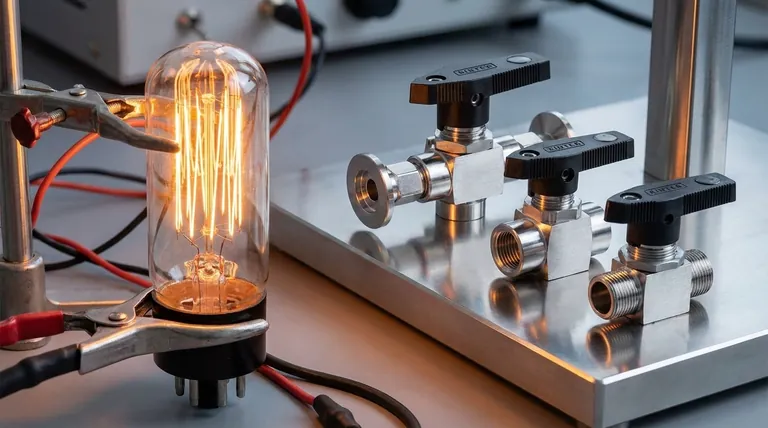
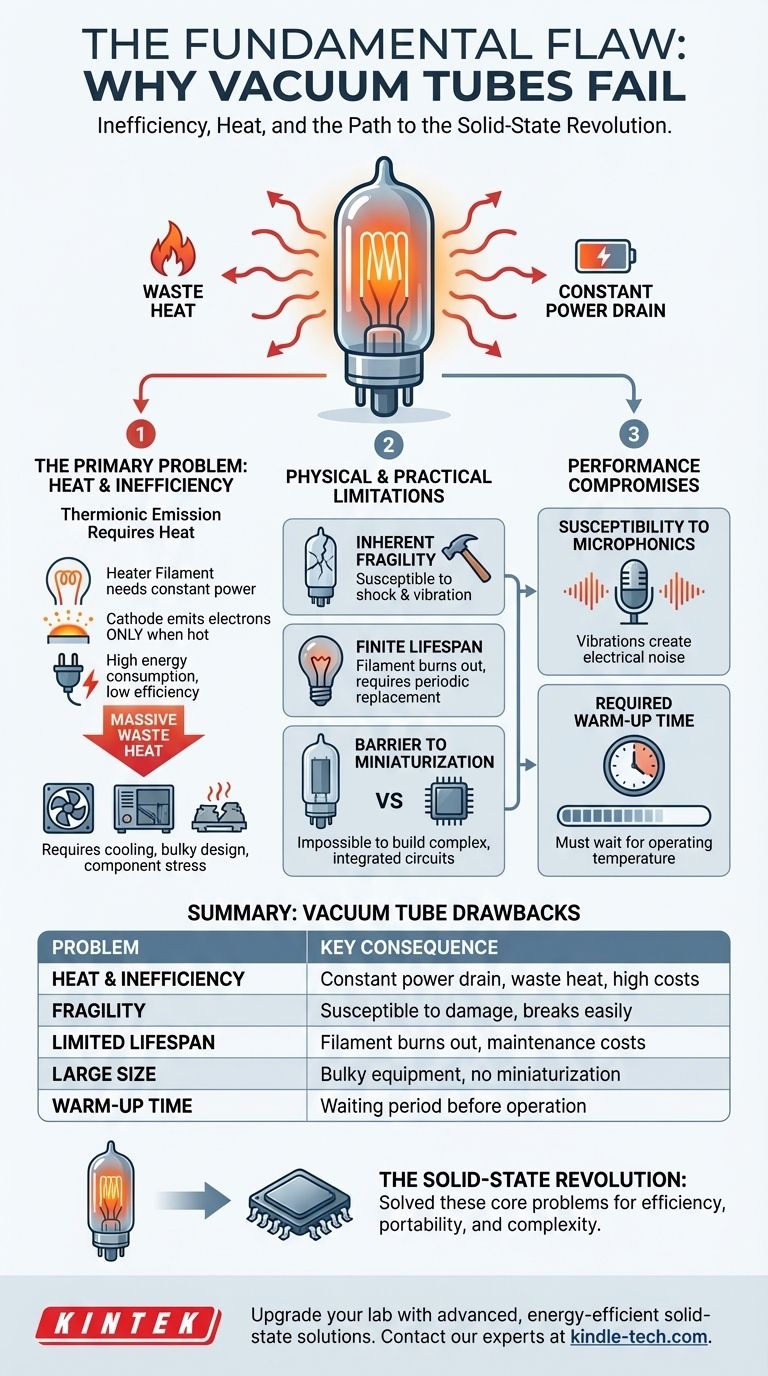
The primary problem with vacuum tubes is their fundamental inefficiency, driven by the immense amount of energy they waste as heat. To function, a tube must heat a filament to a glow, constantly consuming power and creating thermal stress, which in turn leads to a cascade of other issues including fragility, large size, and a limited lifespan.
