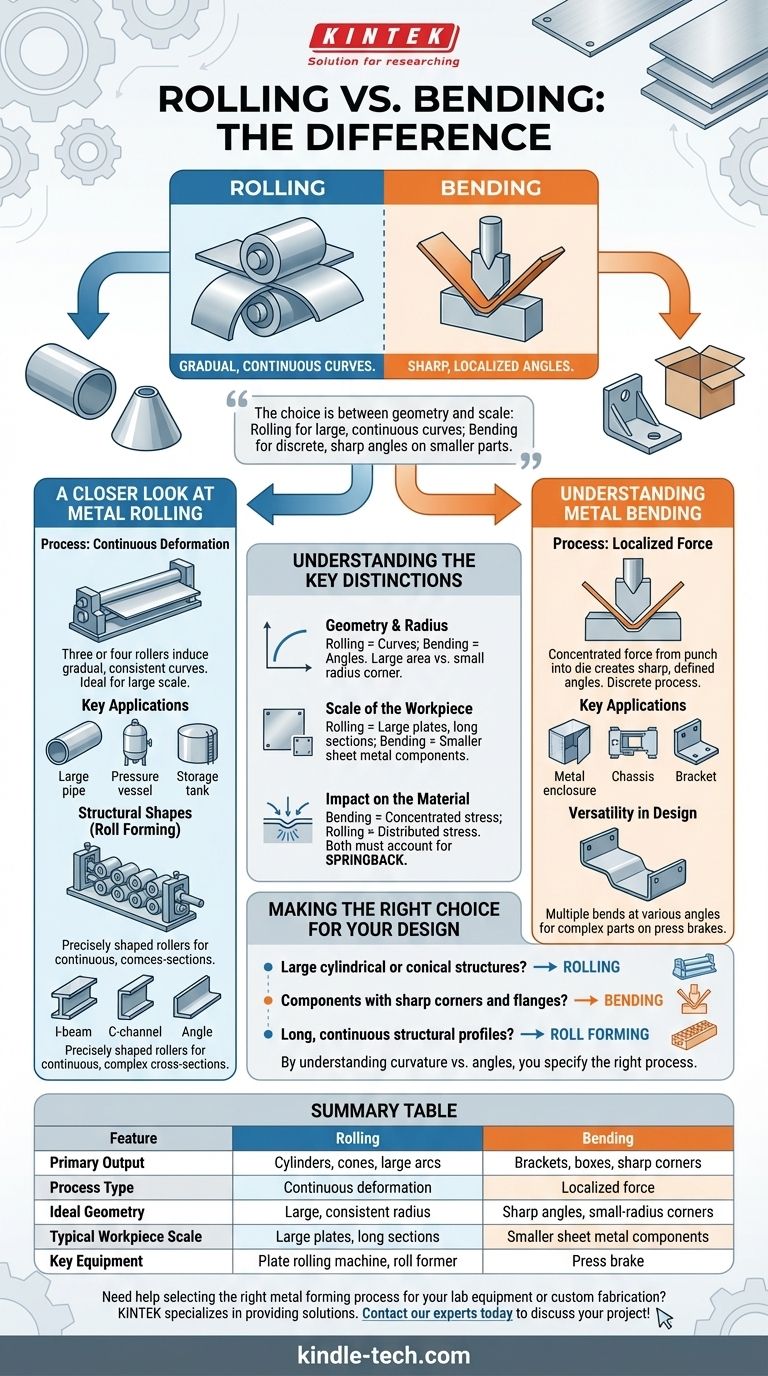
The fundamental difference between rolling and bending lies in how a material is shaped: rolling creates gradual, large-radius curves through continuous pressure, while bending creates sharp, localized angles or small-radius curves by applying force at a specific point. Rolling is used to make cylinders, cones, and large arcs, whereas bending is used to create brackets, boxes, and sharp corners.
The choice between rolling and bending is a choice between geometry and scale. Select rolling for continuous, large-radius curvatures on large workpieces, and select bending for creating discrete, sharp angles on smaller, more complex parts.

A Closer Look at Metal Rolling
Metal rolling is a forming process that uses a set of rollers to reduce the thickness of, or impart a desired shape to, a piece of metal. It's a continuous process ideal for large-scale production and large parts.
