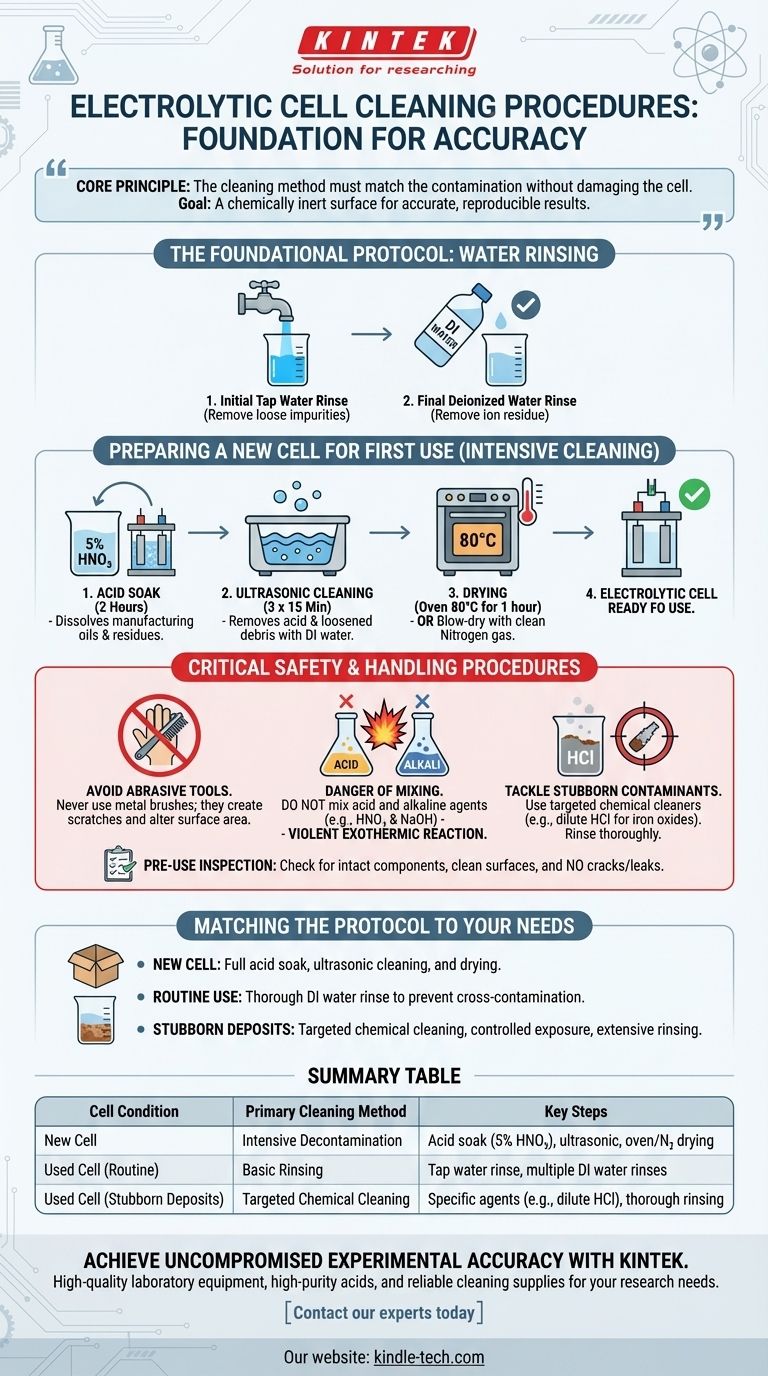
Properly cleaning an electrolytic cell involves a multi-step process tailored to its condition. For a new cell, the procedure is intensive, typically requiring an acid soak to remove manufacturing residues, followed by ultrasonic cleaning and thorough rinsing. For a cell already in use, cleaning focuses on removing experimental byproducts, starting with water rinses and using targeted chemical agents only when necessary.
The core principle is that the cleaning method must match the type of contamination without damaging the cell. The ultimate goal is not just a visually clean cell, but a chemically inert surface that ensures the accuracy and reproducibility of your experimental results.
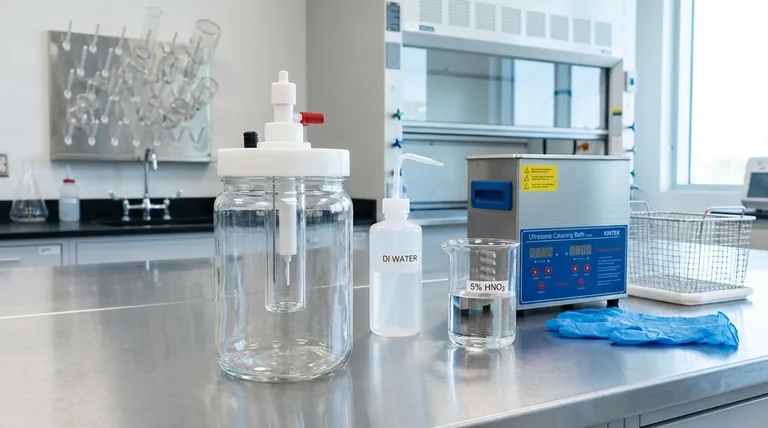

The Foundational Protocol: Water Rinsing
This two-step rinsing process is the starting point for cleaning any electrolytic cell, whether it is new or has been used.
