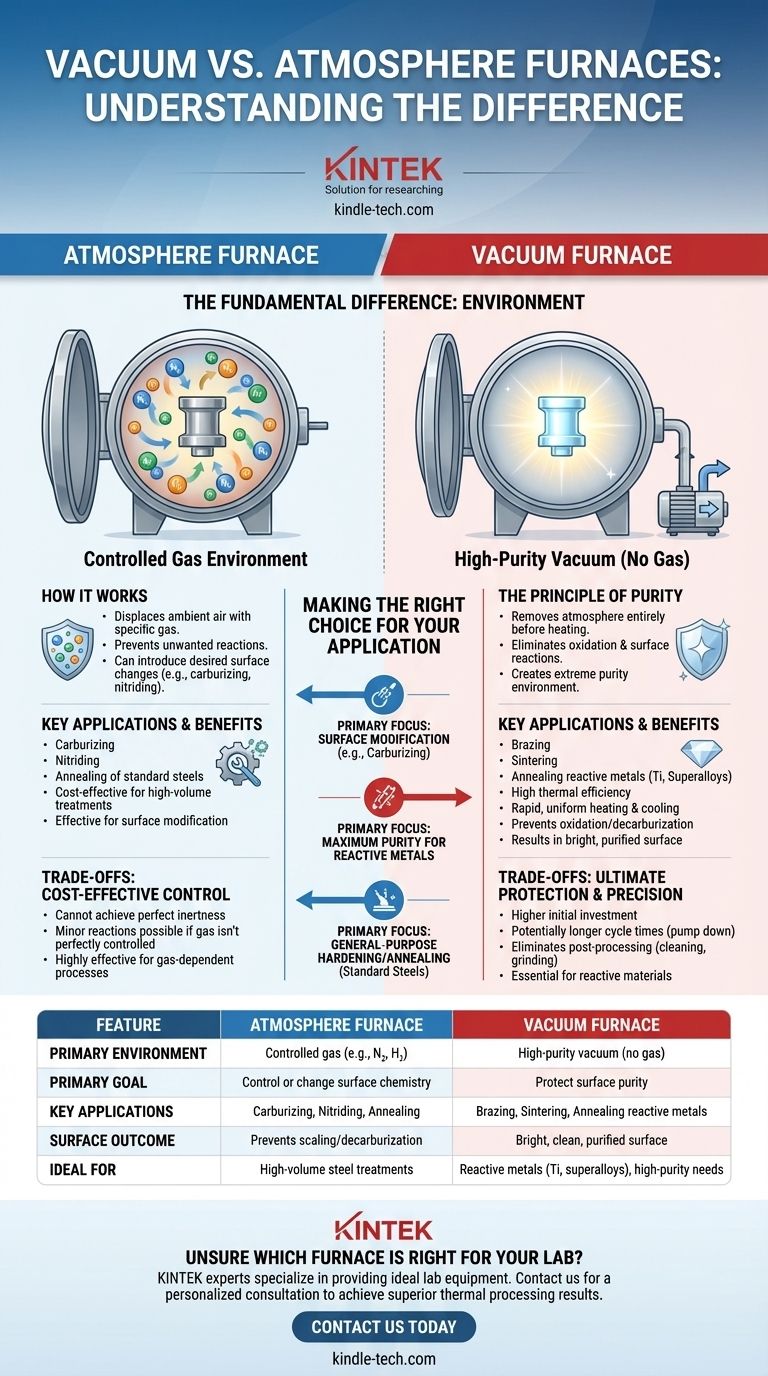
The fundamental difference between a vacuum furnace and an atmosphere furnace lies in the environment they create to heat a material. An atmosphere furnace uses a controlled gas to surround the part, while a vacuum furnace removes virtually all gases, creating a high-purity, non-reactive environment for processing.
The choice between these furnaces is a strategic decision about surface chemistry. Atmosphere furnaces are used to control or actively change a material's surface with gas, whereas vacuum furnaces are used to protect it by eliminating any potential for gas-based reactions.

