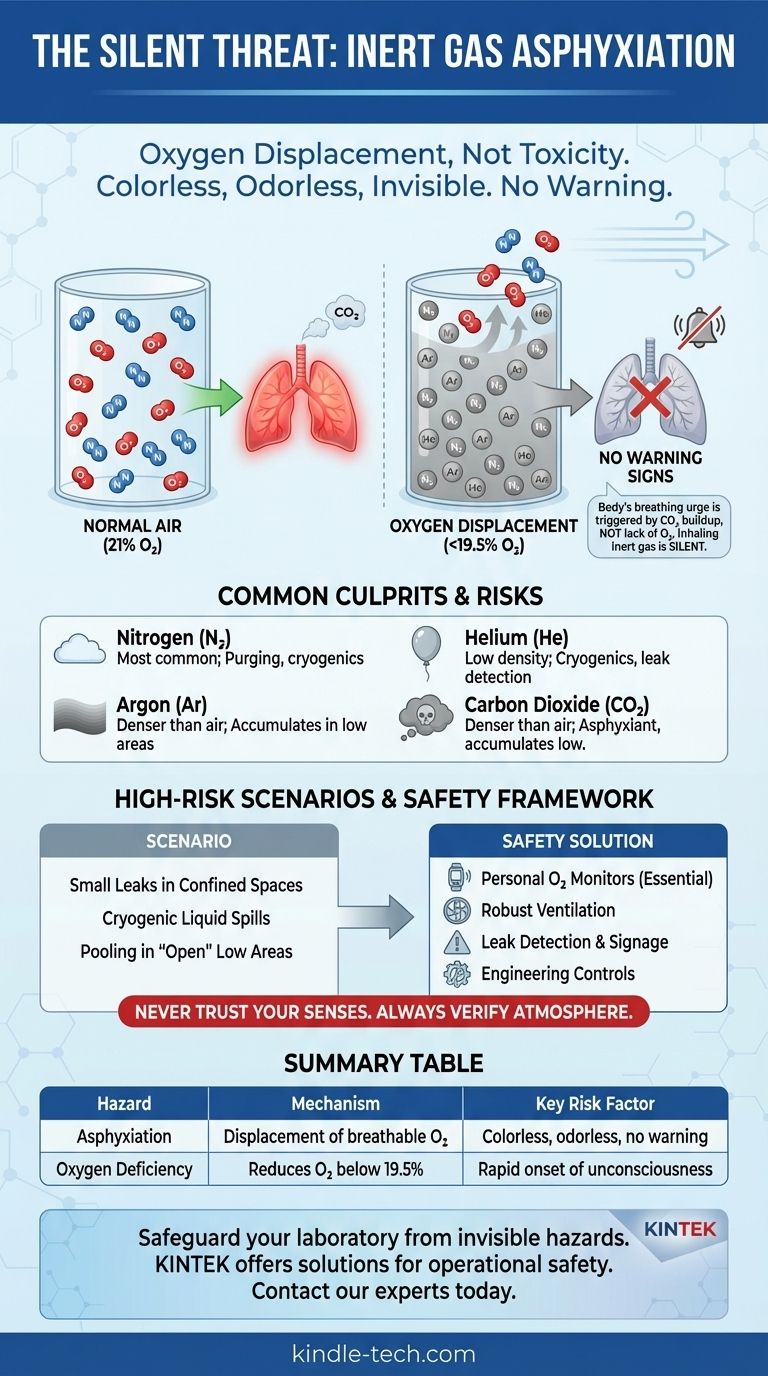
The main hazard associated with inert gases is asphyxiation by oxygen displacement. Unlike toxic gases that poison the body, inert gases are dangerous because they dilute the concentration of breathable oxygen in the air. Because these gases are typically colorless and odorless, this life-threatening oxygen depletion can occur without any sensory warning, leading to rapid confusion, unconsciousness, and death.
The core danger of inert gases is not an active attack on the body, but the passive removal of what the body needs to survive. The complete lack of warning signs—no smell, no irritation, no choking sensation—makes inert gas asphyxiation an exceptionally insidious and underestimated workplace hazard.

The Invisible Threat: How Inert Gases Cause Asphyxiation
The danger of inert gases is fundamentally a problem of physics, not biology. They don't react with the body; they simply take up space that oxygen needs to occupy.
Understanding Oxygen Displacement
Normal air contains approximately 21% oxygen, which is essential for cellular respiration. An inert gas, such as nitrogen or argon, released into a room physically pushes the normal air out of the way.
