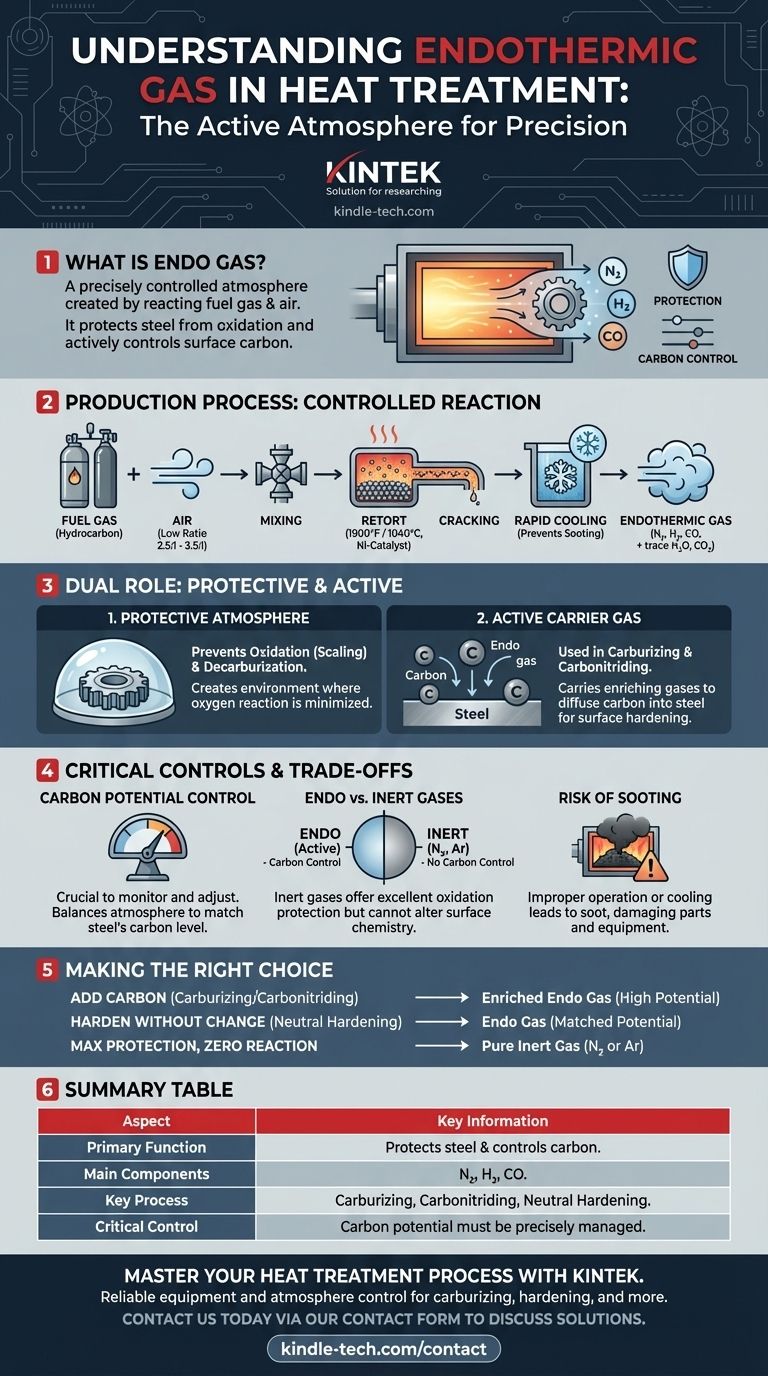
In heat treatment, endothermic gas is a precisely controlled atmosphere, commonly called "Endo" gas, created by reacting a fuel gas and air. This process generates a gas mixture—primarily nitrogen, hydrogen, and carbon monoxide—that is actively used to protect steel parts from oxidation and to control their surface carbon content during high-temperature processing.
Endothermic gas is not merely a protective shield; it is an active chemical environment engineered to achieve a specific carbon equilibrium with the steel being treated. Understanding how to generate and control this gas is fundamental to processes like carburizing and neutral hardening.

How Endothermic Gas Is Produced
The generation of endothermic gas is a controlled chemical reaction designed to prevent full combustion and produce a specific blend of gases.
The Core Ingredients and Ratio
Production begins by mixing a hydrocarbon fuel gas, like natural gas, with air. The air-to-gas ratio is critical and is kept low, typically between 2.5:1 and 3.5:1, which is insufficient for complete combustion.
