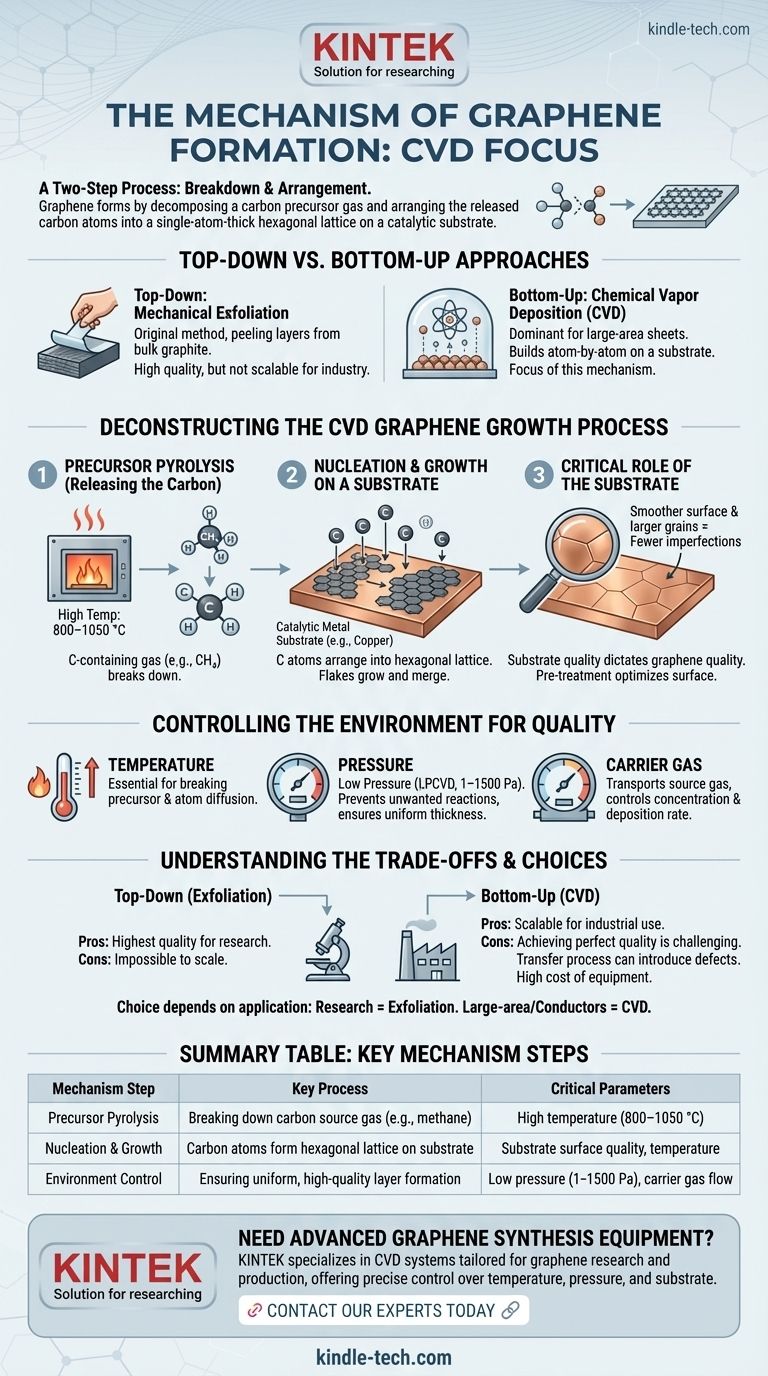
The formation of graphene is fundamentally a two-step process, particularly in scalable methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). First, a carbon-containing precursor gas is broken down at high temperatures to release individual carbon atoms. Second, these atoms adsorb onto a catalytic metal substrate, such as copper, where they arrange themselves into the characteristic hexagonal, single-atom-thick lattice of graphene.
Graphene synthesis is not a single process but a collection of methods, with Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) being one of the most scalable. The core mechanism involves decomposing a carbon source and carefully guiding the carbon atoms to form a single atomic layer, where success hinges on meticulous control of temperature, pressure, and the substrate surface.

A Tale of Two Mechanisms: Top-Down vs. Bottom-Up
To understand graphene formation, it's useful to separate the methods into two fundamental approaches.
