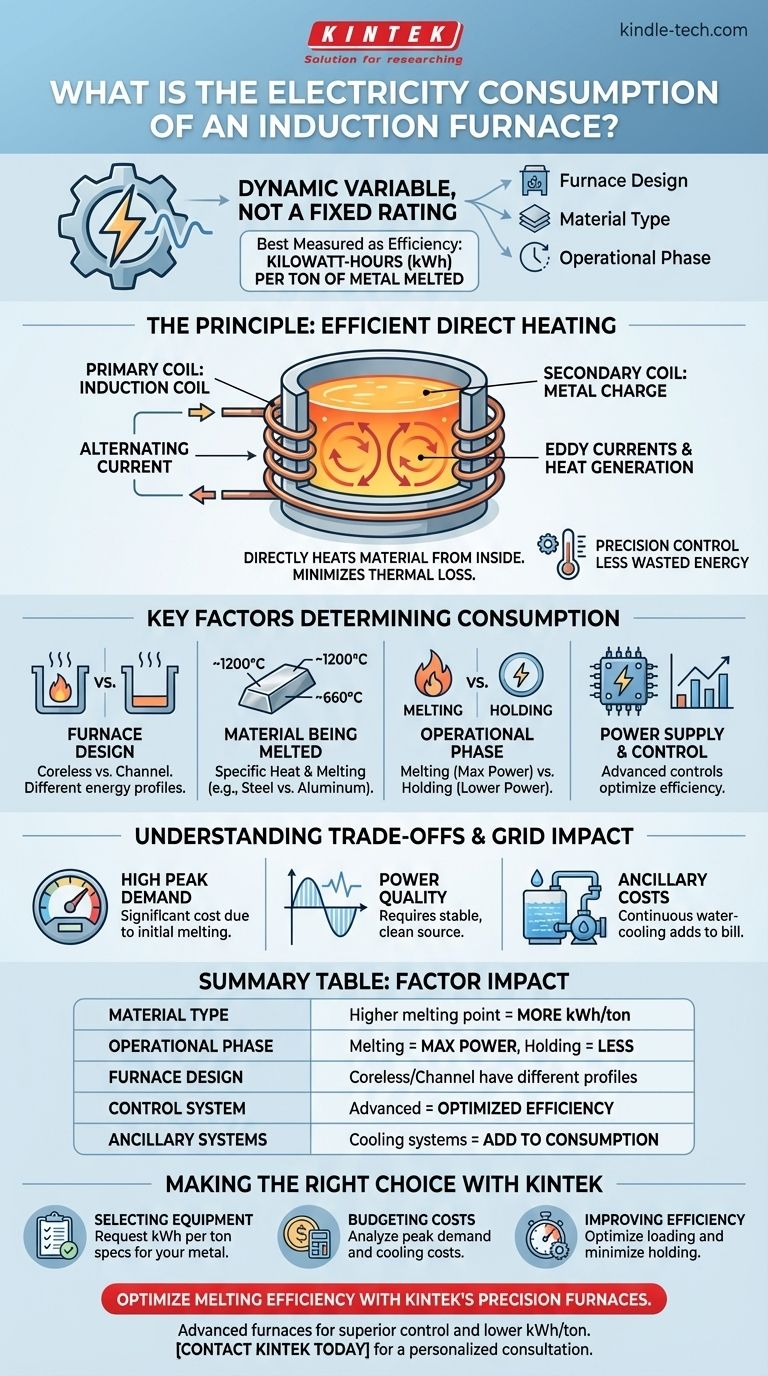
Pinpointing the electricity consumption of an induction furnace is not a matter of a single, universal figure. Instead, its consumption is a dynamic variable determined by the furnace's design, the specific material being processed, and its operational phase. The most accurate way to understand it is to see consumption as a measure of efficiency for a specific task, such as kilowatt-hours (kWh) per ton of metal melted.
The core principle to understand is that an induction furnace's electricity consumption is a function of its efficiency, not a fixed rating. Instead of seeking a single number, you must evaluate the key factors that influence its power draw, from the type of metal being melted to the sophistication of its control systems.