The Reaction Process
This air-fuel mixture is fed into an externally heated chamber called a retort, which is filled with a nickel-based catalyst. At high temperatures (around 1900°F or 1040°C), the catalyst "cracks" the hydrocarbon and air mixture into its primary components.
The Final Composition
The resulting endothermic gas is a mixture primarily composed of nitrogen (N₂), hydrogen (H₂), and carbon monoxide (CO), with smaller amounts of water vapor and carbon dioxide.
Critical Step: Rapid Cooling
Immediately after leaving the retort, the gas must be rapidly cooled. This crucial step prevents the carbon monoxide from breaking down and reforming into solid carbon (soot), a reaction known as carbon reversal. Soot can clog equipment and disrupt the furnace atmosphere.
The Dual Role in Heat Treatment
Endothermic gas serves two primary functions, which depend on how it is controlled and applied within the furnace.
As a Protective Atmosphere
In its most basic role, endo gas prevents high-temperature oxidation (scaling) and decarburization (the loss of carbon from the steel's surface). It creates an environment where the tendency for oxygen to react with the steel is minimized.
As an Active Carrier Gas
In processes like gas carburizing and carbonitriding, endo gas acts as a "carrier" for enriching gases. Additional hydrocarbon gas is added to the endo gas atmosphere, which then transports this carbon to the surface of the steel, causing it to diffuse into the part and harden the surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Controls
Using endothermic gas effectively requires a clear understanding of its reactive nature and the need for precise control.
The Necessity of Carbon Potential Control
The most critical variable is the carbon potential—the ability of the atmosphere to either add carbon to, remove carbon from, or remain neutral to the steel. This potential must be constantly monitored and adjusted to match the carbon content of the material being treated. Failure to do so can result in unintended carburizing or decarburizing.
Endo Gas vs. Inert Gas Atmospheres
Endothermic gas is an active atmosphere. In contrast, gases like pure nitrogen (N₂) or argon (Ar) are inert. Inert gases provide excellent protection from oxidation but do not offer any carbon control. They are chosen when the primary goal is simply to prevent any surface reaction on sensitive materials.
The Persistent Risk of Sooting
Improper generator operation, incorrect gas ratios, or temperature drops in the furnace can lead to sooting. This soot formation can negatively impact the surface finish of parts and requires furnace burnouts and maintenance to remove.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal furnace atmosphere depends entirely on the desired outcome for your material.
- If your primary focus is adding carbon to the surface (Carburizing/Carbonitriding): Use endo gas as an active carrier, enriched with a hydrocarbon gas to achieve a high carbon potential.
- If your primary focus is hardening without changing surface chemistry (Neutral Hardening): Use endo gas with a carbon potential precisely matched to the carbon content of the steel you are treating.
- If your primary focus is maximum protection with zero surface reaction: Use a pure inert gas like nitrogen or argon, especially for highly reactive alloys or applications where any change is unacceptable.
Ultimately, mastering your heat treatment process means selecting and controlling the furnace atmosphere to dictate the final properties of the component.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Protects steel from oxidation & controls surface carbon content. |
| Main Components | Nitrogen (N₂), Hydrogen (H₂), Carbon Monoxide (CO). |
| Key Process | Gas carburizing, carbonitriding, and neutral hardening. |
| Critical Control | Carbon potential must be precisely monitored and adjusted. |
Master your heat treatment process with the right equipment and expertise.
Endothermic gas is fundamental for achieving precise metallurgical results, but its effectiveness depends on proper generation and control. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the reliable furnaces and atmosphere control systems your laboratory needs for successful carburizing, hardening, and more.
Contact us today via our Contact Form to discuss how our solutions can enhance your heat treatment capabilities and ensure consistent, high-quality results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an inert oven? A Guide to Oxidation-Free Thermal Processing
- What is the inert air technique? Protect Your Sensitive Materials from Oxygen and Moisture
- What does inert atmosphere mean in science? Control Chemical Reactions and Ensure Process Safety
- What is the necessity of controlled atmosphere furnaces for gas corrosion? Ensure Precise Material Failure Modeling
- Why is a high-pressure nitrogen environment of 1 to 3 MPa required for Si2N2O synthesis? Optimize Ceramic Phase Purity
- What is the role of an Atmosphere Furnace in the preparation of lignin-based graphene oxide? Key Carbonization Insights
- How do inert gas, airflow, and pressure work together in a furnace? Master Precise Atmosphere Control
- What function does a high-temperature atmosphere furnace serve in the activation of Aux/TiO2? Master Catalyst Precision



















