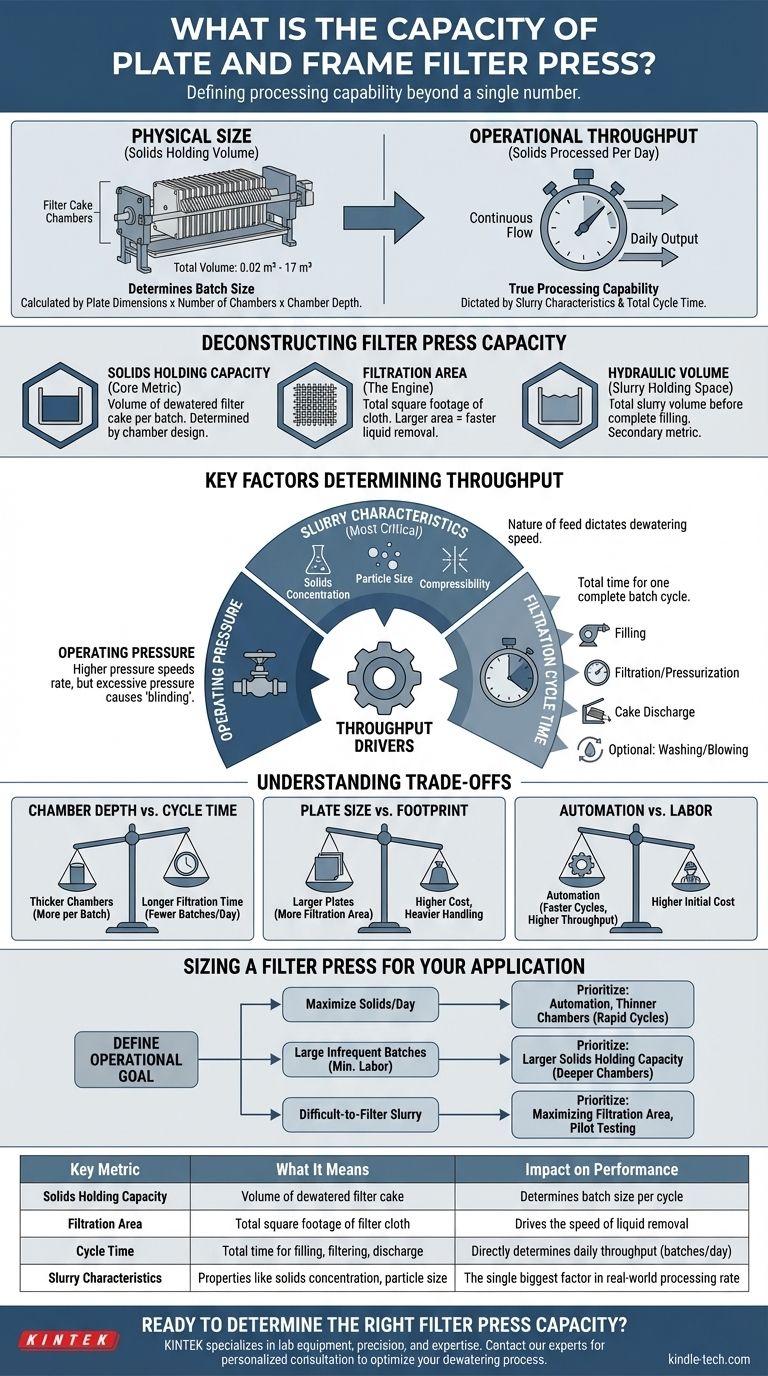
To define the capacity of a plate and frame filter press, you must look beyond a single number. Its capacity is fundamentally determined by its solids holding volume, which can range from less than 1 cubic foot (0.02 m³) to over 600 cubic feet (17 m³). However, the true processing capability, or throughput, is dictated entirely by the characteristics of the slurry being filtered and the total cycle time required for each batch.
The term "capacity" is misleading because it implies a fixed rate. It's more accurate to think of a filter press in two parts: its physical size (solids holding volume) and its operational throughput (solids processed per day), which are two very different metrics.
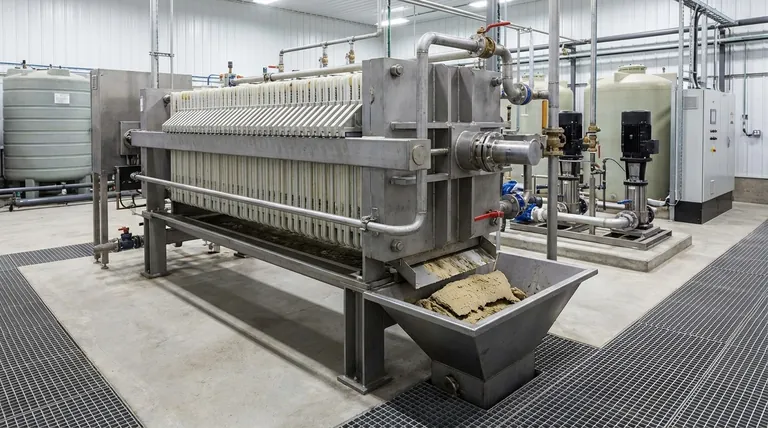

Deconstructing Filter Press "Capacity"
A filter press's specifications sheet lists its physical dimensions. Understanding these is the first step, but they don't tell the whole story of its real-world performance.