How an Atmosphere Furnace Works
An atmosphere furnace is designed to displace the ambient air with a specific, engineered atmosphere. This prevents unwanted reactions and can even introduce desired ones.
The Role of Controlled Gas
The primary goal is to prevent the heated metal from reacting with oxygen and water vapor in the air, which causes scaling (oxidation) and decarburization (loss of carbon from the surface).
Gases like nitrogen, argon, hydrogen, and endothermic or exothermic gas mixtures are used. Each gas provides a different level of protection or reactivity for specific processes.
Common Applications
Atmosphere furnaces are workhorses for processes that require a specific gas-surface interaction. This includes carburizing, where carbon is intentionally added to a steel surface, and nitriding, where nitrogen is added to create a hard case.
The Vacuum Furnace Advantage
A vacuum furnace operates on the opposite principle: it removes the atmosphere entirely before heating begins. This creates an environment of extreme purity.
The Principle of Purity
By pumping out air and other molecules, the furnace eliminates the possibility of oxidation and other surface reactions. This is achieved at various levels, from low to ultra-high vacuum, depending on the material's sensitivity.
Key Benefits of a Vacuum
The vacuum environment provides several distinct advantages. It offers high thermal efficiency and allows for rapid, uniform heating and cooling.
Crucially, it prevents oxidation and decarburization entirely. This process also has a cleaning effect, removing contaminants and degassing the material, which results in a bright, purified surface straight from the furnace.
Unmatched Process Versatility
Vacuum furnaces are incredibly versatile, capable of performing nearly all heat treatment processes. This includes quenching, annealing, tempering, brazing, and sintering for a wide range of sensitive and high-performance materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right furnace technology requires understanding the balance between cost, complexity, and the desired final properties of your component.
Atmosphere Furnaces: Cost-Effective Control
For many high-volume steel heat treatments, atmosphere furnaces are highly effective and more economical. They excel at processes like carburizing that fundamentally rely on a specific gas to achieve their goal.
Their primary limitation is that they cannot achieve the perfect inertness of a vacuum. Minor surface reactions can still occur if the gas composition isn't perfectly controlled.
Vacuum Furnaces: Ultimate Protection and Precision
A vacuum furnace is the superior choice when absolute surface integrity is non-negotiable. It is essential for reactive materials like titanium, refractory metals, and certain superalloys that would be ruined by any exposure to oxygen at high temperatures.
The trade-off is typically a higher initial investment and potentially longer cycle times due to the need to pump down the chamber. However, this often eliminates the need for post-processing steps like cleaning or surface grinding, saving costs downstream.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision depends entirely on the material you are processing and the properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is surface modification like carburizing: An atmosphere furnace is the direct, industry-standard tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity for reactive metals: A vacuum furnace is the only technology that can guarantee a pristine, bright, and uncompromised surface.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose hardening or annealing of standard steels: An atmosphere furnace often provides the necessary protection in the most cost-effective manner.
Ultimately, understanding this core difference empowers you to select the precise tool for achieving your material's ideal properties.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Atmosphere Furnace | Vacuum Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Environment | Controlled gas (e.g., N₂, H₂) | High-purity vacuum (no gas) |
| Primary Goal | Control or change surface chemistry | Protect surface purity |
| Key Applications | Carburizing, Nitriding, Annealing | Brazing, Sintering, Annealing reactive metals |
| Surface Outcome | Prevents scaling/decarburization | Bright, clean, purified surface |
| Ideal For | High-volume steel treatments | Reactive metals (Ti, superalloys), high-purity needs |
Unsure which furnace is right for your lab's specific materials and processes? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the ideal lab equipment, including both vacuum and atmosphere furnaces, to meet your precise thermal processing needs.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation to enhance your lab's capabilities and achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- What is meant by inert atmosphere? A Guide to Preventing Oxidation & Ensuring Safety
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments
- What is the purpose of using an atmosphere-controlled heating furnace for Cu reduction? Achieve Active Catalytic States
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety



