The Principle: Why Induction Furnaces Are Energy-Efficient
To understand what drives electricity consumption, you must first grasp how an induction furnace works. Its efficiency stems from its method of direct, targeted heating.
The Transformer Analogy
An induction furnace operates like a transformer. A water-cooled copper coil acts as the primary coil, and the metal charge placed inside the crucible acts as the secondary coil.
When a powerful alternating current flows through the primary coil, it induces a strong secondary current directly within the metal itself.
Direct Heating via Eddy Currents
These induced secondary currents are known as eddy currents. As they swirl through the metal, the metal's natural electrical resistance generates intense, precise heat.
This method is highly efficient because the heat is generated inside the target material, not applied from an external source. This minimizes thermal loss to the surrounding environment.
Precision and Control
Modern induction furnaces have highly integrated control systems. These systems ensure a small temperature difference between the core and the surface of the melt.
This high level of temperature control accuracy prevents overshooting target temperatures, which directly translates to less wasted energy.
Key Factors That Determine Power Consumption
The actual kWh consumed during an operation depends on several critical variables. Answering "how much electricity does it use?" is impossible without defining these parameters first.
Furnace Design and Type
There are different designs, like coreless and channel furnaces. A channel furnace, for example, is often used for holding molten metal at temperature or melting low-temperature alloys, which has a different energy profile than a coreless furnace designed for primary melting.
The Material Being Melted
The single biggest factor is the specific heat and melting point of the material. Melting a ton of cast iron (melting point ~1200°C) will require significantly more energy than melting a ton of aluminum (melting point ~660°C).
The Operational Phase
A furnace's power draw changes drastically based on what it's doing. The melting phase requires maximum power output. The holding phase, where the metal is simply kept liquid at a stable temperature, consumes far less energy.
The Power Supply and Control System
Advanced power supplies with constant power circuit control automatically adjust voltage and current based on the furnace charge. This ensures the furnace operates at peak efficiency throughout the melt cycle, preventing wasted power.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Grid Impact
While efficient in terms of kWh per ton, an induction furnace has specific power requirements that must be managed.
High Peak Power Demand
During the initial melting phase, the furnace draws a very high amount of power to bring the cold charge up to temperature. This peak demand can be a significant factor in your electricity costs, as many utility providers have separate charges for peak usage.
The Importance of Power Quality
The sophisticated electronic components, such as silicon-controlled rectifiers and inverter boards, are sensitive to fluctuations in the power grid. A stable and clean power source is essential for reliable and efficient operation.
Ancillary Energy Costs
The furnace itself is not the only source of consumption. The powerful water-cooling system, required to protect the copper induction coil, runs continuously and adds to the overall electricity bill.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To properly assess the electricity consumption for your needs, you must shift from asking for a single number to analyzing the system based on your objective.
- If your primary focus is selecting new equipment: Request manufacturer specifications that state consumption in kWh per ton for the specific metals you plan to melt.
- If your primary focus is budgeting for operational costs: Analyze your utility rates for peak demand charges and factor in the energy costs of the cooling system, not just the furnace itself.
- If your primary focus is improving efficiency: Concentrate on operational discipline, such as using clean and dry charge material, optimizing furnace loading, and minimizing the time spent in the less-efficient "holding" phase.
Ultimately, managing an induction furnace’s energy consumption is less about finding a static value and more about mastering a dynamic process.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Electricity Consumption |
|---|---|
| Material Type | Higher melting point (e.g., steel) requires more kWh/ton than lower (e.g., aluminum). |
| Operational Phase | Melting phase uses maximum power; holding phase uses significantly less. |
| Furnace Design | Coreless vs. channel furnaces have different energy profiles for specific tasks. |
| Control System | Advanced controls with constant power circuits optimize efficiency and reduce waste. |
| Ancillary Systems | Water-cooling systems add to the total energy consumption. |
Optimize your lab's melting efficiency with KINTEK's precision induction furnaces.
Whether you're melting steel, aluminum, or specialty alloys, our advanced furnaces deliver superior temperature control and energy efficiency, reducing your kWh per ton costs. Our experts will help you select the right system based on your specific materials and operational goals.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and see how our lab equipment solutions can lower your energy consumption and enhance your research outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting



















