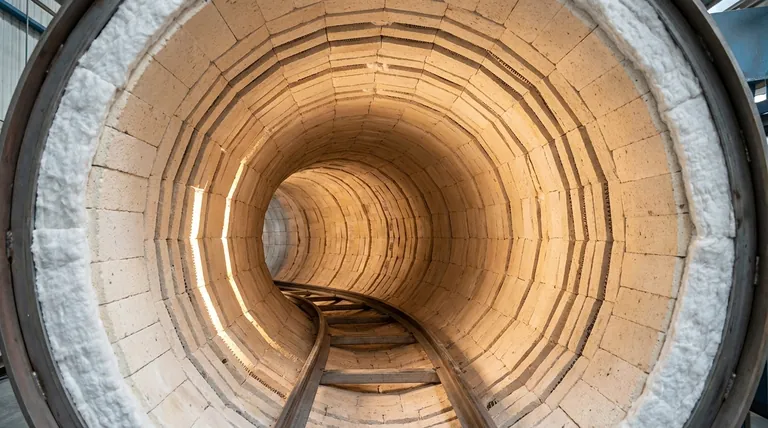
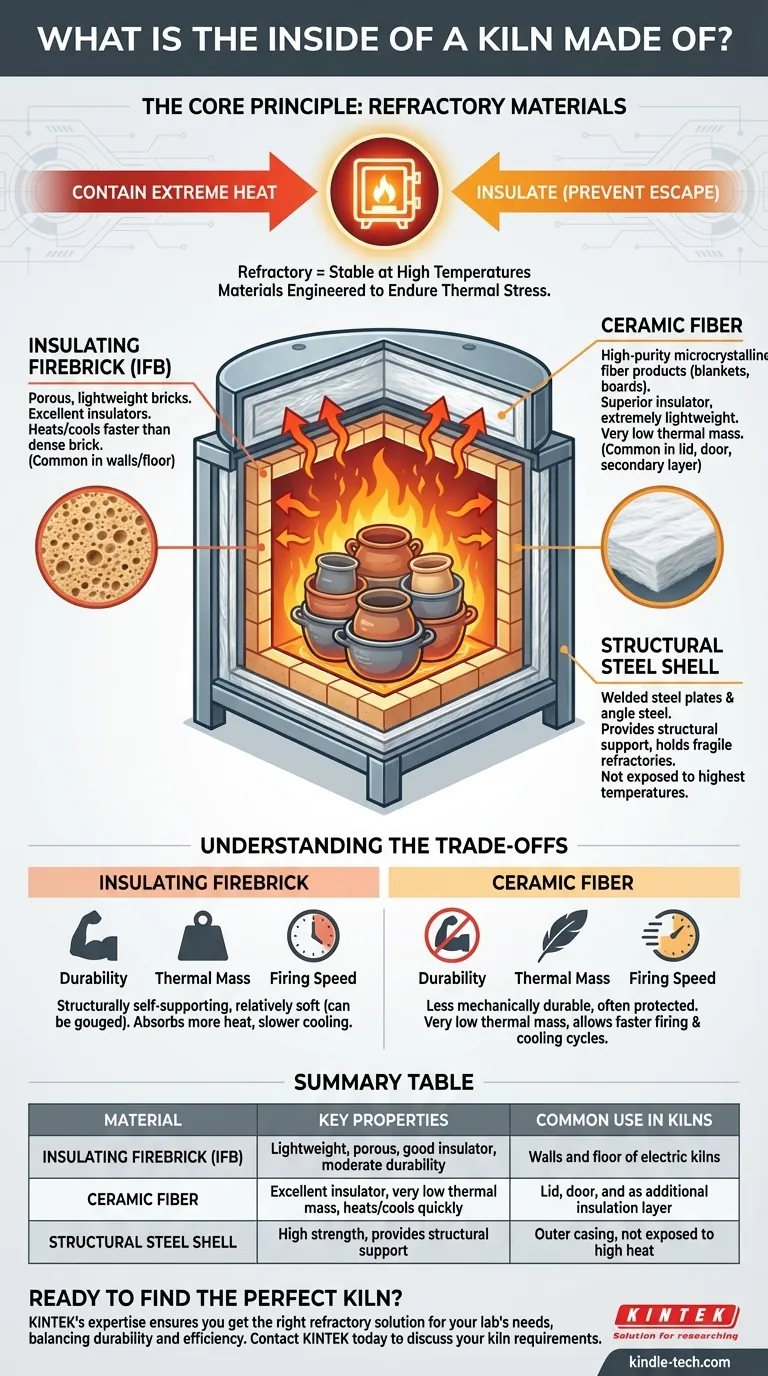
At its core, the inside of a kiln is constructed from special non-melting materials known as refractories. Modern electric kilns most commonly use a combination of lightweight insulating firebricks and high-purity ceramic fiber products, which are designed to contain extreme heat while remaining structurally stable.
