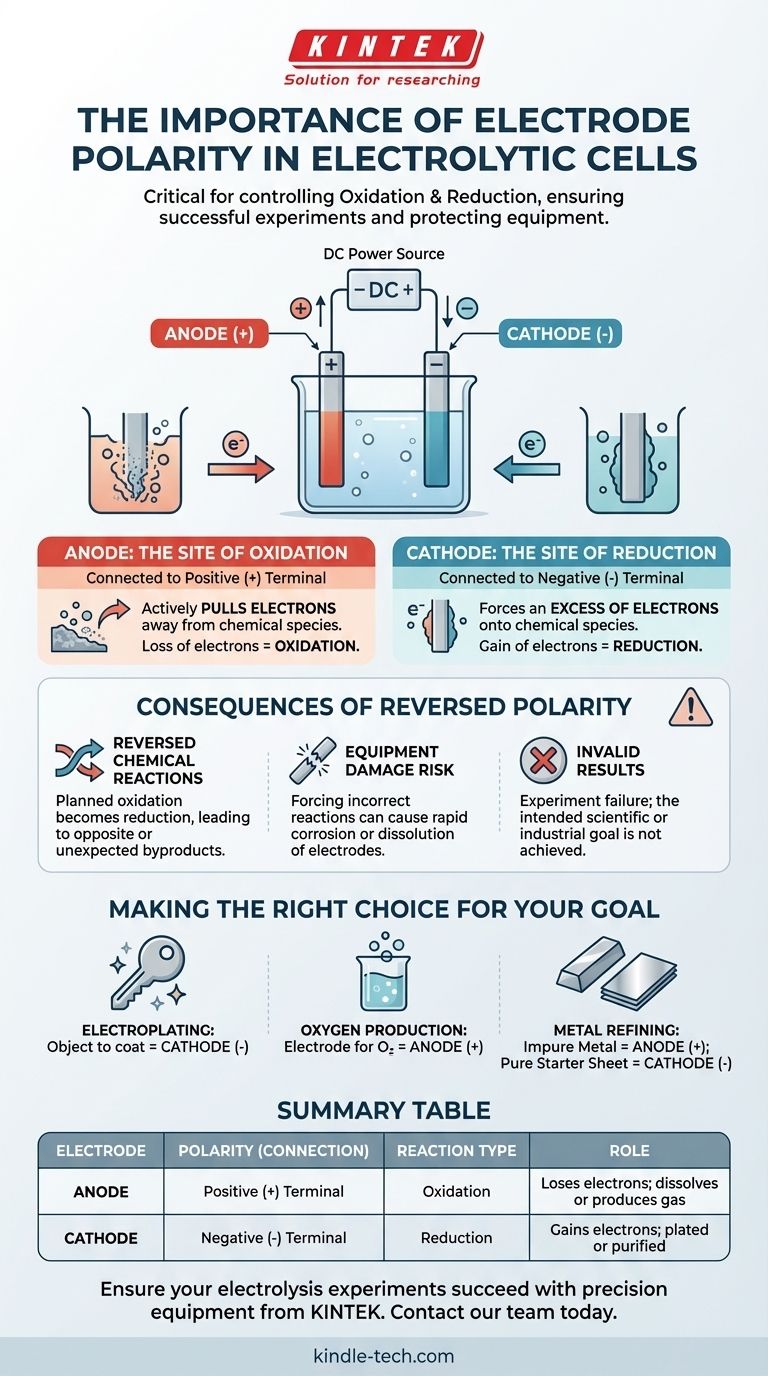
In an electrolytic cell, correct electrode polarity is critical because it dictates where the fundamental chemical reactions of oxidation and reduction occur. The positive terminal of the power source defines the anode (the site of oxidation), and the negative terminal defines the cathode (the site of reduction). Reversing these connections will reverse the intended chemical transformation, leading to experimental failure and potential equipment damage.
The core principle is this: electrode polarity is not an arbitrary label, but the direct control mechanism for your chemical reaction. It determines which electrode loses electrons (oxidation) and which one gains them (reduction), thereby controlling which substances are formed or consumed.
