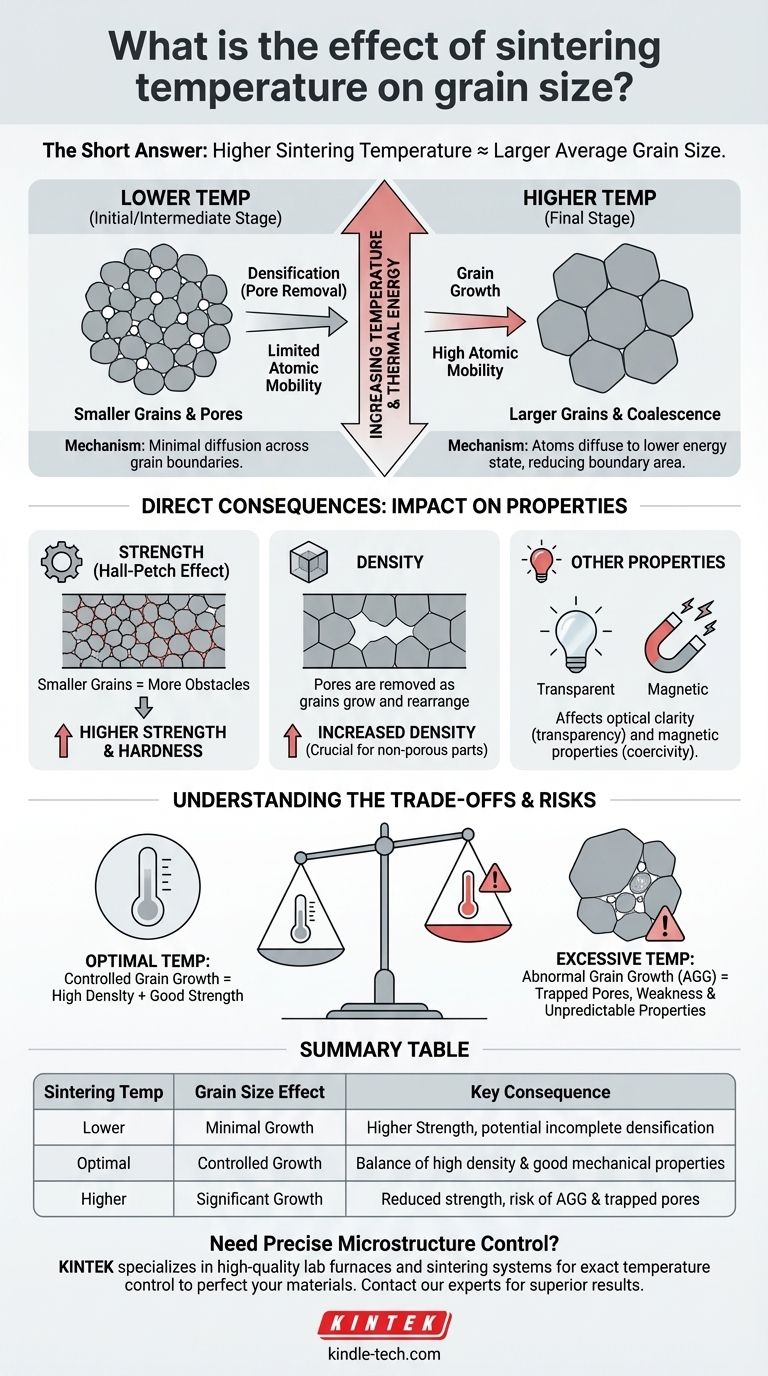
The short answer is clear: a higher sintering temperature almost always results in a larger average grain size. This is a fundamental relationship in materials science because the thermal energy supplied during sintering directly fuels the atomic processes that cause grains to grow and coalesce.
The central principle to grasp is that sintering is a thermally activated process. Temperature provides the energy for two competing phenomena: densification (the removal of pores) and grain growth. The key challenge is to achieve full density without allowing excessive grain growth, which can degrade the material's final properties.

The Fundamental Mechanism: Why Temperature Drives Grain Growth
Sintering is more than just fusing particles together; it's a process of microstructural evolution. Temperature is the primary catalyst for the atomic movement that reshapes the material from the inside out.
