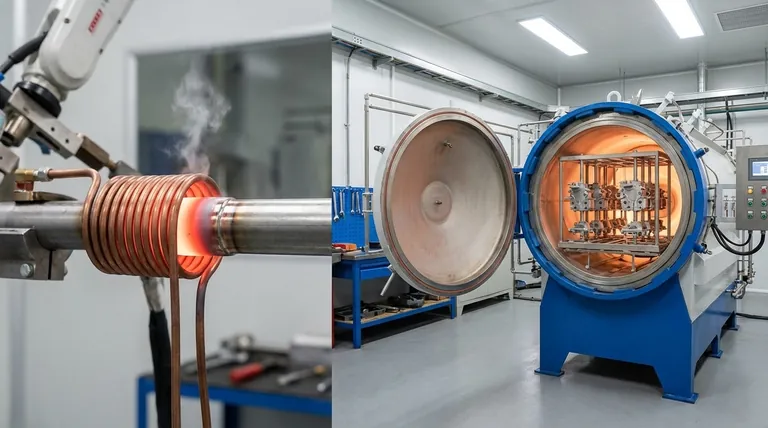
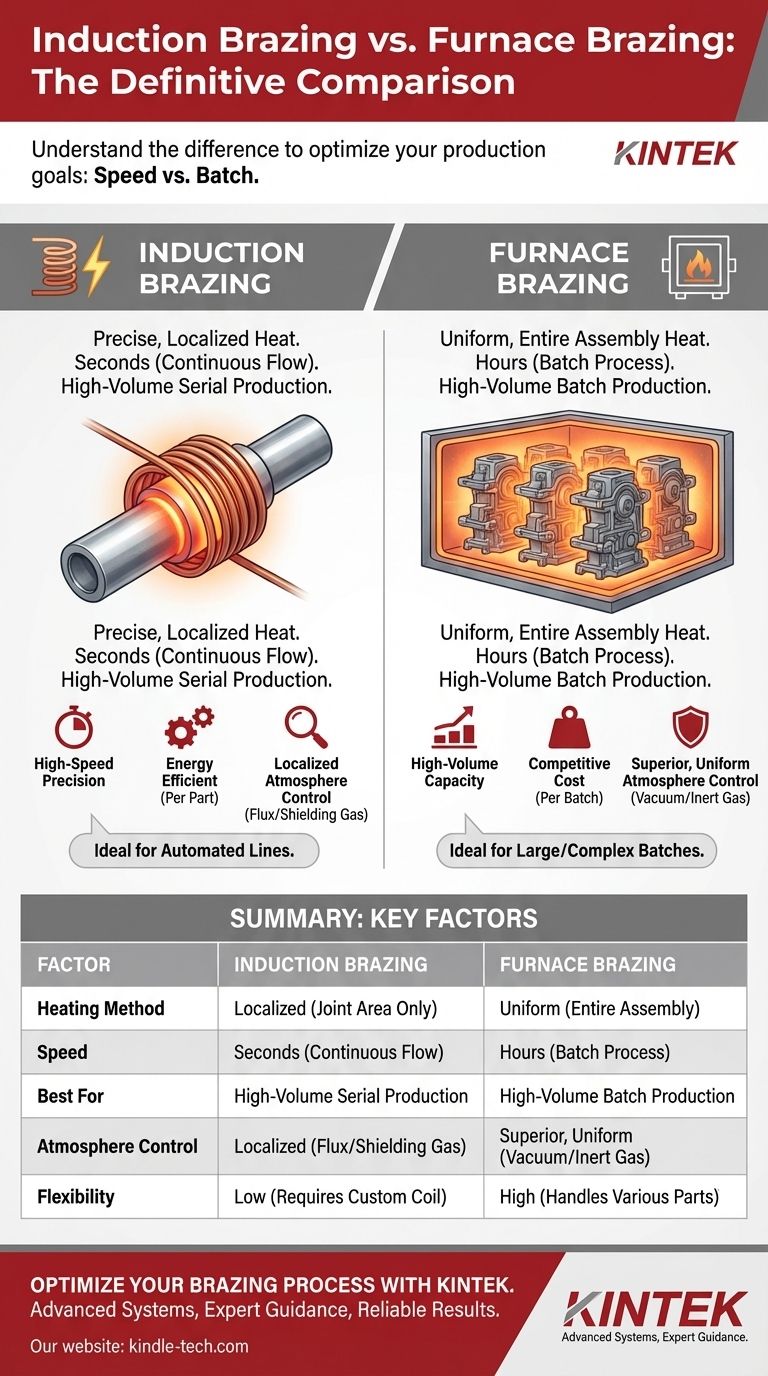
The primary difference between induction brazing and furnace brazing lies in the method of heating. Furnace brazing heats the entire assembly uniformly within a controlled chamber, while induction brazing uses a magnetic field to generate rapid, localized heat only at the joint area. This fundamental distinction drives every other difference in speed, cost, and application.
Your choice between these two methods is not about which is universally "better," but which aligns with your specific production goals. The decision hinges on a core trade-off: the batch-processing capability of a furnace versus the high-speed precision of induction.
