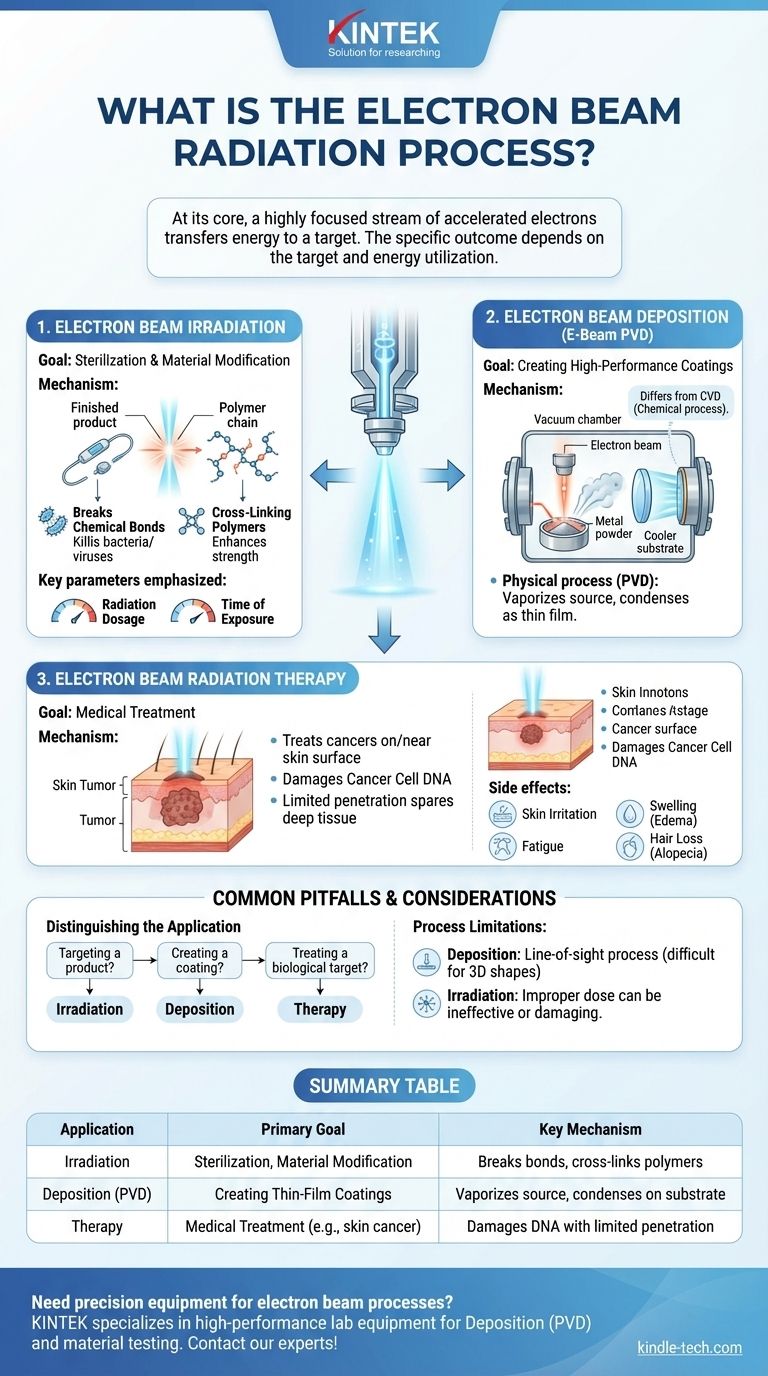
At its core, the electron beam radiation process uses a highly focused stream of accelerated electrons to transfer energy to a target. However, the term is ambiguous because it describes several distinct applications, from sterilizing medical devices and creating advanced material coatings to treating medical conditions. The specific outcome depends entirely on what the beam is aimed at and how its energy is utilized.
The central takeaway is that "electron beam radiation" is not a single process, but a versatile energy delivery method. The key to understanding it is to first identify the goal: Are you trying to modify a target, build a new layer on a target, or treat a biological target?
The Core Principle: A Focused Beam of Energy
What is an Electron Beam?
An electron beam is a stream of electrons generated and accelerated to high speeds, typically within a vacuum. This concentration of high-energy particles creates a powerful and precise tool for transferring energy.
How It Transfers Energy
When this beam of high-velocity electrons strikes a material, the kinetic energy is transferred to the target. This energy transfer can induce a range of effects, including intense localized heating, breaking chemical bonds, or triggering chemical reactions.