The Fundamental Roles of Anode and Cathode
To understand the importance of polarity, we must first define the roles of the two electrodes in an electrolytic process. These roles are driven entirely by their connection to an external power source.
The Anode: The Site of Oxidation
The anode is the electrode connected to the positive (+) terminal of the power supply.
This positive connection actively pulls electrons away from the chemical species in the electrolyte solution that are near the anode's surface. This forced loss of electrons is called oxidation.
The Cathode: The Site of Reduction
The cathode is the electrode connected to the negative (-) terminal of the power supply.
This negative connection creates an excess of electrons on the cathode's surface. These electrons are then forced onto the chemical species in the solution, causing them to gain electrons. This process is called reduction.
The Power Supply: The Driving Force
Unlike a standard battery (a galvanic cell) which produces energy from a spontaneous reaction, an electrolytic cell uses energy to drive a non-spontaneous reaction.
The external power supply acts like a pump for electrons. It pulls them from the anode and pushes them to the cathode, forcing a chemical change that would not happen on its own.
Understanding the Consequences of Reversed Polarity
Connecting the electrodes to the wrong terminals is not a minor mistake; it fundamentally alters the entire experiment. This is often referred to as "reversing the polarity."
You Reverse the Chemical Reactions
If you reverse the connections, the electrode you intended to be the anode becomes the cathode, and vice versa.
The chemical reaction you planned for the anode (oxidation) will not happen. Instead, a reduction reaction will occur there. This means your experiment will produce the opposite of your intended results, or create entirely unexpected byproducts.
You Risk Damaging Your Equipment
Forcing a reaction on the wrong material can have destructive consequences. For example, if you are electroplating, reversing the polarity will start to dissolve the object you intended to coat.
In some cases, attempting to oxidize an electrode that is not designed for it can cause it to corrode rapidly. This can contaminate your solution and permanently damage the electrode.
Your Results Will Be Invalid
Ultimately, reversed polarity invalidates the experiment. If you are trying to plate a layer of copper onto a key, reversing the setup will cause the copper source to be plated with metal from the key, effectively dissolving the key. The outcome is a failure to achieve the scientific or industrial goal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Correctly assigning polarity is how you command the chemical outcome. Before you connect your power source, confirm which electrode must be the anode (+) and which must be the cathode (-).
- If your primary focus is electroplating an object: The object you want to coat must be the cathode (-), as this is where positive metal ions will be reduced into a solid metal layer.
- If your primary focus is producing oxygen gas from water: The electrode where you want oxygen to form must be the anode (+), as this is where water molecules are oxidized.
- If your primary focus is refining impure metal: The impure metal block must be the anode (+) so it can be oxidized and dissolve into the solution, while a pure starter sheet must be the cathode (-) to collect the newly purified metal.
Mastering electrode polarity gives you direct control over the electrochemical reactions you wish to perform.
Summary Table:
| Electrode | Polarity (Connection) | Reaction Type | Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anode | Positive (+) Terminal | Oxidation | Loses electrons; target dissolves or produces gas (e.g., O₂) |
| Cathode | Negative (-) Terminal | Reduction | Gains electrons; target is plated or purified |
Ensure your electrolysis experiments succeed with precision equipment from KINTEK.
Whether you are refining metals, electroplating, or conducting research, our specialized lab equipment and consumables are designed for accuracy and durability. Our experts can help you select the right power supplies and electrodes to perfectly control your chemical reactions.
Don't risk invalid results or damaged equipment—contact our team today to discuss your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Customizable CO2 Reduction Flow Cell for NRR ORR and CO2RR Research
People Also Ask
- What is the proper procedure for post-experiment cleanup and storage of an all-quartz electrolytic cell? Ensure Longevity and Reproducibility
- What materials are used to construct the all-quartz electrolytic cell? A Guide to Purity and Performance
- What are the necessary steps to prepare an all-quartz electrolytic cell before an experiment? Ensure Accuracy and Safety
- Why is a quartz electrolytic cell used for acrylic acid wastewater? Ensure Chemical Stability & Data Integrity
- What precautions should be taken when handling and using an all-quartz electrolytic cell? Ensure Safe, Accurate, and Durable Performance



