The Fundamental Difference: How Heat is Applied
The heating mechanism is the defining characteristic that separates these two powerful brazing processes. Understanding this is the key to choosing the correct one for your needs.
Furnace Brazing: Soaking the Entire Assembly
In furnace brazing, parts with pre-placed filler metal are loaded into a furnace. The entire chamber, along with all the parts inside it, is slowly and uniformly brought up to the brazing temperature.
This process is most often performed in a controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation. Methods like vacuum brazing, where air is pumped out, or gas-shielded brazing ensure a clean environment, resulting in strong, high-quality joints across the entire batch.
Induction Brazing: Precise, Localized Heat
Induction brazing uses a high-frequency alternating current passed through a copper coil. This creates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around the joint area.
This magnetic field induces electrical currents (eddy currents) directly within the metal parts, causing them to heat up extremely quickly due to their own electrical resistance. The heat is generated internally and is concentrated only where it's needed, leaving the rest of the assembly cool.
Comparing Key Process Characteristics
The different heating methods lead to vastly different outcomes in terms of speed, quality control, volume, and flexibility.
Heating Speed and Cycle Time
Furnace brazing is a batch process with a long cycle time. Heating an entire furnace and its contents can take hours. However, it can process thousands of joints simultaneously, making the time per joint very low.
Induction brazing is a continuous-flow process with an extremely short cycle time. Heating is often completed in seconds. This makes it ideal for integrating into an automated production line where parts are processed one by one.
Joint Quality and Atmosphere Control
Furnace brazing offers superior, uniform atmospheric control. A vacuum or inert gas atmosphere protects the entire part from oxidation during the long heating cycle, which is critical for sensitive materials and complex geometries.
Induction brazing provides localized atmosphere control. While it can be performed in a special chamber, it's often done in open air using a flux to prevent oxidation, or with a targeted stream of shielding gas aimed at the joint. The quality is excellent at the joint, but the rest of the part is not protected.
Production Volume and Scalability
Furnace brazing excels at high-volume batch production. Its strength lies in its ability to handle a large quantity of parts, whether they are large, complex, or a mix of different sizes, in a single run. The filler alloy is typically pre-positioned on each part before loading.
Induction brazing excels at high-volume serial production. It is designed to braze one joint at a time but at an incredible speed, making it perfect for dedicated manufacturing cells producing millions of identical parts per year.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is without its limitations. Your decision requires weighing the operational benefits against the potential downsides.
Energy Consumption
Induction heating is highly energy-efficient on a per-part basis. It converts electrical energy into heat directly within the workpiece, with very little waste.
Furnace brazing is less energy-efficient per part, as it requires heating the entire furnace chamber, the racks, and the full mass of every assembly inside. However, for a fully loaded furnace, the energy cost per joint can be very competitive.
Part Distortion and Stress
The slow, uniform heating and cooling of furnace brazing minimizes thermal shock and stress, making it an excellent choice for delicate or complex assemblies prone to distortion.
The rapid, localized heating of induction can create thermal stress if not properly engineered. The steep temperature difference between the hot joint and the cool bulk of the part must be managed.
Tooling and Flexibility
A furnace is highly flexible, capable of processing a wide variety of part shapes and sizes in a single batch with minimal specific tooling.
Induction brazing requires a custom-designed induction coil for each specific joint geometry. This makes it less flexible for low-volume, high-mix production but ensures perfect repeatability once set up.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct process, analyze your project's primary constraints and goals.
- If your primary focus is brazing large, complex assemblies or thousands of small parts in a single run: Furnace brazing is the ideal choice for its batch capacity and uniform heating.
- If your primary focus is integrating a brazing step into a high-speed, automated production line for a specific part: Induction brazing provides the unmatched speed, precision, and repeatability you need.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute highest-purity joint and preventing any oxidation on the entire component: Vacuum furnace brazing offers the most controlled environment possible.
Ultimately, your decision is guided by whether your operation benefits more from the uniform control of batch processing or the focused speed of a continuous flow.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Induction Brazing | Furnace Brazing |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Localized (joint area only) | Uniform (entire assembly) |
| Speed | Seconds (continuous flow) | Hours (batch process) |
| Best For | High-volume serial production | High-volume batch production |
| Atmosphere Control | Localized (flux/shielding gas) | Superior, uniform (vacuum/inert gas) |
| Flexibility | Low (requires custom coil) | High (handles various parts) |
Optimize Your Brazing Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right brazing method is critical for your production efficiency and product quality. Whether you need the high-speed precision of induction brazing for automated lines or the batch-processing capability of furnace brazing for complex assemblies, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your laboratory and manufacturing needs.
We provide:
- Advanced brazing systems and consumables
- Expert guidance to select the ideal method for your application
- Reliable equipment that ensures consistent, high-quality results
Ready to enhance your brazing operations? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can drive your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- Why would you braze instead of solder? For Superior Joint Strength and High-Temperature Performance
- What is a braze repair process? A Low-Heat Solution for Strong, Seamless Metal Joining
- Which element made stainless steel difficult to brazed? It's Chromium's Oxide Layer
- Does brazing require heat? Yes, it's the catalyst for creating strong, permanent bonds.



















