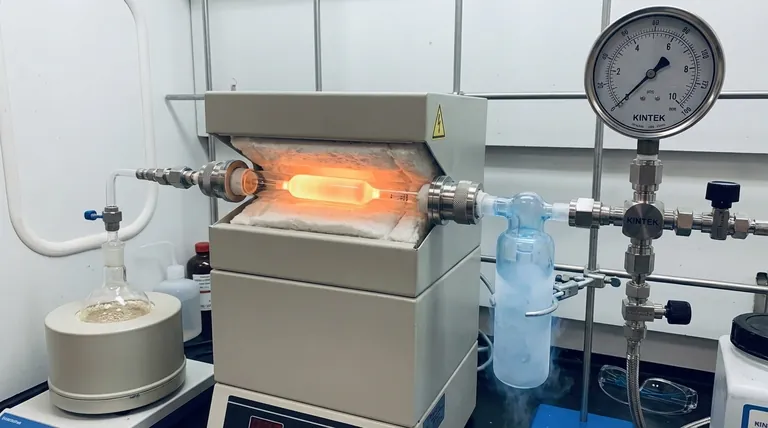
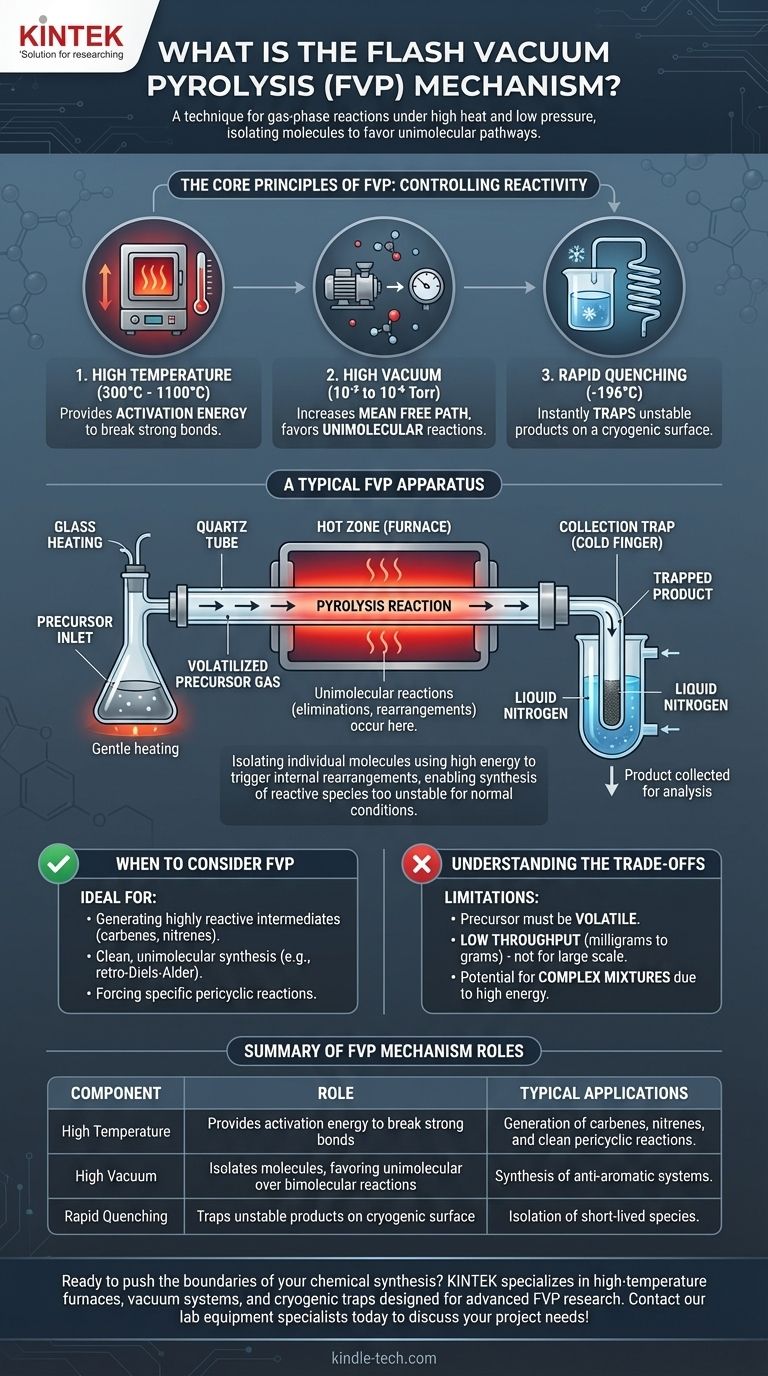
At its core, Flash Vacuum Pyrolysis (FVP) is a technique in synthetic chemistry used to carry out reactions in the gas phase under high heat and low pressure. The "mechanism" is not one specific reaction type, but rather a set of controlled conditions that force molecules to undergo unimolecular reactions—reacting with themselves—rather than bimolecular reactions with each other. This is achieved by rapidly heating a precursor in a vacuum, which allows for the formation of highly reactive or unstable products that are immediately trapped at very low temperatures.
Flash Vacuum Pyrolysis is best understood not as a single mechanism, but as a physical environment designed to isolate individual molecules in the gas phase. This isolation uses high energy to trigger internal rearrangements or fragmentations, enabling the synthesis of chemical species that are too reactive to exist under normal conditions.

