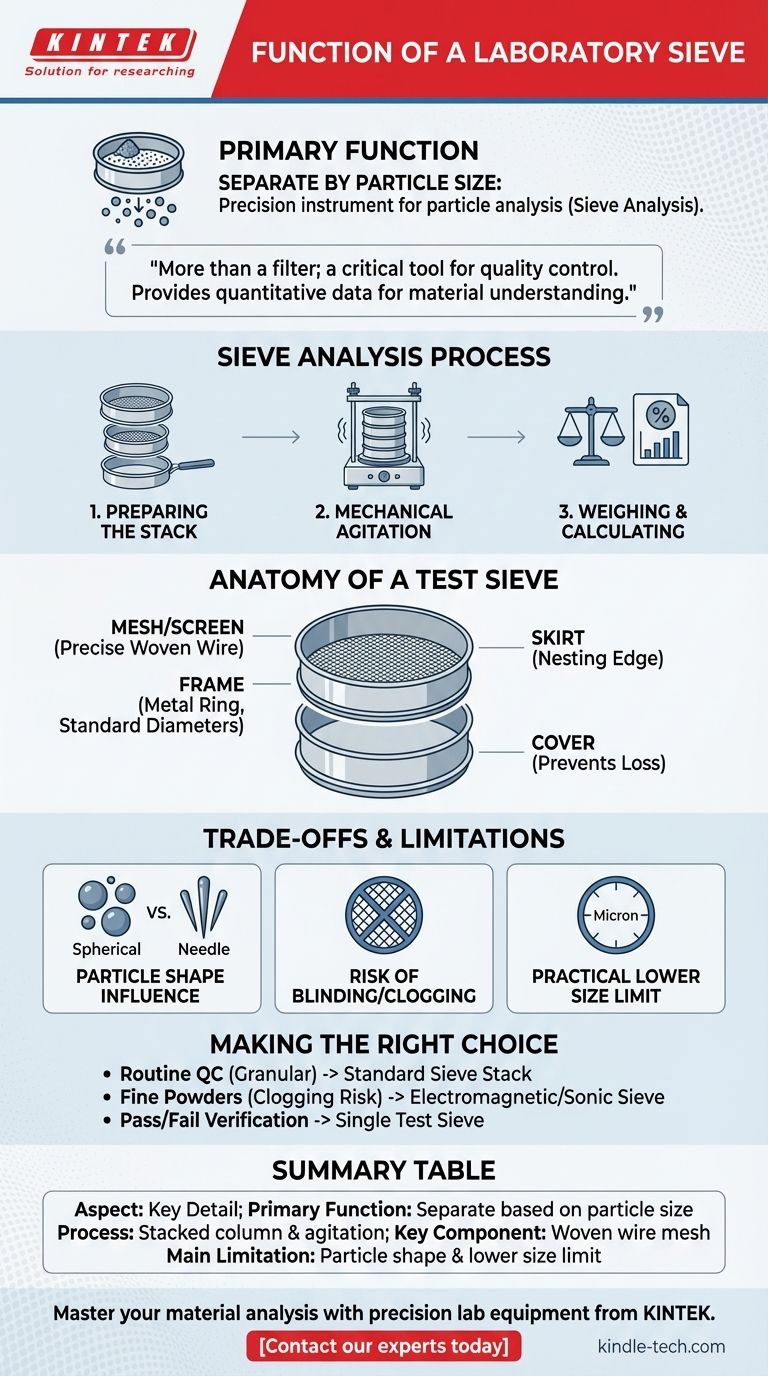
The primary function of a laboratory sieve is to separate a granular sample into fractions based on particle size. It is a precision instrument used for particle analysis, also known as a sieve analysis or gradation test. By passing a sample through a mesh screen with specific aperture sizes, a sieve allows you to physically sort particles and quantify the distribution of their sizes within the material.
A laboratory sieve is more than just a simple filter; it is a critical tool for quality control. Its purpose is not just to separate particles, but to provide the quantitative data needed to understand a material's particle size distribution, which directly impacts its physical properties and performance.

The Sieve Analysis Process: From Sample to Data
Sieve analysis is a standardized procedure used to determine the size range of particles within a given production line or sample. The process provides a clear picture of a material's granular makeup.