At their core, vacuum tubes are thermal devices that operate like a specialized light bulb. This reliance on generating heat makes them inherently inefficient, fragile, and impossible to miniaturize, placing a hard limit on the complexity and portability of any device that uses them.

The Fundamental Flaw: Heat and Inefficiency
The defining characteristic of a vacuum tube is its method of operation, known as thermionic emission. This process is the source of its most significant drawbacks.
The Heater Filament
Every vacuum tube contains a small filament, similar to the one in an incandescent light bulb. This filament must be supplied with power to heat up the tube's cathode.
Only when the cathode is sufficiently hot can it emit the electrons necessary for the tube to amplify or switch a signal. This heating process requires a constant and significant power supply.
Constant Power Drain
This need for a heated filament means tubes consume a large amount of power even when idle. A significant portion of the energy going into a tube-based device is used just to keep the tubes in a ready state.
This results in very low energy efficiency, generating high electricity bills and making battery-powered operation impractical for most applications.
The Problem of Waste Heat
All the energy used to heat the filament is ultimately lost as waste heat. This heat must be managed with ventilation, fans, and large chassis, increasing the size and weight of the equipment.
Excess heat also accelerates the degradation of other electronic components, reducing the overall reliability of the system.
Physical and Practical Limitations
The thermal and mechanical design of vacuum tubes imposes severe practical constraints that solid-state technology solved decades ago.
Inherent Fragility
Vacuum tubes are constructed from glass envelopes enclosing a near-perfect vacuum. They are highly susceptible to damage from physical shock or vibration.
A simple drop or hard knock can easily break the glass or damage the delicate internal structures, causing the tube to fail instantly.
Finite Lifespan
Like light bulbs, vacuum tubes are consumable components. The filament eventually burns out, and the cathode's ability to emit electrons degrades over time.
This means tubes must be periodically replaced, adding to maintenance costs and creating potential points of failure.
The Barrier to Miniaturization
The physical requirements of a glass envelope, a vacuum, and internal heating elements mean there is a lower limit to how small a vacuum tube can be.
This physical reality made it impossible to build the complex, integrated circuits that are the foundation of all modern electronics, from smartphones to supercomputers. Transistors, by contrast, can be shrunk to an atomic scale.
Common Performance Compromises
Beyond inefficiency and fragility, the physical nature of vacuum tubes introduces performance issues that are not present in their solid-state counterparts.
Susceptibility to Microphonics
The internal components of a vacuum tube can act like a microphone, converting mechanical vibrations into unwanted electrical noise in the signal path.
In sensitive applications like audio amplification, this means tapping on the device can create an audible ringing or noise, a phenomenon known as microphonics.
Required Warm-Up Time
Unlike a transistor-based device that works instantly, vacuum tube equipment requires a warm-up period. Users must wait for the tube filaments to reach their optimal operating temperature before the device will function correctly.
Why This Led to the Solid-State Revolution
Understanding these limitations makes it clear why the invention of the transistor was so transformative. It directly solved the core problems inherent in vacuum tube technology.
- If your primary focus is efficiency, portability, and complexity: The transistor is the only viable choice. Its low power consumption and microscopic size are what enable all modern computing and mobile devices.
- If your primary focus is a specific sonic character in audio: The inherent non-linearities of vacuum tubes can produce a "warm" distortion that some audiophiles find pleasing, making them a niche but valid choice for high-end audio amplifiers where efficiency is a secondary concern.
Ultimately, the vacuum tube's reliance on heat, bulk, and fragile mechanics made it an evolutionary dead end for mainstream electronics, paving the way for the solid-state revolution that defines our modern world.
Summary Table:
| Problem | Key Consequence |
|---|---|
| Heat & Inefficiency | Constant power drain, waste heat, high electricity bills |
| Fragility | Susceptible to shock/vibration, glass envelope can break |
| Limited Lifespan | Filament burns out, requires periodic replacement |
| Large Size | Impossible to miniaturize, bulky equipment |
| Warm-Up Time | Requires waiting period before operation |
Upgrade your lab's efficiency and reliability with modern solid-state equipment from KINTEK.
While vacuum tubes have inherent limitations, KINTEK specializes in advanced, energy-efficient lab equipment and consumables designed for precision, durability, and long-term performance. If you're looking to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with reliable technology, contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 304 316 Stainless Steel Vacuum Ball Valve Stop Valve for High Vacuum Systems
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- Can vacuum tubes be rebuilt? A Guide to Restoring High-Power Industrial Tubes
- What function does a throttle valve perform during the deposition of SiOxCyHz thin films? Ensure Pressure Stability.
- What are the considerations for vacuum system design? Achieve Optimal Performance for Your Lab
- How can a gas ballast valve be used as a diagnostic tool? Identify Oil Contamination vs. System Leaks
- Why is a Back Pressure Regulator Necessary for High-Temp Systems? Ensure Liquid Stability & Prevent Boiling



















