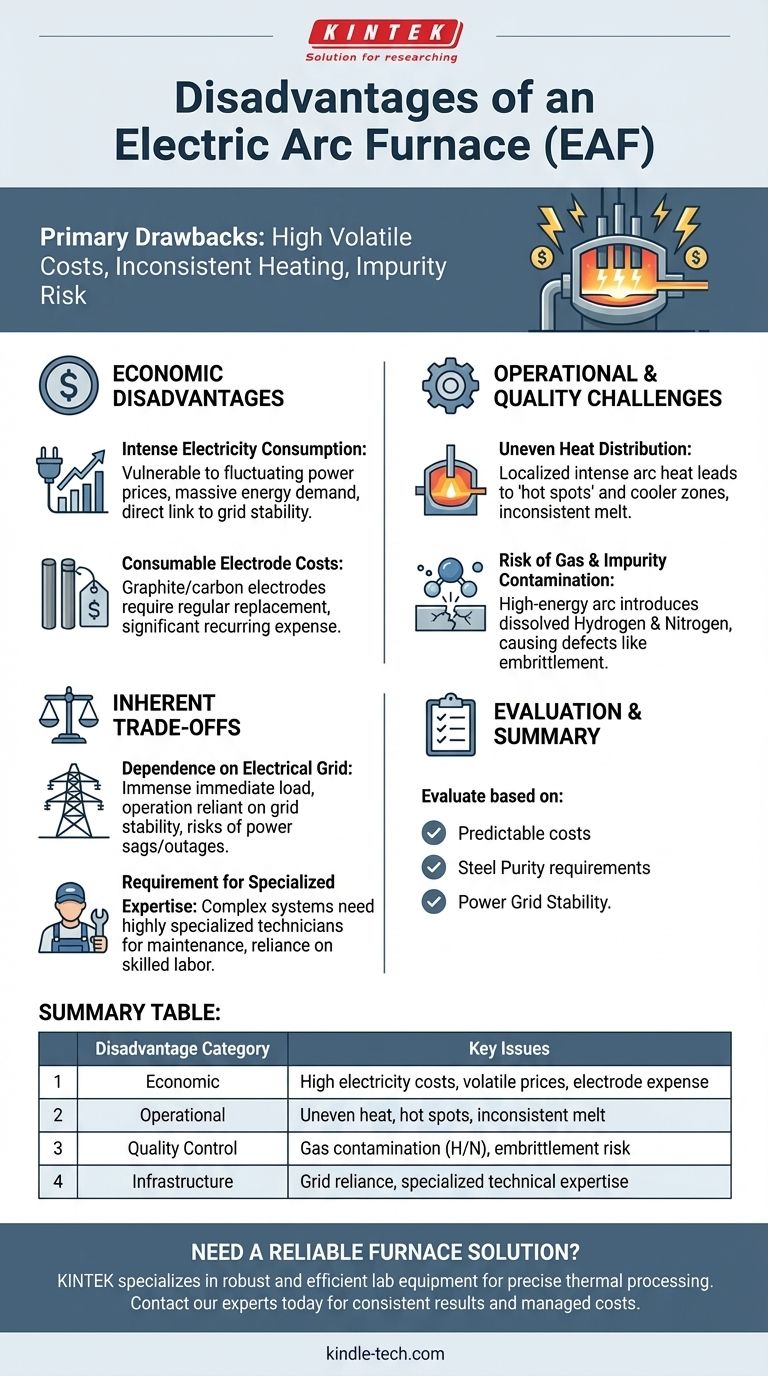
The primary disadvantages of an electric arc furnace (EAF) are its high and often volatile operating costs driven by electricity consumption, the potential for inconsistent heating within the furnace, and the risk of introducing undesirable gases and impurities into the steel from the electric arc and raw materials.
While electric arc furnaces offer significant flexibility and lower initial investment compared to traditional blast furnaces, their core disadvantages stem from a direct reliance on the electrical grid and the quality of scrap metal, creating distinct economic and metallurgical challenges.
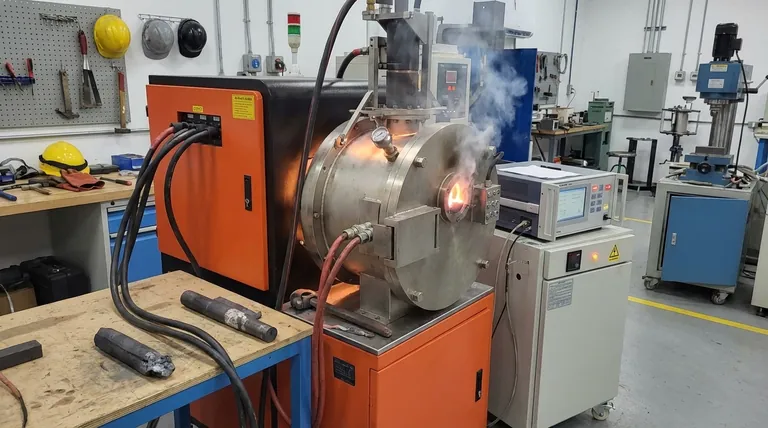

The Core Economic Disadvantage: High Operating Costs
The most significant and persistent drawback of an EAF is its operational expenditure, which is heavily influenced by factors outside the steel plant's direct control.
