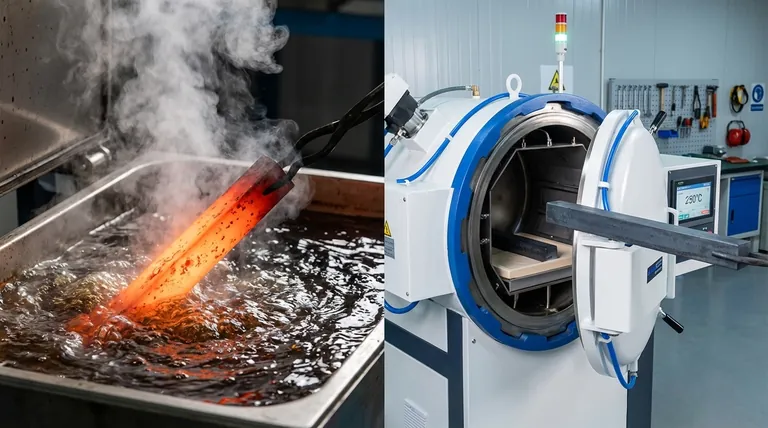
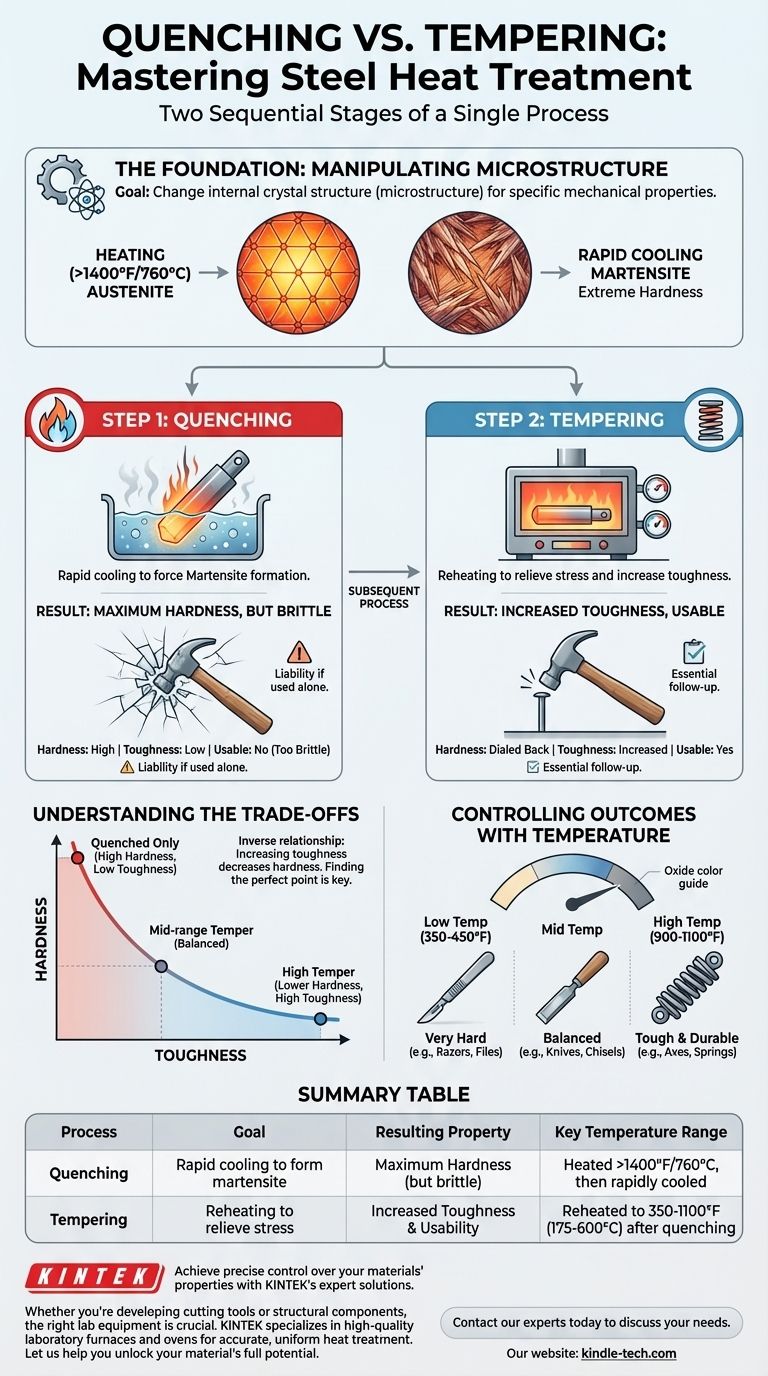
In short, quenching and tempering are two distinct, sequential stages of a single heat-treatment process. Quenching is the rapid cooling of steel to make it extremely hard but also brittle. Tempering is a subsequent, lower-temperature heating process that reduces that brittleness, increases toughness, and makes the steel usable for its intended purpose.
The core mistake is viewing quenching and tempering as alternatives. In reality, they are two sides of the same coin: you quench to create maximum hardness, and then you temper to dial back that hardness to the precise level of toughness your application requires.

The Foundation: Why We Heat Treat Steel
The Goal: Manipulating Microstructure
The properties of steel—its hardness, toughness, and flexibility—are determined by its internal crystal structure, known as its microstructure.