Application 1: Electron Beam Irradiation
The Goal: Sterilization and Material Modification
In this context, the electron beam is aimed directly at a finished product. The goal is to alter the product's properties by exposing it to a controlled dose of radiation.
The Mechanism
The bombardment of high-energy electrons creates a cascade effect within the target material. This process is highly effective at breaking chemical bonds, which can be used to destroy the DNA of bacteria and viruses for sterilization or to create new links between polymers (cross-linking) to enhance a material's strength and durability.
Key Parameters
The effectiveness of irradiation is determined by two main factors: the radiation dosage (the amount of energy absorbed by the material) and the time of exposure. These must be carefully controlled to achieve the desired effect without damaging the product.
Application 2: Electron Beam Deposition
The Goal: Creating High-Performance Coatings
This process, also known as E-Beam PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition), does not modify the target directly. Instead, it uses the electron beam to create a new, thin film of material on a target's surface, such as an optical lens or a semiconductor wafer.
The Mechanism
The electron beam is aimed at a source material (like a ceramic or metal powder) inside a vacuum chamber, heating it until it vaporizes. This vapor then travels and condenses onto the cooler substrate (the object being coated), forming a thin, uniform, and highly pure film.
How It Differs from CVD
It is crucial to distinguish this physical process from Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
- E-Beam Deposition (PVD): A physical process. A solid material is vaporized and then condenses onto a surface, much like steam condensing on a cold mirror.
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): A chemical process. Precursor gases are introduced into a chamber where they react on a hot substrate, and the product of that chemical reaction forms the coating.
Application 3: Electron Beam Radiation Therapy
The Goal: Medical Treatment
In medicine, electron beam radiation is a form of external beam radiotherapy used primarily to treat cancers on or near the surface of the skin.
The Mechanism
The beam's energy is directed at a tumor or cancerous lesion. The radiation damages the DNA of the cancer cells, preventing them from replicating and causing them to die. Because electrons don't penetrate very deeply, this method is ideal for treating surface-level conditions while sparing deeper, healthy tissue.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
Distinguishing the Application
The most common mistake is assuming the term "electron beam radiation" refers to only one process. The context is everything. Language about "coatings," "vapor," or "thin films" points to deposition, while terms like "sterilization," "cross-linking," or "dosages" suggest irradiation.
Side Effects in Therapy
While effective, medical radiation is not without trade-offs. Common side effects for patients can include skin irritation, fatigue, swelling (edema), and localized hair loss (alopecia). These effects are a direct result of the energy affecting healthy cells near the treatment area.
Process Limitations
Electron beam deposition is a line-of-sight process, meaning it can be difficult to coat complex, three-dimensional shapes uniformly. For irradiation, an improper dose can either be ineffective or cause unwanted degradation of the target material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is sterilization or enhancing a material's intrinsic properties: You are looking for Electron Beam Irradiation, where the product itself is the target.
- If your primary focus is applying a new, high-purity layer or coating onto a substrate: You are dealing with Electron Beam Deposition, a physical vapor process.
- If your primary focus is the medical treatment of surface-level tumors: You are referencing Electron Beam Radiation Therapy, a specialized form of radiotherapy.
Ultimately, understanding your objective is the key to deciphering which electron beam process is being discussed.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Goal | Key Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Irradiation | Sterilization, Material Modification | Breaks chemical bonds to destroy pathogens or cross-link polymers |
| Deposition (PVD) | Creating Thin-Film Coatings | Vaporizes a source material that condenses onto a substrate |
| Therapy | Medical Treatment (e.g., skin cancer) | Damages DNA of cancer cells with limited tissue penetration |
Need precision equipment for electron beam processes? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for applications like electron beam deposition (PVD) and material testing. Whether you are developing advanced coatings, sterilizing medical devices, or conducting research, our solutions ensure accuracy and reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 16L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Do liquids boil in an autoclave? How to Safely Sterilize Media Without Boil-Over
- Is autoclave an instrument or equipment? A Clear Guide to Classification
- What is the pressure required in an autoclave? Achieve Sterile Results with 15 PSI
- What lab supplies should be autoclaved? A Guide to Safe Sterilization and Decontamination
- What are the chambers of the autoclave? Understanding Single-Wall vs. Jacketed Designs


