The Core Principles of FVP
To understand how FVP works, you must grasp its three defining conditions: high temperature, high vacuum, and rapid quenching. These elements work in concert to control chemical reactivity at a fundamental level.
High Temperature: Providing Activation Energy
The "pyrolysis" part of the name refers to breaking down molecules with heat, typically in a furnace heated to between 300°C and 1100°C.
This intense, localized heat provides the necessary activation energy to drive reactions that would not occur at lower temperatures, such as breaking strong carbon-carbon bonds.
High Vacuum: Isolating the Molecules
The "vacuum" is the most critical element for controlling the reaction pathway. Creating a very low-pressure environment (typically 10⁻² to 10⁻⁶ Torr) has two profound effects.
First, it allows the starting material (precursor) to be volatilized at a much lower temperature than its atmospheric boiling point, getting it into the gas phase without premature decomposition.
Second, and more importantly, the vacuum dramatically increases the mean free path of the gas molecules. This means they are far more likely to collide with the hot walls of the reaction tube than with each other, strongly favoring unimolecular reactions (eliminations, rearrangements) and suppressing bimolecular reactions (dimerization, polymerization).
Rapid Quenching: Trapping the Product
The products formed during FVP are often extremely reactive and have short lifetimes.
To prevent them from decomposing or reacting further, the gas stream immediately exits the hot zone and collides with a cryogenic surface, such as a "cold finger" chilled with liquid nitrogen (-196°C). This process, known as quenching, freezes the product out of the gas phase, trapping it in an inert state for collection and analysis.
A Look at a Typical FVP Apparatus
Visualizing the setup helps clarify the process. An FVP apparatus is purpose-built to maintain these precise conditions.
The Precursor Inlet
The solid or liquid precursor is placed in a flask that is gently heated. Under vacuum, the material sublimes or evaporates, creating a slow, steady flow of molecules into the reaction tube.
The Hot Zone
This is typically a quartz tube passing through a high-temperature tube furnace. The tube may be packed with an inert material like quartz wool to increase the hot surface area, ensuring efficient heat transfer to the gas molecules as they pass through. This is where the pyrolysis reaction occurs.
The Collection Trap
Immediately following the furnace is a cold trap. The newly formed product molecules exit the hot zone and are instantly frozen onto the cold surface, preventing any subsequent reactions. Once the experiment is complete, the vacuum is released, and the product can be scraped from the cold finger for analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, FVP is a specialized technique with specific limitations that make it unsuitable for all applications.
Precursor Volatility is Required
The starting material must be volatile enough to enter the gas phase under vacuum without decomposing. Non-volatile or thermally sensitive precursors cannot be used.
Low Throughput and Small Scale
FVP is fundamentally a laboratory-scale technique. The requirement for high vacuum and controlled flow rates means that only small quantities (milligrams to a few grams) can be processed at a time, making it impractical for industrial production.
Potential for Complex Mixtures
While FVP favors unimolecular reactions, the high energy involved can sometimes open up multiple competing reaction pathways. This can lead to the formation of a complex mixture of products, which may be difficult to separate and purify.
When to Consider FVP for Your Research
Choosing a synthetic method depends entirely on your objective. FVP is an exceptional tool for very specific goals.
- If your primary focus is generating highly reactive intermediates: FVP is the gold-standard method for creating and isolating species like carbenes, nitrenes, or anti-aromatic systems for spectroscopic study.
- If your primary focus is clean, unimolecular synthesis: FVP is ideal for forcing specific pericyclic reactions, such as a retro-Diels-Alder, by preventing intermolecular side reactions that plague solution-phase chemistry.
- If your primary focus is large-scale production: FVP is generally unsuitable due to its low throughput, high energy cost, and requirement for specialized high-vacuum equipment.
By precisely controlling energy and isolation at the molecular level, FVP provides a unique window into chemical reactivity and remains a powerful tool for modern synthesis.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Role in FVP Mechanism |
|---|---|
| High Temperature | Provides activation energy to break strong bonds and drive reactions. |
| High Vacuum | Isolates molecules, favoring unimolecular reactions over bimolecular ones. |
| Rapid Quenching | Traps unstable products on a cryogenic surface to prevent decomposition. |
| Typical Applications | Generation of carbenes, nitrenes, and clean pericyclic reactions. |
Ready to push the boundaries of your chemical synthesis? The precise control of FVP requires specialized lab equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnaces, vacuum systems, and cryogenic traps designed for advanced research. Let our experts help you build or optimize your FVP apparatus to unlock new reactive intermediates. Contact our lab equipment specialists today to discuss your project needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
People Also Ask
- Why are high-pressure autoclaves essential for preparing bio-based polyamide curing agents from dimeric acid?
- What is the role of high-pressure reactors in the study of alloy oxidation? Essential Tools for Supercritical Research
- What roles do autoclaves play in MFI zeolite synthesis? Master Hydrothermal Crystalline Growth
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature hydrothermal reactor? Enhance Iodine@Activated Carbon Cathode Synthesis
- Why are sealed laboratory reaction vessels necessary in the hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites? Ensure Purity and Yield


