Heat treatment is the controlled process of heating and cooling steel to deliberately change this microstructure and achieve a specific, desired set of mechanical properties.
The Key Players: Austenite and Martensite
When you heat steel above a specific critical temperature (typically over 1400°F or 760°C), its internal structure transforms into a state called austenite.
If you cool it very quickly from this state, you trap the carbon atoms in a new, highly strained, and needle-like structure called martensite. This martensitic structure is what gives steel its extreme hardness.
Step 1: Quenching for Maximum Hardness
The Goal of Quenching
The sole purpose of quenching is to cool the steel fast enough to force the formation of martensite. The goal is to achieve the steel's maximum potential hardness.
The Process
First, the steel part is heated evenly until it fully transforms into austenite. It is held at this temperature long enough for the change to be uniform throughout the entire piece.
Then, the part is plunged into a cooling medium for an extremely rapid drop in temperature.
The Result: Hard but Brittle
Immediately after a successful quench, the steel is at its hardest. However, it is also under immense internal stress and is extremely brittle.
In this state, the steel is like glass. It can resist scratching and abrasion very well, but it will shatter if dropped or struck with force. For almost all applications, this brittleness makes the part useless and unreliable.
Step 2: Tempering for Increased Toughness
The Goal of Tempering
Tempering is the essential follow-up step that makes the hardened steel practical. Its purpose is to relieve the internal stresses created during quenching and to trade some of the extreme, unusable hardness for much-needed toughness.
Toughness is a material's ability to absorb energy and deform without fracturing. It's the opposite of brittleness.
The Process
The quenched, brittle part is cleaned and then gently reheated to a temperature well below the critical point where austenite was formed (typically between 350°F and 1100°F or 175°C and 600°C).
The part is held at this tempering temperature for a specific duration, allowing the microstructure to relax and reform slightly. It is then cooled back to room temperature.
Controlling the Outcome with Temperature
The tempering temperature is the most critical variable.
- Lower tempering temperatures (e.g., 350-450°F) relieve only a small amount of stress. This results in a very hard part with only a slight increase in toughness, suitable for things like files or razor blades.
- Higher tempering temperatures (e.g., 900-1100°F) relieve much more stress. This results in a significantly tougher, more ductile part with lower hardness, suitable for springs, axes, or structural components.
As the steel heats up, a thin oxide layer forms on its surface, creating distinct colors (from light straw to blue and gray) that act as a reliable visual guide for the temperature achieved.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Hardness vs. Toughness Curve
The most important principle to understand is the inverse relationship between hardness and toughness. When you temper a piece of steel, as you increase its toughness, you will inevitably decrease its hardness. You cannot maximize both.
The art of heat treatment is finding the perfect point on this curve for your specific application.
The Problem with Quenching Alone
A part that is only quenched is a liability. A quenched-only knife blade might be incredibly sharp, but it could snap in half while cutting a carrot. A quenched-only hammer could shatter upon its first strike. This is why tempering is almost never an optional step.
The Risk of Over-Tempering
Heating the steel to too high a temperature during the temper, or holding it there for too long, can make it too soft. An over-tempered knife will not hold an edge, and an over-tempered spring will not return to its shape.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The final properties of your steel are a direct result of the tempering temperature you select.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance (e.g., cutting tools, files): Use a low tempering temperature to retain the maximum amount of hardness while only adding enough toughness to prevent chipping.
- If your primary focus is impact resistance and durability (e.g., axes, hammers, structural parts): Use a high tempering temperature to sacrifice hardness in favor of gaining the maximum possible toughness.
- If your primary focus is a balanced performance (e.g., chisels, knives, springs): Use a mid-range tempering temperature to achieve a compromise that offers good hardness and good toughness.
By mastering the relationship between quenching and tempering, you gain complete control over the final performance of your steel.
Summary Table:
| Process | Goal | Resulting Property | Key Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quenching | Rapid cooling to form martensite | Maximum Hardness (but brittle) | Heated above critical point (~1400°F/760°C), then rapidly cooled |
| Tempering | Reheating to relieve stress | Increased Toughness & Usability | Reheated to 350-1100°F (175-600°C) after quenching |
Achieve precise control over your materials' properties with KINTEK's expert solutions.
Whether you're developing cutting tools that require extreme hardness or structural components that need superior impact resistance, the right lab equipment is crucial for perfecting the quenching and tempering process. KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory furnaces, ovens, and consumables that provide the accurate temperature control and uniform heating essential for reliable heat treatment.
Let us help you unlock your material's full potential. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application needs and find the perfect equipment for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of quenching? Managing the Risks of Distortion and Cracking
- Why is a laboratory vacuum drying oven necessary for single-crystal cathode powders? Ensure Peak Material Stability
- How does a vacuum affect heat transfer? Master Precise Thermal Control in Your Lab
- What gas can be used for brazing? Select the Right Atmosphere for Metallurgical Success
- What is the critical role of a vacuum furnace in the calcination of TiO2? Optimize Your Powder Microstructure
- Why is Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) preferred for ODS iron-based alloys? Achieve 95% Density and Fine-Grained Strength
- Why is a high-precision furnace necessary for T91 steel heat treatment? Ensure 1050°C and 770°C Thermal Stability
- What are the advantages of powder sintering? Unlock Superior Strength, Conductivity & Translucency



















