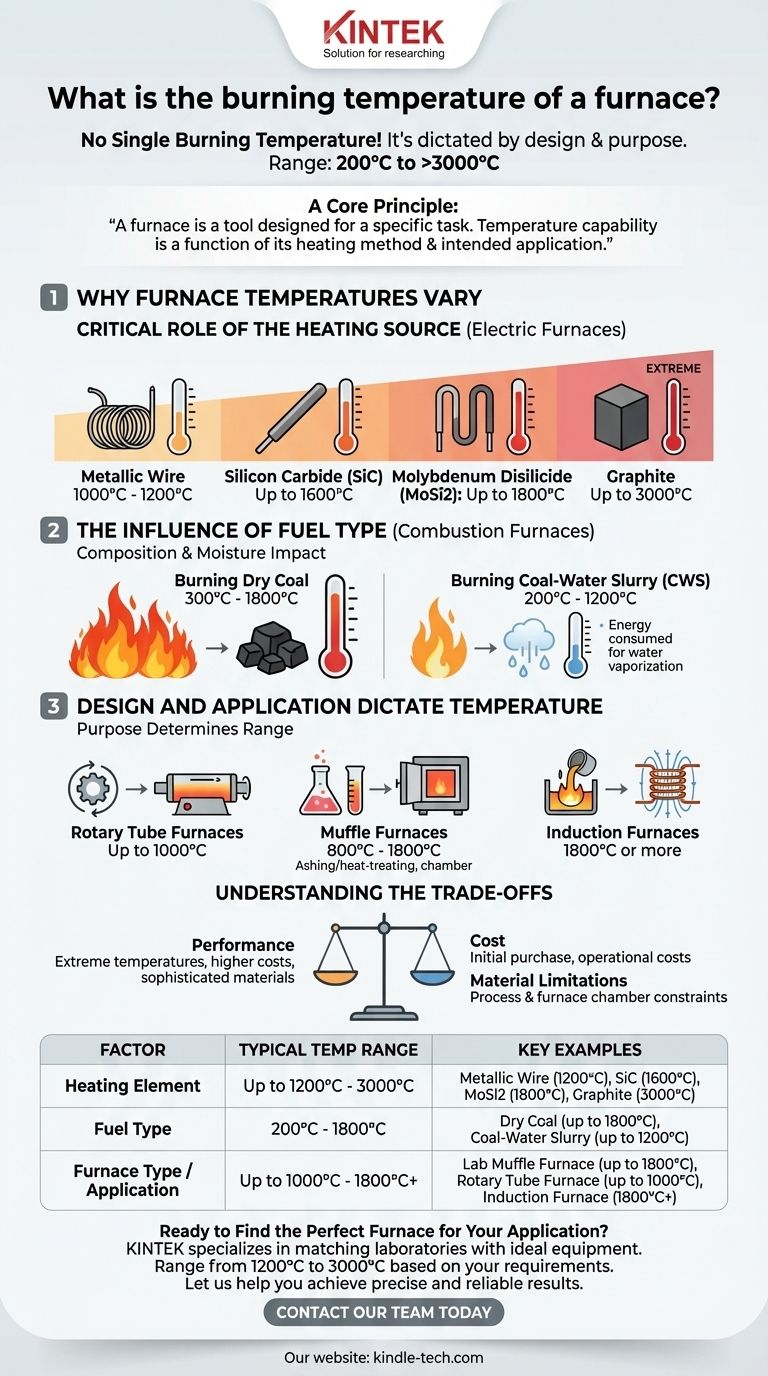
To be direct, there is no single burning temperature for a furnace. The operating temperature of a furnace is dictated entirely by its design and purpose, with a vast operational range from as low as 200°C for some processes to over 3000°C for highly specialized industrial applications.
The core principle to understand is that a furnace is a tool designed for a specific task. Its temperature capability is a direct function of its heating method (fuel or electric elements) and its intended application, whether that's melting steel, heat-treating ceramics, or conducting laboratory research.

Why Furnace Temperatures Vary So Widely
The term "furnace" covers an enormous category of equipment. The temperature one can achieve is not an arbitrary number but a result of deliberate engineering choices driven by the specific process it needs to perform.