This process lowers the percentage of oxygen. An environment with less than 19.5% oxygen is considered oxygen-deficient and hazardous.
The Body's Deceptive Response
Crucially, the human body's primary urge to breathe is triggered by a build-up of carbon dioxide (CO₂) in the blood, not by a lack of oxygen.
When you breathe in an inert gas, you continue to exhale CO₂ normally. Your body's alarm system is never triggered. You do not gasp for air or feel a sense of suffocation.
The result is a rapid, silent progression from light-headedness to unconsciousness and death, often in less than a minute, with no struggle.
Common Culprits in the Workplace
While many gases are inert, a few are overwhelmingly common in industrial, medical, and research settings.
- Nitrogen (N₂): The most common inert gas, widely used for purging systems, blanketing tanks, and in cryogenics (as liquid nitrogen).
- Argon (Ar): Frequently used in welding to create a protective atmosphere. It is denser than air and can accumulate in low-lying areas.
- Helium (He): Known for its low density, it's used in cryogenics, leak detection, and breathing mixtures for deep-sea diving.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): While not truly inert, it is often treated as a simple asphyxiant. It is denser than air and is also a respiratory stimulant and toxicant at high concentrations, but its primary hazard in a leak is oxygen displacement.
Common Pitfalls and High-Risk Scenarios
Understanding the mechanism is only half the battle. Recognizing the scenarios where this silent hazard manifests is critical for survival.
Misinterpreting "Non-Toxic"
This is the most dangerous cognitive trap. Personnel see "non-toxic" on a safety data sheet and equate it with "safe." For inert gases, non-toxic is the defining feature of the hazard because it guarantees there will be no warning.
Small Leaks in Confined Spaces
A slow, unnoticed leak from a cylinder fitting or pipe in a small, poorly ventilated room is a classic fatality scenario. Over hours, the inert gas can build up to a lethal concentration without anyone realizing it.
The Cryogenic Factor
Liquids like nitrogen and argon expand enormously when they turn into gas (a liquid-to-gas expansion ratio of nearly 1:700 for nitrogen). A small spill of cryogenic liquid on the floor can rapidly vaporize and fill a large room, displacing all breathable air in minutes.
The Illusion of Safety in "Open" Areas
Heavier-than-air gases like argon and carbon dioxide can pool in pits, trenches, or any low-lying area, creating an invisible and deadly pocket of unbreathable atmosphere even in an otherwise open space.
A Framework for Inert Gas Safety
Mitigating this hazard requires moving from assumption to verification. You cannot trust your senses; you must trust your instruments and procedures.
- If your primary focus is management or safety oversight: Your priority must be engineering controls (like ventilation) and robust procedures, including the mandatory use of personal oxygen monitors in all at-risk areas.
- If your primary focus is hands-on operations: Never trust your senses. Always assume a space could be oxygen-deficient and verify the atmosphere with a calibrated, personal gas monitor before entry and during work.
- If your primary focus is system design: Prioritize ventilation and leak detection. Ensure fail-safes are in place and that enclosed areas with a potential for gas accumulation are clearly marked with signage and equipped with fixed monitoring systems.
Ultimately, safety with inert gases is achieved not by reacting to a danger you can feel, but by respecting a risk you cannot see.
Summary Table:
| Hazard | Mechanism | Common Gases | Key Risk Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asphyxiation | Displacement of breathable oxygen (O₂) | Nitrogen (N₂), Argon (Ar), Helium (He) | Colorless, odorless, and provides no sensory warning |
| Oxygen Deficiency | Reduces O₂ concentration below safe level (19.5%) | Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) | Can accumulate in low-lying areas |
| Rapid Onset | Unconsciousness can occur in under a minute | All inert gases | Body's breathing reflex is triggered by CO₂, not lack of O₂ |
Safeguard your laboratory from invisible hazards. The silent threat of inert gas asphyxiation requires reliable safety protocols and equipment. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with solutions that enhance safety and operational integrity. Ensure your team's safety—contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Air Valve Applications
- 304 316 Stainless Steel Vacuum Ball Valve Stop Valve for High Vacuum Systems
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Buchner Funnel and Triangular Funnel
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- What are the four main types of sensors? A Guide to Power Source and Signal Type
- Does temperature affect compression of gases? Why Hot Gases Resist Compression More
- What inspections should be performed on the PTFE electrode stand before use? Ensure Safe & Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- What is the adaptability principle regarding the load capacity of the PTFE electrode stand? Ensure Stability and Safety in Your Lab
- What cleaning procedure is required for the PTFE electrode stand before an experiment? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Results



















