metal foils and gases.
- Characterization Tools: Verify your graphene's properties with recommended analytical equipment.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your lab's graphene synthesis needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth



