The specific material is less important than its fundamental property: being refractory. This means it can withstand incredibly high temperatures without melting, warping, or breaking down, making it possible to safely fire ceramics.

The Core Principle: Refractory Materials
A kiln's primary job is to create and contain a high-temperature environment. The materials used for its interior are chosen specifically for this purpose.
What "Refractory" Means
The term refractory simply means a material is physically and chemically stable at high temperatures. Unlike steel, which melts, or wood, which burns, these materials are engineered to endure the thermal stress of a firing cycle.
The Dual Role: Containing and Insulating
Refractory materials inside a kiln serve two critical functions. First, they must contain the heat, forming a stable chamber that doesn't degrade. Second, they must insulate, preventing that heat from escaping into the surrounding room, which improves energy efficiency and ensures the kiln's exterior remains at a safe temperature.
Common Materials Used Inside a Kiln
While many materials are refractory, a few are overwhelmingly common in modern kilns due to their specific properties.
Insulating Firebrick (IFB)
Insulating firebricks are the most common material you will see lining the walls of an electric kiln. These are porous, lightweight bricks that are excellent insulators. Their low density means they heat up and cool down faster than dense "hardbricks," which is ideal for the controlled cycles of ceramic firing.
Ceramic Fiber
Many kilns also use high-purity microcrystalline fiber products, often made from materials like alumina. This comes in the form of flexible blankets, rigid boards, or even vacuum-formed shapes. Ceramic fiber is an exceptionally effective insulator and is extremely lightweight, contributing to the efficiency of modern kilns. You often find it in the lid, door, or between the brick and the outer steel shell.
The Structural Steel Shell
It is important to distinguish the inside from the outside. The outer "shell" of a kiln is typically made of welded steel plates and angle steel. This metal framework provides the necessary structural support, holding the fragile refractory bricks and fiber in place, but it is not exposed to the highest temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between brick and fiber is not arbitrary; it's a decision based on performance, durability, and cost.
Durability vs. Insulation
Insulating firebricks are relatively soft and can be damaged by gouges or bumps when loading and unloading a kiln. However, they are structurally self-supporting.
Ceramic fiber is a superior insulator but is less mechanically durable. It is often protected by brick or used in areas that don't see physical contact.
Thermal Mass and Firing Speed
A key difference is thermal mass. Firebricks, being denser than fiber, absorb and hold more heat. This results in slightly slower heating and much slower cooling, which can be beneficial for certain glaze effects.
Ceramic fiber has very low thermal mass. Kilns built primarily with fiber heat and cool very quickly, allowing for faster firing cycles and greater energy efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The materials used in a kiln directly impact its performance and suitability for different tasks.
- If your primary focus is general hobby ceramics: Most top-loading electric kilns offer a perfect balance, using insulating firebricks for structure and ceramic fiber for enhanced lid insulation.
- If your primary focus is efficiency and fast turnarounds: A kiln that incorporates more ceramic fiber in its construction will heat and cool faster, saving time and energy.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability in a high-use environment: Kilns used in industrial settings might use dense "hardbrick" on the floor to withstand the abuse of heavy kiln shelves and ware.
Ultimately, knowing that the inside of a kiln is a system of refractory materials allows you to better understand its operation and performance.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Properties | Common Use in Kilns |
|---|---|---|
| Insulating Firebrick (IFB) | Lightweight, porous, good insulator, moderate durability | Walls and floor of electric kilns |
| Ceramic Fiber | Excellent insulator, very low thermal mass, heats/cools quickly | Lid, door, and as additional insulation layer |
| Structural Steel Shell | High strength, provides structural support | Outer casing, not exposed to high heat |
Ready to find the perfect kiln for your lab's specific needs? Whether you require the durability of firebrick or the rapid cycling of ceramic fiber insulation, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment ensures you get the right solution. Our team can help you select a kiln that delivers the performance, efficiency, and reliability your work demands.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory's kiln requirements and discover our range of high-quality solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker



