Intense Electricity Consumption
An EAF's entire operation is fueled by massive amounts of electricity needed to generate the arc that melts steel. This makes the furnace's operating budget directly vulnerable to fluctuations in regional electricity prices.
Unlike furnaces that use coke or natural gas, an EAF cannot easily switch fuels. This ties profitability directly to the stability and cost of the local power grid, making it a significant financial risk in volatile energy markets.
Consumable Electrode Costs
The graphite or carbon electrodes that create the electric arc are a critical component, but they are also a consumable good.
These large electrodes are gradually consumed during the melting process and must be replaced regularly. The cost of these specialized components can be substantial and adds another major variable to the operational budget.
Operational and Quality Control Hurdles
Beyond the cost, the EAF process itself introduces challenges that require careful management to ensure the quality and consistency of the final product.
Uneven Heat Distribution
The electric arc is an incredibly intense but localized heat source. This can lead to "hot spots" in the furnace directly under the electrodes and cooler zones elsewhere.
This uneven heat distribution can result in an inconsistent melt and require additional energy and time to homogenize the molten metal, reducing overall efficiency.
Risk of Gas and Impurity Contamination
The high-energy electric arc can react with gases in the furnace atmosphere. This process can introduce significant amounts of dissolved hydrogen and nitrogen into the molten steel.
These dissolved gases can lead to defects like embrittlement and reduced toughness in the final steel product, requiring additional downstream processing and quality control to mitigate.
Understanding the Inherent Trade-offs
The disadvantages of an EAF are best understood as trade-offs against its benefits, such as its ability to use 100% recycled steel scrap and its smaller physical footprint.
Dependence on the Electrical Grid
The EAF places an immense and immediate load on the power grid. This not only drives cost but also means the furnace's operation is entirely dependent on the grid's stability.
In regions with unreliable power infrastructure, running an EAF can be a significant operational risk, with power sags or outages causing costly production stoppages.
Requirement for Specialized Expertise
While generally robust, the systems that power and control an EAF are complex. Diagnosing and repairing issues with the high-voltage electrical systems, control mechanisms, or refractory linings often requires highly specialized technicians.
This creates a reliance on a skilled labor pool that may not be available in all locations, adding another layer of operational risk.
How to Evaluate These Disadvantages for Your Project
Choosing a furnace technology requires weighing these drawbacks against your specific goals and operating environment.
- If your primary focus is predictable operational cost: The EAF's direct exposure to electricity price volatility presents a significant financial risk compared to fuel-based furnaces.
- If your primary focus is producing the highest purity steel grades: You must be prepared to invest in secondary refining and degassing processes to mitigate the impurity and gas risks inherent in the EAF.
- If you are located in a region with an unstable or expensive power grid: The EAF's immense power demand makes it a potentially unreliable and uneconomical choice without a dedicated, stable power source.
Understanding these specific drawbacks is the first step toward mitigating them and making an informed decision about this powerful and flexible steelmaking technology.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Issues |
|---|---|
| Economic | High electricity costs, volatile energy prices, expensive consumable electrodes |
| Operational | Uneven heat distribution, potential for hot spots, inconsistent melt |
| Quality Control | Risk of hydrogen/nitrogen gas contamination, potential for steel embrittlement |
| Infrastructure | Heavy reliance on stable power grid, requires specialized technical expertise |
Need a reliable furnace solution for your lab or production facility? The challenges of electric arc furnaces highlight the importance of choosing the right equipment for your specific needs. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust and efficient lab equipment, including furnaces tailored for precise thermal processing. Whether you're in research, quality control, or small-scale production, we can help you find a solution that ensures consistent results, manages operational costs, and maintains material integrity. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory and processing requirements with the right equipment for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different melting methods? A Guide to Choosing the Right Industrial Furnace
- What is RF magnetron sputtering? A Guide to Depositing Insulating Thin Films
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- What is the difference between VAR and VIM? Legacy Vimscript Variables vs. Modern Neovim API
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