The Critical Role of the Heating Source
For electric furnaces, the material used in the heating element is the primary limiting factor for its maximum temperature. Different materials have vastly different capabilities.
- Metallic wire elements are common and typically achieve maximum temperatures between 1000°C and 1200°C.
- Silicon carbide (SiC) elements allow for significantly higher temperatures, reaching up to 1600°C.
- Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) elements are used in high-performance laboratory and production furnaces, achieving up to 1800°C.
- Graphite elements, used in specialized vacuum or inert-atmosphere furnaces, can reach extreme temperatures of 3000°C.
The Influence of Fuel Type
In combustion furnaces, the fuel being burned has a profound impact on the achievable temperature. The composition and moisture content of the fuel are critical variables.
For example, burning dry coal can produce intense heat, with temperatures in different areas of the furnace ranging from 300°C to 1800°C.
In contrast, burning a coal-water slurry (CWS) fuel results in a lower temperature range, typically from 200°C to 1200°C, because energy is consumed to vaporize the water.
Design and Application Dictate Temperature
The furnace's construction and ultimate purpose determine its required temperature range. A unit designed for one task may be completely unsuitable for another.
- Rotary tube furnaces used for continuous processing might operate up to 1000°C.
- Muffle furnaces, common in laboratories for ashing or heat-treating, typically operate between 800°C and 1800°C, depending on their heating elements.
- Induction furnaces, which heat conductive materials like metal directly, can efficiently reach temperatures of 1800°C or more.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting or designing a furnace is a balance of performance, cost, and material science. Higher temperatures always come with engineering challenges.
Performance vs. Cost
Achieving extreme temperatures is expensive. Furnaces using advanced elements like molybdenum disilicide or graphite require more sophisticated power supplies, insulation, and structural materials, increasing both the initial purchase price and operational costs.
Material Limitations
The maximum temperature is often limited not by the heat source, but by the material being processed or the furnace chamber itself. The process dictates the required temperature, and the furnace must be able to sustain it without damaging the product or itself.
Matching the Furnace to the Task
To determine the temperature of a furnace, you must first define its purpose.
- If your primary focus is general lab work or basic heat-treating: A furnace with metallic wire elements operating up to 1200°C is often the standard.
- If your primary focus is melting most metals or working with advanced ceramics: A high-temperature furnace with silicon carbide or molybdenum disilicide elements (1600°C to 1800°C) is necessary.
- If your primary focus is specialized industrial research or processing unique materials: An advanced system, such as an induction or graphite tube furnace (1800°C to 3000°C), would be required.
Ultimately, understanding that a furnace's temperature is defined by its function is the key to asking the right questions for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Typical Temperature Range | Key Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Element | Up to 1200°C - 3000°C | Metallic Wire (1200°C), SiC (1600°C), MoSi2 (1800°C), Graphite (3000°C) |
| Fuel Type | 200°C - 1800°C | Dry Coal (up to 1800°C), Coal-Water Slurry (up to 1200°C) |
| Furnace Type / Application | Up to 1000°C - 1800°C+ | Lab Muffle Furnace (up to 1800°C), Rotary Tube Furnace (up to 1000°C), Induction Furnace (1800°C+) |
Ready to Find the Perfect Furnace for Your Application?
This guide shows that the 'right' furnace temperature is entirely dependent on your specific process, whether it's basic heat-treating, advanced ceramics work, or specialized research. KINTEK specializes in matching laboratories with the ideal equipment.
We provide a full range of lab furnaces and consumables, from standard 1200°C models to high-temperature systems reaching 3000°C. Our experts will help you select a furnace based on your exact temperature requirements, materials, and budget.
Let us help you achieve precise and reliable results. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and discover the KINTEK difference in lab performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the calibration frequency of a muffle furnace? A Risk-Based Guide to Ensure Precision
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Precision Heating
- What is melt loss? The Ultimate Guide to Reducing Metal Loss in High-Temp Processing
- What is the importance of muffle furnace in laboratory? Achieve Precise, Contaminant-Free Heating
- What is the debinding process? A Guide to Critical Binder Removal for MIM & 3D Printing



