Solids Holding Capacity (The Core Metric)
This is the most common measure of a press's size. It refers to the total volume of dewatered "filter cake" the press can hold when all chambers between the plates are full.
This volume is a simple calculation based on three design factors:
- Plate Dimensions: The length and width of the plates.
- Number of Chambers: The count of empty spaces created between plates.
- Chamber Depth (Cake Thickness): The thickness of the space between two plates, which determines the final thickness of your filter cake.
Filtration Area (The Engine of a Press)
This is the total square footage of filter cloth surface available for dewatering. A larger filtration area allows for a faster liquid removal rate.
Two presses with the same solids holding capacity can have different filtration areas. A press with more, thinner chambers will have a larger filtration area than a press with fewer, thicker chambers, and will generally filter faster.
Hydraulic Volume (Slurry Holding Space)
This refers to the total volume of slurry the press can contain before it is completely filled with solids. It's a useful number for process calculations but is secondary to the solids holding capacity for sizing the equipment.
Key Factors That Determine Real-World Throughput
The actual amount of material a filter press can process in a day (its throughput) is rarely determined by its physical size alone. Operational factors have a far greater impact.
Slurry Characteristics
This is the most critical variable. The nature of your feed material dictates how quickly and effectively it can be dewatered.
Key properties include solids concentration (the percentage of solids in the slurry), particle size and shape, and the compressibility of the solids. A granular slurry with 30% solids will dewater much faster than a fine, slimy slurry with 5% solids.
Filtration Cycle Time
A filter press operates in batches, and the total time for one complete cycle determines your daily throughput. A shorter cycle means more batches per day and higher effective capacity.
The cycle consists of several stages:
- Filling: Pumping slurry into the press.
- Filtration/Pressurization: Pumping continues as pressure builds and liquid is forced out.
- Cake Discharge: Opening the press and removing the solid filter cake.
Optional steps like cake washing or air blowing can add significant time to the cycle.
Operating Pressure
Higher feed pressure can speed up the filtration rate, but only up to a point. For some slurries, excessive pressure can compact the solids against the filter cloth, blocking liquid from passing through—a phenomenon known as "blinding."
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a filter press involves balancing competing priorities. An increase in one performance metric often comes at the expense of another.
Chamber Depth vs. Cycle Time
A press with thicker chambers holds more solids per batch, reducing the number of cycles you need to run. However, it takes significantly longer for liquid to pass through a thicker cake, increasing the filtration time for each batch.
Conversely, a press with thinner chambers dewaters very quickly, allowing for more cycles per day, but requires more frequent cake discharge, which involves more labor or automation.
Plate Size vs. Footprint
Using larger plates (e.g., 1500mm vs. 1000mm) provides more filtration area for a given machine footprint. However, larger plates are more expensive, heavier, and can be more difficult to handle during maintenance.
Automation vs. Labor
A manual press requires an operator to physically move each plate to discharge the filter cake, which can be time-consuming. An automatic press uses a mechanical shifter to perform this task in minutes.
While automation dramatically reduces cycle time and increases daily throughput, it comes with a significantly higher initial capital cost.
Sizing a Filter Press for Your Application
To determine the right capacity, you must first define your primary operational goal. Pilot-scale testing on your specific slurry is almost always necessary to gather the data needed for accurate sizing.
- If your primary focus is maximizing solids processed per day: Prioritize features that minimize cycle time, such as automation and thinner cake chambers, to achieve rapid, frequent batches.
- If your primary focus is handling large, infrequent batches with minimal labor: A press with a larger solids holding capacity (deeper chambers) is more suitable, even if the individual cycle time is longer.
- If you are dealing with a difficult-to-filter slurry: Focus on maximizing the filtration area and conduct pilot testing to determine realistic cycle times before committing to a full-scale machine.
Ultimately, selecting the right filter press capacity comes from matching the equipment's design to the unique properties of your slurry and your specific operational goals.
Summary Table:
| Key Metric | What It Means | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Solids Holding Capacity | Volume of dewatered filter cake the press can hold. | Determines batch size per cycle. |
| Filtration Area | Total square footage of filter cloth for dewatering. | Drives the speed of liquid removal. |
| Cycle Time | Total time for filling, filtering, and cake discharge. | Directly determines daily throughput (batches/day). |
| Slurry Characteristics | Properties like solids concentration and particle size. | The single biggest factor in real-world processing rate. |
Ready to determine the right filter press capacity for your specific slurry and operational goals?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision and expertise. Our team can help you analyze your slurry characteristics and process requirements to select a filter press that delivers the exact throughput and efficiency you need.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and let us help you optimize your dewatering process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Hydraulic Diaphragm Lab Filter Press for Laboratory Filtration
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy



