The Rolling Process: Continuous Deformation
In processes like plate rolling, a sheet or plate of metal is fed through three or four rollers. By adjusting the distance and position of these rollers, the machine induces a gradual, consistent curve along the entire length or width of the workpiece. This progressive pressure ensures a smooth, uniform radius.
Key Applications for Rolling
This method is the go-to choice for manufacturing parts with a large, consistent radius. Common examples include large-diameter pipes, pressure vessels, storage tanks, and the conical sections of hoppers.
Structural Shapes
A specialized form called roll forming uses a series of precisely shaped rollers to progressively bend a continuous strip of metal into complex cross-sections, such as I-beams, C-channels, and angle iron.
Understanding Metal Bending
Bending is a fabrication process that produces a V-shape, U-shape, or channel shape along a straight axis in ductile materials. It is most commonly performed on a machine tool called a press brake.
The Bending Process: Localized Force
A press brake uses a punch and a die to apply concentrated force to a specific line on a sheet of metal. The punch presses the sheet into the die, forcing it to bend at a sharp, defined angle. The process is discrete, creating one bend at a time.
Key Applications for Bending
Bending is essential for creating components that require sharp corners and flanges. Think of metal enclosures for electronics, chassis for equipment, small brackets, and sheet metal boxes.
Versatility in Design
Because each bend is a separate operation, press brakes offer immense versatility for creating complex parts with multiple bends at various angles and in different directions on a single workpiece.
Understanding the Key Distinctions
While both processes shape metal, their core principles, applications, and equipment are fundamentally different. The decision of which to use is rarely ambiguous.
Geometry and Radius
This is the most critical distinction. Rolling is for curves; bending is for angles. Rolling excels at producing a true radius over a large area. Bending excels at creating a small-radius corner along a straight line.
Scale of the Workpiece
Rolling machines are built to handle large plates and long sections of metal, often many feet in length or width. Press brakes are typically used for smaller, more manageable sheet metal components, although very large brakes exist for specialized applications like forming ship hulls.
Impact on the Material
Bending concentrates stress along a very narrow line, which can affect the material's properties at the corner. Rolling distributes the forming stress more evenly across the entire curved surface of the part. Both processes must account for springback, where the material tries to return to its original shape after the force is removed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Design
Selecting the correct process is critical for achieving your design intent efficiently and cost-effectively. Your part's geometry will almost always provide a clear answer.
- If your primary focus is creating large cylindrical or conical structures: Rolling is the only practical and efficient method for this task.
- If your primary focus is fabricating components with sharp corners and flanges: Bending on a press brake is the correct and necessary process.
- If your primary focus is forming long, continuous structural profiles: Roll forming is the ideal high-volume production method.
By understanding the distinction between continuous curvature and localized angles, you can specify the right manufacturing process for a more robust and economical design.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Rolling | Bending |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Output | Cylinders, cones, large arcs | Brackets, boxes, sharp corners |
| Process Type | Continuous deformation | Localized force |
| Ideal Geometry | Large, consistent radius | Sharp angles, small-radius corners |
| Typical Workpiece Scale | Large plates, long sections | Smaller sheet metal components |
| Key Equipment | Plate rolling machine, roll former | Press brake |
Need help selecting the right metal forming process for your lab equipment or custom fabrication project? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing solutions for laboratory needs, from custom metal enclosures to specialized components. Our expertise ensures you get the most efficient and cost-effective manufacturing method for your design. Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Small Lab Rubber Calendering Machine
- Precision Wire Saw Laboratory Cutting Machine with 800mm x 800mm Workbench for Diamond Single Wire Circular Small Cutting
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of an electrolytic polishing device for EK-181 steel TEM samples? Ensure Peak Sample Integrity
- What role do laboratory grinding and polishing systems play in nitriding? Ensure Superior Mirror-Finish & Ion Penetration
- What is the purpose of using epoxy resin and laboratory mounting equipment? Precision in U71Mn Weld Area Analysis
- What is the general procedure and what precautions should be taken during the polishing process? Achieve a Flawless Electrode Finish
- How should an RVC sheet be handled and set up during an experiment? Ensure Precision and Data Integrity



