Top-Down: Mechanical Exfoliation
This is the original method of isolating graphene. It involves starting with a bulk crystal of graphite and physically peeling away layers until a single, atomic-thick sheet is left. While it can produce pristine graphene, this method is not scalable for industrial production.
Bottom-Up: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is the dominant method for producing large-area graphene sheets. This approach builds the graphene layer from the ground up, atom by atom, on a suitable substrate. The rest of our discussion will focus on the mechanism of this critical process.
Deconstructing the CVD Graphene Growth Process
The CVD mechanism is a carefully controlled sequence designed to assemble carbon atoms into a flawless sheet.
Step 1: Precursor Pyrolysis (Releasing the Carbon)
The process begins with a carbon-containing source gas, such as methane (CH4), which is introduced into a high-temperature chamber.
Temperatures typically range from 800–1050 °C. This extreme heat provides the energy needed to break the chemical bonds in the precursor gas, a process called pyrolysis, which releases individual carbon atoms.
Step 2: Nucleation and Growth on a Substrate
These free carbon atoms then deposit onto a catalytic substrate, most commonly a copper foil. The copper surface lowers the energy required for the atoms to bond into the stable hexagonal graphene structure.
Graphene "flakes" begin to form at various points on the substrate and grow outwards until they merge into a continuous, single-layer sheet covering the copper foil.
The Critical Role of the Substrate
The quality of the substrate directly dictates the quality of the graphene. Pre-treating the copper foil can increase its grain size and optimize its surface morphology.
A smoother, more uniform substrate with larger crystal grains helps facilitate the growth of graphene with fewer imperfections, wrinkles, or grain boundaries.
Controlling the Environment for High-Quality Graphene
Physical conditions are not just parameters; they are the levers used to control the reaction and ensure a high-quality, uniform final product.
The Importance of Temperature
High temperature is essential not only for breaking down the source gas but also for allowing the carbon atoms to diffuse and arrange themselves properly on the copper surface.
The Impact of Pressure
Most systems use low-pressure chemical vapor deposition (LPCVD), with pressures between 1 and 1500 Pa.
Operating at low pressure helps prevent unwanted gas-phase reactions and promotes a more uniform thickness of the graphene layer across the entire substrate.
The Function of Carrier Gas
An inert carrier gas is used to transport the source gas into the reaction chamber and control its concentration, ensuring a stable and repeatable deposition rate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single method of graphene formation is perfect; each comes with inherent challenges and compromises.
Method vs. Scalability
Mechanical exfoliation can produce the highest-quality graphene for research, but it is impossible to scale. CVD produces large sheets suitable for industrial use, but achieving perfect, defect-free quality consistently is a significant engineering challenge.
The Substrate Challenge
While copper is an excellent catalyst for growing graphene, the graphene sheet must often be transferred to a different substrate (like a silicon wafer) for use in electronics. This transfer process is delicate and can introduce tears, wrinkles, and contamination.
The Cost of Precision
Achieving the high temperatures and low pressures required for quality CVD requires specialized and expensive equipment. This creates a barrier to entry and adds to the final cost of the material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal formation mechanism depends entirely on the intended application of the graphene.
- If your primary focus is producing large-area graphene for applications like transparent conductors: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the most viable mechanism due to its proven scalability.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research requiring pristine, defect-free samples: Mechanical exfoliation remains the gold standard, though it is limited to producing very small flakes.
Understanding these underlying mechanisms is the first step toward controlling the process and producing graphene tailored to a specific need.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism Step | Key Process | Critical Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Precursor Pyrolysis | Breaking down carbon source gas (e.g., methane) | High temperature (800–1050 °C) |
| Nucleation & Growth | Carbon atoms form hexagonal lattice on substrate (e.g., copper) | Substrate surface quality, temperature |
| Environment Control | Ensuring uniform, high-quality layer formation | Low pressure (1–1500 Pa), carrier gas flow |
Need high-quality graphene synthesis equipment or expert consultation? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for materials science, including Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) systems tailored for graphene research and production. Our solutions help you achieve precise control over temperature, pressure, and substrate conditions—critical for scalable, defect-free graphene formation. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's graphene innovation goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Temperatures for Advanced Materials
- Why graphite is used in furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment & Energy Efficiency
- What are the applications of graphite material? Leveraging Extreme Heat and Precision for Industrial Processes
- What is the temperature of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C
- What are the advantages of graphite furnace? Achieve High-Temperature Precision and Purity



















