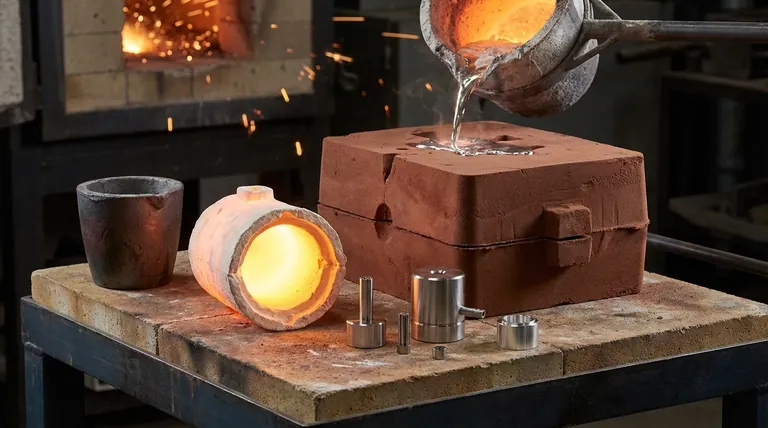
In metal casting, the cavity you're describing is known as a mold, and the empty space itself is the mold cavity. This engineered void is made from refractory materials, which are specialized non-metallic substances chosen specifically for their ability to withstand extreme heat and chemical reaction when in contact with molten metal.
The core challenge of casting is to accurately shape and hold molten metal as it solidifies. The solution is a mold, a heat-resistant cavity whose material and design are critically selected based on the metal being poured, the required precision, and the intended production volume.

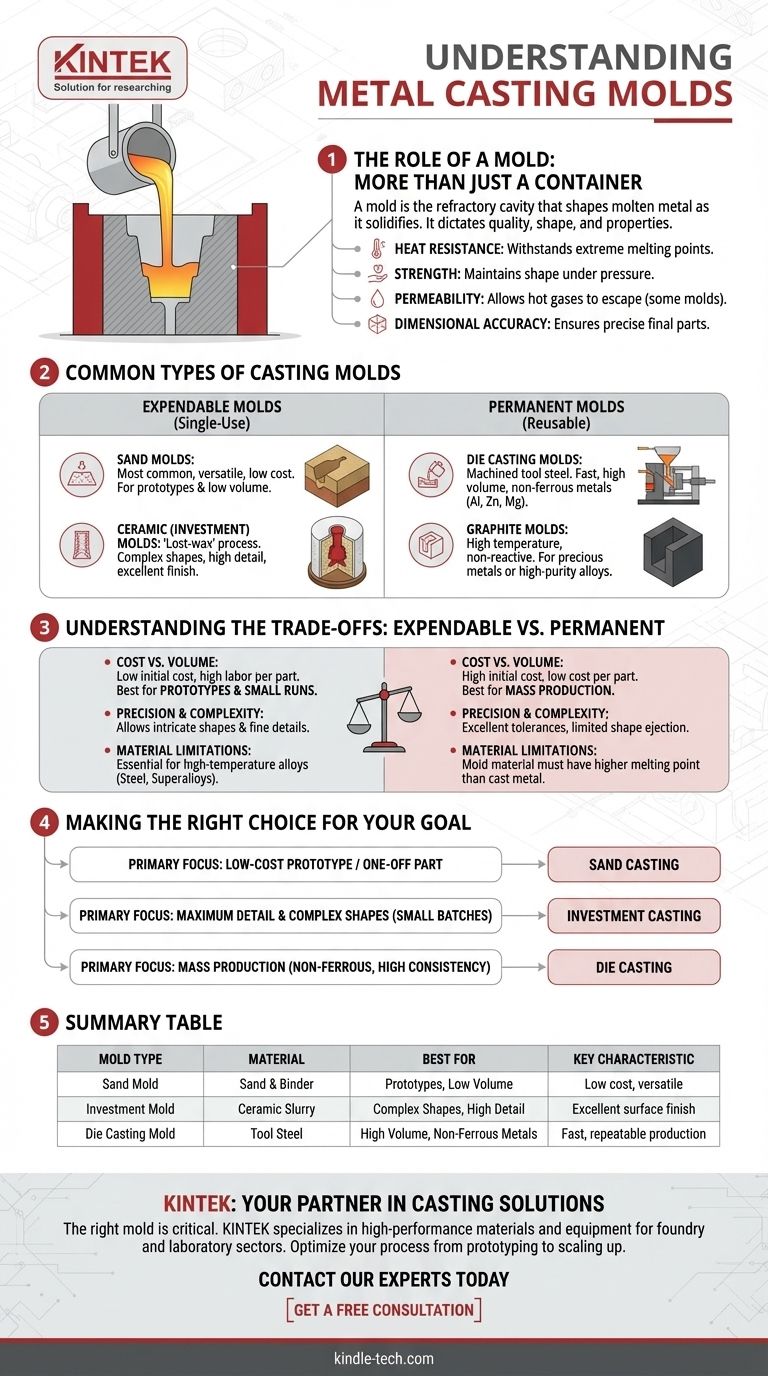
The Role of a Mold: More Than Just a Container
A mold is the heart of the casting process. Its design and material dictate the quality, shape, and properties of the final metal part.