The Role of Thermal Energy
Atoms within a material are in a constant state of vibration. As you increase the temperature, you are adding kinetic energy, causing these atoms to vibrate more intensely and move more freely.
This increased atomic mobility is the essential prerequisite for all sintering mechanisms, including grain growth.
Atomic Diffusion Across Grain Boundaries
The driving force for grain growth is the reduction of the total energy in the system. Grain boundaries—the interfaces between individual crystals—are regions of high energy.
By increasing temperature, you provide atoms with enough energy to detach from the lattice of a smaller grain and diffuse across the boundary to join the lattice of a larger, more stable grain. This process effectively makes the larger grain grow at the expense of the smaller one.
The Goal: A Lower Energy State
A material with a few large grains has a much lower total grain boundary area than a material with many small grains. Therefore, the system is thermodynamically driven to minimize this boundary area.
Higher temperatures simply accelerate the rate at which the material can achieve this lower-energy state, leading to faster and more significant grain growth.
The Direct Consequences of Grain Size
The size of the grains in a final ceramic or metal part is not just an academic detail; it directly dictates many of its most important physical and mechanical properties.
The Link to Density
Initially, as grains grow and rearrange, they help eliminate the pores between the starting particles. This process, known as densification, is crucial for achieving a strong, non-porous final part.
Grain growth and densification are therefore closely linked, especially in the intermediate stages of sintering.
The Impact on Mechanical Strength
This is the most critical consequence. The relationship between grain size and strength is famously described by the Hall-Petch equation. It states that materials with smaller grains are stronger and harder.
Grain boundaries act as obstacles that impede the movement of dislocations (defects) through the material. More boundaries (i.e., smaller grains) mean more obstacles, making the material more resistant to deformation. As grains grow larger, this strengthening effect diminishes.
Effects on Other Properties
Grain size also influences a host of other properties. In transparent ceramics like alumina, scattering at grain boundaries can reduce clarity, so a uniform and controlled grain size is critical. In magnetic materials, grain size can affect coercivity and permeability.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Controlling sintering temperature is a balancing act. Simply increasing the temperature to achieve high density quickly can lead to undesirable outcomes.
The Race Between Densification and Grain Growth
The ideal sintering cycle achieves maximum densification with minimal grain growth. If the temperature is too high, grain growth can accelerate rapidly, sometimes even trapping pores inside the large grains where they become nearly impossible to remove.
This results in a part that is both porous and mechanically weak.
The Risk of Abnormal Grain Growth (AGG)
At excessively high temperatures or with very long hold times, a phenomenon called abnormal or exaggerated grain growth can occur. Here, a few grains grow disproportionately large, consuming all their neighbors.
This creates a non-uniform microstructure with poor and unpredictable mechanical properties, and it is a common failure mode in ceramic processing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal sintering temperature is not a single value but a carefully chosen parameter based on your end goal. It depends on the material, particle size, and desired final properties.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and hardness: Your goal is the smallest possible grain size that still allows for full densification. This often means using the lowest effective temperature and potentially shorter hold times.
- If your primary focus is optical transparency or specific electrical properties: You must prioritize eliminating all porosity. This may require higher temperatures or longer times, accepting some grain growth as a necessary trade-off for perfect density.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production: You will need to find a temperature that provides an acceptable balance of density and strength within the shortest possible time to maximize throughput.
Ultimately, mastering the sintering temperature allows you to precisely engineer the material's microstructure to meet your specific performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Temperature | Effect on Grain Size | Key Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Lower Temperature | Minimal Grain Growth | Higher Strength (Hall-Petch), but potential for incomplete densification |
| Optimal Temperature | Controlled Grain Growth | Balance of high density and good mechanical properties |
| Higher Temperature | Significant Grain Growth | Reduced strength, risk of abnormal grain growth and trapped pores |
Need precise control over your material's microstructure? The sintering process is a delicate balance, and the right equipment is crucial for achieving your target density and grain size. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and sintering systems that provide the exact temperature control and uniformity you need to perfect your ceramics, metals, and advanced materials.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve superior material properties and repeatable results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag



