Preparing the Sieve Stack
For a full particle size distribution, sieves are stacked together in a column. This stack is arranged with the sieve having the largest mesh openings at the top, followed by sieves of progressively smaller mesh sizes. A solid collection pan is placed at the very bottom.
Applying Mechanical Agitation
A representative, weighed sample is placed in the top sieve. The entire stack is then placed in a sieve shaker, a machine that vibrates or agitates the column. This motion ensures that particles have every opportunity to pass through the mesh openings until they arrive at a sieve they are too large to pass through.
Weighing and Calculating Results
After the shaking is complete, the material retained on each individual sieve is weighed. By dividing the mass on each sieve by the total sample mass, you can calculate the percentage of particles that fall within each specific size range. This data forms the particle size distribution profile.
Anatomy of a Laboratory Test Sieve
While simple in concept, a test sieve is a precision instrument made of several key components designed for accuracy and interoperability.
The Mesh or Screen
This is the most technical part of the sieve. It is typically a woven wire stainless steel mesh with highly precise, uniform opening sizes. These sizes can range from several inches down to just 20 microns (0.020 mm), with even finer specialized sieves available.
The Frame
The frame is the circular metal ring that holds the mesh under tension, ensuring the openings remain consistent. Frames come in standard diameters, such as 8 inches (200mm) or 12 inches (300mm), to ensure they are interchangeable and can be stacked.
The Skirt and Cover
The skirt is the bottom edge of the frame, designed to allow one sieve to nest securely on top of another without tipping. A sieve cover is placed on the top of the stack to prevent any loss of the sample during agitation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, sieve analysis is not without its limitations. Understanding these is key to interpreting results correctly.
Influence of Particle Shape
Sieve analysis inherently measures a particle based on its second-smallest dimension. Long, needle-like particles may pass through a mesh that they would be retained on if they were spherical. This can skew results for materials that are not roughly uniform in shape.
Risk of Blinding or Clogging
With very fine powders, particles can become lodged in the mesh openings, a phenomenon known as blinding. This blocks the screen and prevents other particles from passing through, leading to inaccurate results. Specialized devices like electromagnetic sieves are designed to mitigate this issue for particles as fine as 5μm.
Practical Lower Size Limit
Mechanical sieving has a practical lower limit. For particles in the very low micron or sub-micron range, other methods like laser diffraction or light scattering are required for accurate analysis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application and material dictate the appropriate sieving strategy.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control for granular materials (e.g., sand, grains, plastic pellets): A standard stack of woven wire mesh sieves on a mechanical shaker is the most reliable and widely accepted method.
- If your primary focus is analyzing fine powders where clogging is a concern (e.g., pharmaceuticals, metal powders): Consider specialized equipment like an electromagnetic or sonic sieve designed to keep the mesh clear and ensure accurate separation.
- If your primary focus is a simple pass/fail verification: Using a single test sieve is a fast and effective way to confirm that a material meets a maximum or minimum size specification.
Ultimately, mastering sieve analysis empowers you to control the physical properties that define your product's quality and performance.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Separate granular samples into fractions based on particle size. |
| Process | Sieve analysis using a stacked column and mechanical agitation. |
| Key Component | Woven wire mesh screen with precise aperture sizes. |
| Main Limitation | Particle shape can influence results; practical lower size limit exists. |
Master your material analysis with precision lab equipment from KINTEK.
Accurate particle size distribution is critical for your product's quality and performance. Whether you need standard woven wire sieves for routine quality control or specialized electromagnetic sieves for fine powders, KINTEK provides the reliable lab equipment and consumables your laboratory depends on.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect sieving solution for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- How accurate are test sieves? Understand the Variables That Impact Your Particle Analysis
- What is sieve analysis of raw materials? Control Quality with Particle Size Data
- How long do molecular sieves last? Maximize Lifespan with Proper Regeneration and Care
- What is the primary function of fine-mesh test sieves? Master Natural Mordenite Purification
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- What are the sources of error in sieving method? Master Your Particle Analysis for Reliable Results
- What is ASTM standard sieve? Ensure Precision in Particle Size Analysis
- What is the significance of micron-level screening for welding aerosol samples? Boost Precision in Lab Characterization



