Initial Tap Water Rinse
First, rinse all components of the cell with standard tap water. This initial step is effective at removing loose surface dust and other large, non-adhering impurities.
Final Deionized Water Rinse
After the tap water rinse, wash the cell multiple times with deionized (DI) or distilled water. This is a critical step, as it removes the ions present in tap water that could otherwise remain as residue and interfere with subsequent electrochemical reactions.
Preparing a New Cell for First Use
A brand-new cell requires a more aggressive cleaning regimen to ensure all contaminants from the manufacturing process are completely removed.
Why a Deeper Clean is Necessary
Manufacturing processes can leave behind a thin film of oils, greases, and other residues. If not removed, these contaminants will interfere with your experiment, leading to inaccurate data and poor reproducibility.
The Acid Soak Procedure
To remove these stubborn organic and inorganic residues, soak the cell body in a 5% nitric acid (HNO₃) solution for approximately two hours. This acid bath effectively breaks down and dissolves the contaminants.
Ultrasonic Cleaning and Drying
Following the acid soak, perform an ultrasonic cleaning with deionized water. This should be done three times, for 15 minutes each, to ensure all traces of the acid and loosened debris are removed.
Finally, dry the cell completely. You can place it in an oven at 80℃ for one hour or, for a faster method, blow-dry the components thoroughly with clean nitrogen gas.
Critical Safety and Handling Procedures
Improper cleaning techniques can damage your equipment and pose a significant safety risk. Adhering to these guidelines is non-negotiable.
Avoid Abrasive Tools
Never use metal brushes or other hard, abrasive tools to scrub the cell or its electrodes. These can create microscopic scratches on the surfaces, which alters the surface area and can change the electrochemical behavior of the system, compromising your results.
The Danger of Mixing Cleaning Agents
It is strictly forbidden to mix acid and alkaline cleaning agents, such as nitric acid (HNO₃) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH). Combining these chemicals can trigger a violent and dangerous exothermic reaction.
Tackle Stubborn Contaminants
If a cell used in a previous experiment has stubborn deposits like metal oxides, a targeted chemical cleaning may be necessary. For example, dilute hydrochloric acid can effectively remove iron oxides. Always choose a chemical that targets the specific deposit and rinse thoroughly with deionized water afterward.
The Pre-Use Inspection
Before every use, perform a quick visual inspection. Ensure all components are intact, the electrode surfaces appear clean and undamaged, and the cell body is free from any cracks or leaks.
Matching the Protocol to Your Needs
The right cleaning procedure depends entirely on the state of your cell and the demands of your experiment.
- If you are preparing a brand-new cell: Commit to the full acid soak and ultrasonic cleaning process to establish a pristine, uncontaminated surface for your first experiment.
- If you are cleaning between routine experiments: A thorough deionized water rinse is often sufficient to prevent cross-contamination, assuming no stubborn products were formed.
- If you are dealing with visible deposits or oxides: Use a carefully selected chemical cleaner specific to the residue, control the exposure time, and follow with extensive rinsing.
A meticulously cleaned cell is the foundation of reliable and reproducible electrochemical data.
Summary Table:
| Cell Condition | Primary Cleaning Method | Key Steps |
|---|---|---|
| New Cell | Intensive Decontamination | Acid soak (5% HNO₃), ultrasonic cleaning, oven/N₂ drying |
| Used Cell (Routine) | Basic Rinsing | Tap water rinse, followed by multiple DI water rinses |
| Used Cell (Stubborn Deposits) | Targeted Chemical Cleaning | Application of specific agents (e.g., dilute HCl for oxides), thorough rinsing |
Achieve Uncompromised Experimental Accuracy with KINTEK
Proper lab equipment maintenance is critical for reliable data. Whether you are setting up a new electrolytic cell or maintaining existing equipment, using the right tools and consumables is the first step to success.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables, including durable electrolytic cells, high-purity acids, and reliable cleaning supplies, all designed to meet the stringent demands of your research.
Let us support your laboratory's success. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solutions for your electrochemical and general lab needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
People Also Ask
- What is the proper way to handle a five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Ensure Accurate and Safe Electrochemical Experiments
- What are the proper storage procedures for the multifunctional electrolytic cell? Protect Your Investment and Ensure Data Accuracy
- What general precaution should be taken when handling the electrolytic cell? Ensure Safe and Accurate Lab Results
- How can contamination be avoided during experiments with the five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Master the 3-Pillar Protocol
- What are the standard components of the five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Master the Precision Instrument for Electrochemical Analysis



