What Makes a Material "Refractory"?
A refractory material is defined by its high-temperature performance. Key characteristics include a very high melting point and thermal stability, ensuring it does not break down or deform when filled with liquid metal.
These materials are also chosen for chemical inertness. They must resist reacting with the molten alloy, which would otherwise contaminate the metal and degrade the mold surface.
Essential Properties of a Mold
Beyond heat resistance, a good mold must possess several key properties:
- Strength: It must be strong enough to withstand the pressure of the liquid metal and maintain its shape during solidification.
- Permeability: For some mold types, like sand casting, the material must be permeable enough to allow hot gases and steam to escape, preventing defects in the casting.
- Dimensional Accuracy: The mold cavity must be made with precision to ensure the final part meets its required dimensions and tolerances.
Common Types of Casting Molds
Molds are broadly categorized into two families: expendable (single-use) and permanent (reusable). The choice between them is a fundamental decision in manufacturing.
Expendable Molds
These molds are destroyed in the process of removing the cast part. They are ideal for complex shapes and low-to-medium production volumes.
- Sand Molds: The most common type, made from a mixture of fine sand and a bonding agent (like clay or a chemical binder). Sand casting is versatile and inexpensive.
- Ceramic (Investment) Molds: Used in investment casting, or "lost-wax casting." A wax pattern is coated in a ceramic slurry, which is then fired to create a hard, highly detailed shell. This method provides excellent surface finish and accuracy.
Permanent Molds
These molds are machined from durable materials, typically metal, and are used for thousands of casting cycles. They are suited for high-volume production.
- Die Casting Molds: Machined from high-grade tool steel, these are used for casting non-ferrous metals like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium at high pressure. This process is extremely fast and repeatable.
- Graphite Molds: Graphite can withstand very high temperatures and provides a non-reactive surface, making it useful for casting certain precious metals or high-purity alloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Expendable vs. Permanent
Choosing the right mold type involves balancing cost, quality, and volume. There is no single "best" option; the optimal choice is always specific to the application.
Cost vs. Production Volume
An expendable sand mold is cheap to create, but the labor required for each casting is high. This makes it ideal for prototypes or small production runs.
A permanent steel die is extremely expensive to design and manufacture, but the automated process results in a very low cost per part. This is only economical for mass production.
Precision and Geometric Complexity
Investment casting (an expendable method) allows for extremely intricate shapes and fine details that would be impossible to machine from a permanent mold.
Die casting (a permanent method) offers excellent dimensional tolerances and smooth surfaces but is limited to shapes that can be easily ejected from the steel die.
Material Limitations
The mold material must have a significantly higher melting point than the metal being cast. You cannot use a steel permanent mold to cast steel, as the mold would melt.
Expendable sand and ceramic molds are essential for casting high-temperature alloys like steel, stainless steel, and nickel-based superalloys.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal mold depends entirely on your project's specific priorities of cost, detail, and volume.
- If your primary focus is a low-cost prototype or a one-off part: Sand casting is the most accessible and cost-effective method.
- If your primary focus is maximum detail and complex shapes for small batches: Investment casting (lost-wax) provides exceptional accuracy and design freedom.
- If your primary focus is mass production of non-ferrous parts with high consistency: Die casting offers unmatched speed and a low per-unit cost despite the high initial investment.
Understanding the function and material of the mold is the first step toward mastering the casting process.
Summary Table:
| Mold Type | Material | Best For | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sand Mold | Sand & Binder | Prototypes, Low Volume | Low cost, versatile |
| Investment Mold | Ceramic Slurry | Complex Shapes, High Detail | Excellent surface finish |
| Die Casting Mold | Tool Steel | High Volume, Non-Ferrous Metals | Fast, repeatable production |
Ready to choose the right mold for your metal casting project?
The right mold is critical to achieving the quality, precision, and cost-efficiency you need. KINTEK specializes in supplying high-performance materials and equipment for the foundry and laboratory sectors. Whether you are prototyping with sand casting or scaling up with die casting, our expertise can help you optimize your process.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific metal and production requirements. We'll help you select the best solution to ensure your castings are a success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- XRF & KBR plastic ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What functions do high-purity graphite molds serve for IZO targets? Ensure Density and Prevent Sintering Cracks
- Why are high-strength graphite molds essential for vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Your Diamond/Copper Composites
- What technical characteristics are required for specialty pressure molds used in the compaction of Li10GeP2S12? Expert Tips
- How does a stainless steel pressure die ensure the quality of the electrolyte layer? Unlock Precision Battery Assembly
- Why are custom pressure molds used during the hot pressing process for solid polymer electrolytes?



















